|
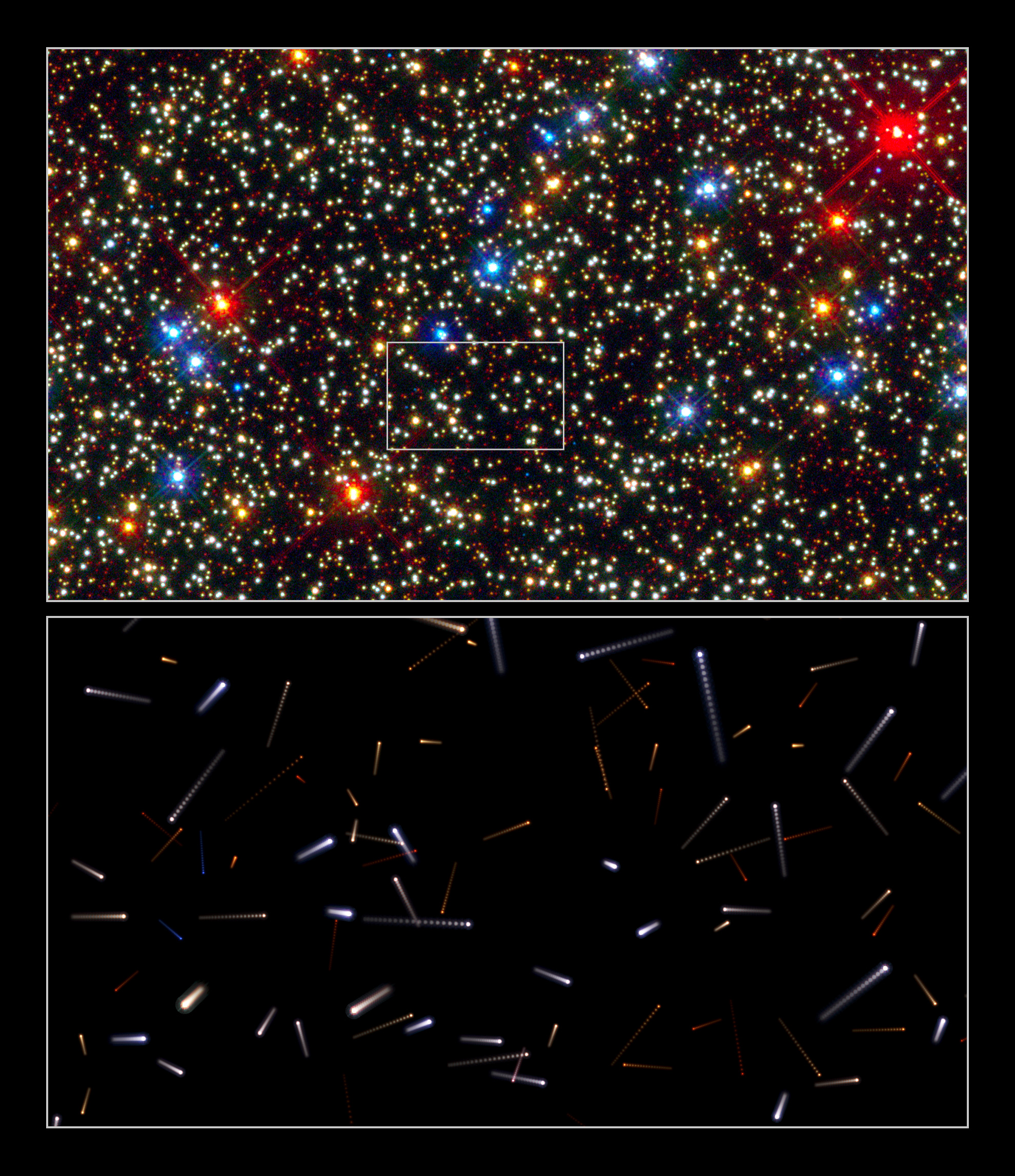
Messier 22
Messier 22 or M22, also known as NGC 6656, is an elliptical globular cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius, near the Galactic bulge region. It is one of the brightest globulars visible in the night sky. The brightest stars are 11th magnitude, with hundreds of stars bright enough to resolve with an 8 " telescope. It is just south of the sun's position in mid-December , and northwest of Lambda Sagittarii (Kaus Borealis), the northernmost star of the "Teapot" asterism. M22 was one of the first globulars to be discovered, in 1665 by Abraham Ihle and it was included in Charles Messier's catalog of comet-like objects in 1764. It was one of the first globular clusters to be carefully studied – first by Harlow Shapley in 1930. He placed within it roughly 70,000 stars and found it had a dense core. Then Halton Arp and William G. Melbourne continued studies in 1959. Due to the large color spread of its red giant branch (RGB) sequence, akin to that in Omega Centaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the positions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harlow Shapley
Harlow Shapley (November 2, 1885 – October 20, 1972) was an American scientist, head of the Harvard College Observatory (1921–1952), and political activist during the latter New Deal and Fair Deal. Shapley used Cepheid variable stars to estimate the size of the Milky Way Galaxy and the Sun's position within it by using parallax.Bart J. Bok. Harlow Shapely 1885–1972 A Biographical Memoir. National Academy of Sciences In 1953 he proposed his "liquid water belt" theory, now known as the concept of a habitable zone.Richard J. Hugget, ''uGeoecology: an evolutionary approach''. p. 10 Background Shapley was born on a farm five miles outside Nashville, Missouri, to Willis and Sarah (née Stowell) Shapley. He went to school in Jasper, Missouri, but not beyond elementary school. He worked as a journalist after studying at home and covering crime stories as a newspaper reporter for the ''Daily Sun'' in Chanute, Kansas, and intermittently for the ''Times'' of Joplin, Missouri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015. Since 1953 ''The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series'' (''ApJS'') has been published in conjunction with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', with generally longer articles to supplement the material in the journal. It publishes six volumes per year, with two 280-page issues per volume. ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters'' (''ApJL''), established in 1967 by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar as Part 2 of ''The Astrophysical Journal'', is now a separate journal focusing on the rapid publication of high-impact astronomical research. The three journals were published by the University of Chicago Press for the American Astronomical Society unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James E
James is a common English language surname and given name: * James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Centauri
Omega Centauri (ω Cen, NGC 5139, or Caldwell 80) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of , it is the largest-known globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150 light-years. It is estimated to contain approximately 10 million stars, and a total mass equivalent to 4 million solar masses, making it the most massive-known globular cluster in the Milky Way. Omega Centauri is very different from most other galactic globular clusters to the extent that it is thought to have originated as the core remnant of a disrupted dwarf galaxy. Observation history In 150 AD, Greco-Roman writer and astronomer Ptolemy catalogued this object in his ''Almagest'' as a star on the horse's back, "Quae est in principio scapulae". German cartographer Johann Bayer used Ptolemy's data to designate this object "Omega Centauri" with his 1603 publication of '' Uranometria''. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Giant Branch
The red-giant branch (RGB), sometimes called the first giant branch, is the portion of the giant branch before helium ignition occurs in the course of stellar evolution. It is a stage that follows the main sequence for low- to intermediate-mass stars. Red-giant-branch stars have an inert helium core surrounded by a shell of hydrogen fusing via the CNO cycle. They are K- and M-class stars much larger and more luminous than main-sequence stars of the same temperature. Discovery Red giants were identified early in the 20th century when the use of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram made it clear that there were two distinct types of cool stars with very different sizes: dwarfs, now formally known as the main sequence; and giants. The term ''red-giant branch'' came into use during the 1940s and 1950s, although initially just as a general term to refer to the red-giant region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Although the basis of a thermonuclear main-sequence lifetime, followe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Journal
''The Astronomical Journal'' (often abbreviated ''AJ'' in scientific papers and references) is a peer-reviewed monthly scientific journal owned by the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and currently published by IOP Publishing. It is one of the premier journals for astronomy in the world. Until 2008, the journal was published by the University of Chicago Press on behalf of the AAS. The reasons for the change to the IOP were given by the society as the desire of the University of Chicago Press to revise its financial arrangement and their plans to change from the particular software that had been developed in-house. The other two publications of the society, the ''Astrophysical Journal'' and its supplement series, followed in January 2009. The journal was established in 1849 by Benjamin A. Gould. It ceased publication in 1861 due to the American Civil War, but resumed in 1885. Between 1909 and 1941 the journal was edited in Albany, New York. In 1941, editor Benjamin Boss arrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |