|
Mesylate Esters
In organosulfur chemistry, a mesylate is any salt or ester of methanesulfonic acid (). In salts, the mesylate is present as the anion. When modifying the international nonproprietary name of a pharmaceutical substance containing the group or anion, the spelling used is sometimes mesilate (as in ''imatinib mesilate'', the mesylate salt of imatinib). Mesylate esters are a group of organic compounds that share a common functional group with the general structure , abbreviated , where R is an organic substituent. Mesylate is considered a leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Preparation Mesylates are generally prepared by treating an alcohol and methanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of a base, such as triethylamine. Mesyl Related to mesylate is the mesyl (Ms) or methanesulfonyl (CH3SO2) functional group. Methanesulfonyl chloride is often referred to as mesyl chloride. Whereas mesylates are often hydrolytically labile, mesyl groups, when attached to nitrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesylate Anion Structural Formulae
In organosulfur chemistry, a mesylate is any salt or ester of methanesulfonic acid (). In salts, the mesylate is present as the anion. When modifying the international nonproprietary name of a pharmaceutical substance containing the group or anion, the spelling used is sometimes mesilate (as in ''imatinib mesilate'', the mesylate salt of imatinib). Mesylate esters are a group of organic compounds that share a common functional group with the general structure , abbreviated , where R is an organic substituent. Mesylate is considered a leaving group in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Preparation Mesylates are generally prepared by treating an alcohol and methanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of a base, such as triethylamine. Mesyl Related to mesylate is the mesyl (Ms) or methanesulfonyl (CH3SO2) functional group. Methanesulfonyl chloride is often referred to as mesyl chloride. Whereas mesylates are often hydrolytically labile, mesyl groups, when attached to nitro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base. Synthesis and properties Triethylamine is prepared by the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol: :NH3 + 3 C2H5OH → N(C2H5)3 + 3 H2O The pKa of protonated triethylamine is 10.75,David Evans Research Group and it can be used to prepare buffer solutions at that pH. The |
Bitopertin
Bitopertin (developmental code names RG1678; RO-4917838) is a glycine reuptake inhibitor which was under development by Roche as an adjunct to antipsychotics for the treatment of persistent negative symptoms or suboptimally controlled positive symptoms associated with schizophrenia. Research into this indication has been largely halted as a result of disappointing trial results. Bitopertin is a glycine transporter 1 (GlyT1) inhibitor that increases levels of the neurotransmitter glycine by inhibiting its reuptake from the synaptic cleft. Glycine acts as a required co-agonist along with glutamate at ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Dysfunction of NMDA receptors may play a key role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia and modulation of glutamatergic Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/ aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-4031
E-4031 is an experimental class III antiarrhythmic drug that blocks potassium channels of the hERG-type. Chemistry E-4031 is a synthetized toxin that is a methanesulfonanilide class III antiarrhythmic drug. Target E-4031 acts on a specific class of voltage-gated potassium channels mainly found in the heart, the hERG channels. hERG channels (Kv11.1) mediate the IKr current, which repolarizes the myocardial cells. The hERG channel is encoded by ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG). Mode of action E-4031 blocks hERG-type potassium channels by binding to the open channels. Its structural target within the hERG-channel is unclear, but some other methanesulfonanilide class III antiarrhythmic drugs are known to bind to the S6 domain or C-terminal of the hERG-channel. Reducing IKr in myocardial cells prolongs the cardiac action potential and thus prolongs the QT-interval. In non-cardiac cells, blocking Ikr has a different effect: it increases the frequency of action potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dofetilide
Dofetilide is a class III antiarrhythmic agent. It is marketed under the trade name Tikosyn by Pfizer, and is available in the United States in capsules containing 125, 250, and 500 µg of dofetilide. It is not available in Europe or Australia. In the United States it is only available by mail order or through specially trained local pharmacies.TIKOSYN® (dofetilide). Pfizer. . Medical uses Dofetilide is used for the maintenance of sinus rhythm in individuals prone to the occurrence of atrial fibrillation and flutter arrhythmias, and for chemical cardioversion to sinus rhythm from atrial fibrillation and flutter. Based on the results of the Danish Investigations of Arrhythmias and Mortality on Dofetilide ("DIAMOND") study, dofetilide does not affect mortality in the treatment of patients post-myocardial infarction with left ventricular dysfunction, however it was shown to decrease all-cause readmissions as well as CHF-related readmissions. Because of the results of the DIAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dronedarone
Dronedarone, sold under the brand name Multaq, is a medication by Sanofi-Aventis, mainly for the indication of cardiac arrhythmias. It was approved by the FDA on July 2, 2009. It was recommended as an alternative to amiodarone for the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter in people whose hearts have either returned to normal rhythm or who undergo drug therapy or electric shock treatment i.e. direct current cardioversion (DCCV) to maintain normal rhythm. It is a class III antiarrhythmic drug. In the United States, the FDA approved label includes a claim for reducing hospitalization, but not for reducing mortality, as a reduction in mortality was not demonstrated in the clinical development program. A trial of the drug in heart failure was stopped as an interim analysis showed a possible increase in heart failure deaths, in patients with moderate to severe CHF. The U.S. label for dronedarone includes a boxed warning, stating that dronedarone is contraindicated in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sematilide
Sematilide is an antiarrhythmic agent Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular ta .... Sulfonamides Antiarrhythmic agents Benzamides Diethylamino compounds {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibutilide
Ibutilide is a Class III antiarrhythmic agent that is indicated for acute cardioconversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter of a recent onset to sinus rhythm. It exerts its antiarrhythmic effect by induction of slow inward sodium current, which prolongs action potential and refractory period (physiology) of myocardial cells. Because of its Class III antiarrhythmic activity, there should not be concomitant administration of Class Ia and Class III agents. Ibutilide is marketed as Corvert by Pfizer. Administration resulted in successful heart rhythm control in 31-44% of patients within 90 minutes, with sustained polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in 0.9-2.5% of patients. It appears to show better results in atrial flutter as compared to atrial fibrillation. Mechanism of action Ibutilide, like other class III antiarrhythmic drugs, blocks delayed rectified potassium current. It does have action on the slow sodium channel and promotes the influx of sodium through these slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotalol
Sotalol, sold under the brand name Betapace among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent abnormal heart rhythms. It is only recommended in those with significant abnormal heart rhythms due to potentially serious side effects. Evidence does not support a decreased risk of death with long term use. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Common side effects include a slow heart rate, chest pain, low blood pressure, feeling tired, dizziness, shortness of breath, problems seeing, vomiting, and swelling. Other serious side effects may include QT prolongation, heart failure, or bronchospasm. Sotalol is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker which has both class II and class III antiarrhythmic properties. Sotalol was first described in 1964 and came into medical use in 1974. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 296th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
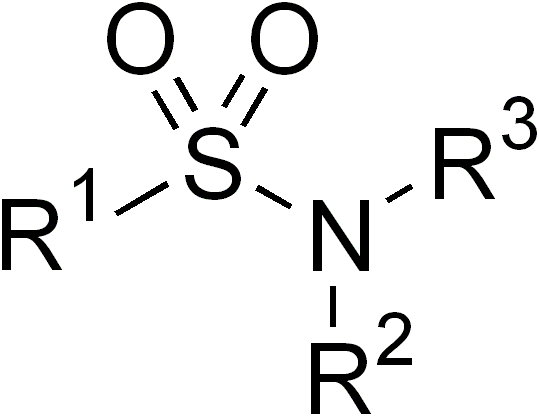
Sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |