|
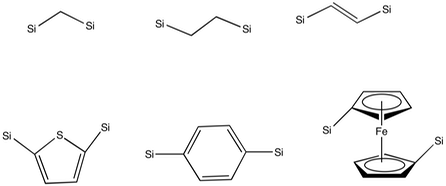
Mesoporous Organosilica
Mesoporous organosilica (periodic mesoporous organosilicas, PMO) are a type of silica containing organic groups that give rise to mesoporosity. They exhibit pore size ranging from 2 nm - 50 nm, depending on the organic substituents. In contrast, zeolites exhibit pore sizes less than a nanometer. PMOs have potential applications as catalysts, adsorbents, trapping agents, drug delivery agents, stationary phases in chromatography and chemical sensors. History The breakthrough report in this area described the use of surfactants to produce periodic mesoporous silicas (PMS) in 1992 with pores larger than that of zeolites. Early mesoporous organosilicas developed had organic groups attached terminally to the silica surface. They were prepared either by grafting of organic group onto the channel walls or by template-directed co-condensation. For example, by modifying the channels of PMSs with alkanethiol groups that could sequester heavy metals. However, there were some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination geometry, tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSC Advances
''RSC Advances'' is an online-only peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on all aspects of the chemical sciences. It was established in 2011 and is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The editor-in-chief is Russell J. Cox ( Leibniz University Hannover). In 2014, the journal moved to a very high publication frequency, initially about 100/year (similar to that of ''ChemComm''), but later in the year (and in 2015) turned to even higher frequency—however it did not become a continuous journal. The number of pages published annually had increased dramatically from about 26,500 in 2013 to over 65,000 in 2014, culminating at 116 issues and 115,000+ pages (~1000 pages per issue) in 2016. In late 2016, it was announced that with effect from January 2017, the journal would convert from a subscription based journal to an open access journal. Meanwhile, the journal experienced a cool-down in publication volume, with each issue having only ~500 pages. There were 89 issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupling Reaction
A coupling reaction in organic chemistry is a general term for a variety of reactions where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon-carbon bond in the product R-R'. The most common type of coupling reaction is the cross coupling reaction. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed cross coupling reactions. Broadly speaking, two types of coupling reactions are recognized: *Heterocouplings combine two different partners, such as in the Heck reaction of an alkene (RC=CH) and an alkyl halide (R'-X) to give a substituted alkene, or the Corey–House synthesis of an alkane by the reaction of a lithium diorganylcuprate (R2CuLi) with an organyl (pseudo)halide (R'X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Catalysis
In acid catalysis and base catalysis, a chemical reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base. By Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, the acid is the proton (hydrogen ion, H+) donor and the base is the proton acceptor. Typical reactions catalyzed by proton transfer are esterifications and aldol reactions. In these reactions, the conjugate acid of the carbonyl group is a better electrophile than the neutral carbonyl group itself. Depending on the chemical species that act as the acid or base, catalytic mechanisms can be classified as either specific catalysis and general catalysis. Many enzymes operate by general catalysis. Applications and examples Brønsted acids Acid catalysis is mainly used for organic chemical reactions. Many acids can function as sources for the protons. Acid used for acid catalysis include hydrofluoric acid (in the alkylation process), phosphoric acid, toluenesulfonic acid, polystyrene sulfonate, heteropoly acids, zeolites. Strong acids catalyze the hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Catalysis
In acid catalysis and base catalysis, a chemical reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base. By Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, the acid is the proton (hydrogen ion, H+) donor and the base is the proton acceptor. Typical reactions catalyzed by proton transfer are esterifications and aldol reactions. In these reactions, the conjugate acid of the carbonyl group is a better electrophile than the neutral carbonyl group itself. Depending on the chemical species that act as the acid or base, catalytic mechanisms can be classified as either specific catalysis and general catalysis. Many enzymes operate by general catalysis. Applications and examples Brønsted acids Acid catalysis is mainly used for organic chemical reactions. Many acids can function as sources for the protons. Acid used for acid catalysis include hydrofluoric acid (in the alkylation process), phosphoric acid, toluenesulfonic acid, polystyrene sulfonate, heteropoly acids, zeolites. Strong acids catalyze the hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen. Organic chemistry In practice, the term is usually used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecular structure. Typical heteroatoms are nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), sulfur (S), phosphorus (P), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and iodine (I), as well as the metals lithium (Li) and magnesium (Mg). Proteins It can also be used with highly specific meanings in specialised contexts. In the description of protein structure, in particular in the Protein Data Bank file format, a heteroatom record (HETATM) describes an atom as belonging to a small molecule cofactor rather than being part of a biopolymer chain. Zeolites In the context of zeolites, the term ''heteroatom'' refers to partial isomorphous substitution of the typical framework atoms (silicon, aluminium, and phosphorus) by other elements such as beryllium, vanadium, and chromium. The goal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). Adsorption is a '' surface phenomenon'', while absorption involves the whole volume of the material, although adsorption does often precede absorption. The term ''sorption'' encompasses both processes, while ''desorption'' is the reverse of it. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in the material. However, atoms on the surface of the adsorbent are not wholly surrounded by other adsorbent atoms and therefore can attract adsorbates. The exact nature of the bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemization
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic (optically inactive) form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred too as a racemic mixture (i.e. contain equal amount of (+) and (−) forms). Plus and minus forms are called Dextrorotation and levorotation. The D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects. Stereochemistry Chiral molecules have two forms (at each point of asymmetry), which differ in their optical characteristics: The ''levorotatory form'' (the ''(−)-form'') will rotate counter-clockwise on the plane of polarization of a beam of light, whereas the ''dextrorotatory'' form (the ''(+)-form'') will rotate clockw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycondensation
In polymer chemistry, condensation polymers are any kind of polymers whose process of polymerization involves a condensation reaction (i.e. a small molecule, such as water or methanol, is produced as a byproduct). Condensation polymers are formed by polycondensation, when the polymer is formed by condensation reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization, or by condensative chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by sequential addition of monomers to an active site in a chain reaction. The main alternative forms of polymerization are chain polymerization and polyaddition, both of which give addition polymers. Condensation polymerization is a form of step-growth polymerization. Linear polymers are produced from bifunctional monomers, i.e. compounds with two reactive end-groups. Common condensation polymers include polyamides, polyacetals, and proteins. Polyamides One important class of condensation polymers are polyamides. They arise from the reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |