|
Mesoblastic Nephroma
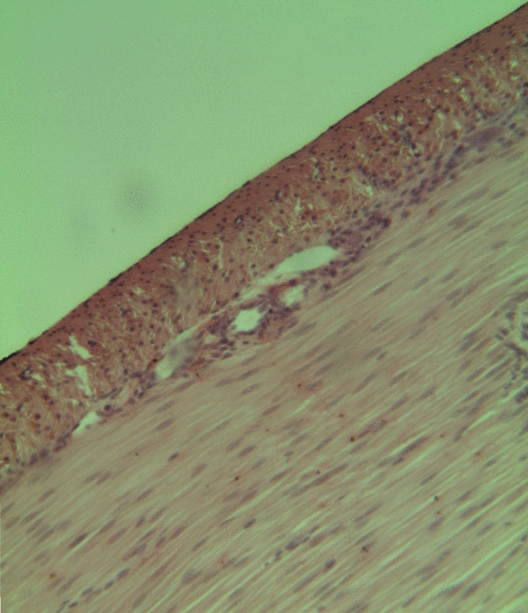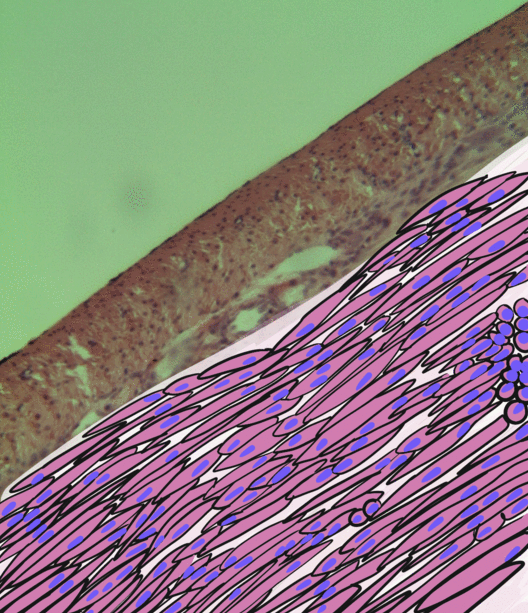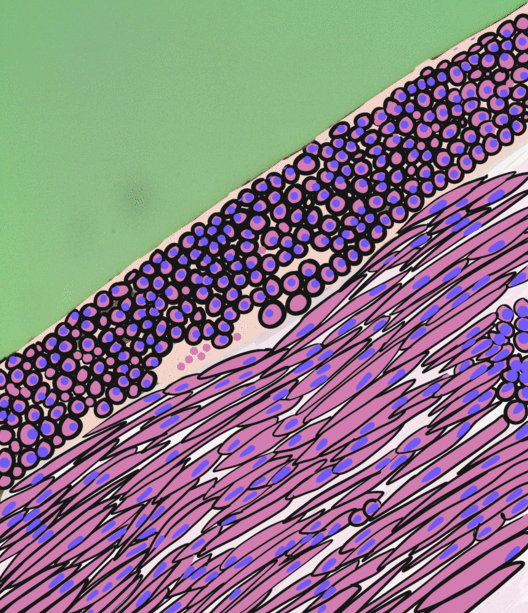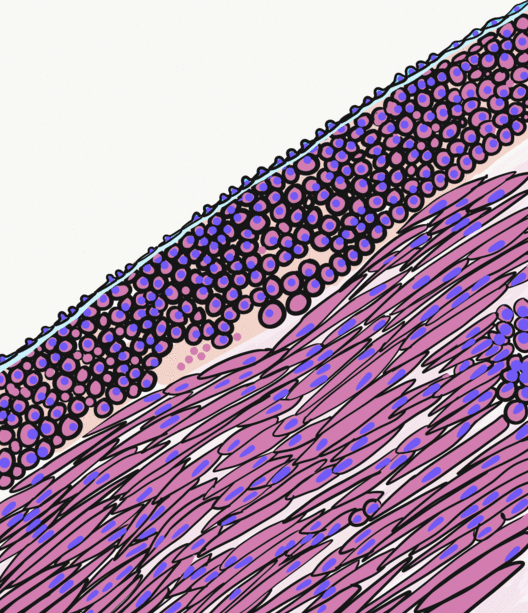
Congenital mesoblastic nephroma, while rare, is the most common kidney neoplasm diagnosed in the first three months of life and accounts for 3-5% of all childhood renal neoplasms. This neoplasm is generally non-aggressive and amenable to surgical removal. However, a readily identifiable subset of these kidney tumors has a more malignant potential and is capable of causing life-threatening metastases. Congenital mesoblastic nephroma was first named as such in 1967 but was recognized decades before this as fetal renal hamartoma or leiomyomatous renal hamartoma. Presentation Congenital mesoblastic nephroma typically (76% of cases) presents as an abdominal mass which is detected prenatally (16% of cases) by ultrasound or by clinical inspection (84% of cases) either at birth or by 3.8 years of age (median age ~1 month). The neoplasm shows a slight male preference. Concurrent findings include hypertension (19% of cases), polyhydramnios (i.e. excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilms Tumor
Wilms' tumor or Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is a cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children, rarely in adults.; and occurs most commonly as a renal tumor in child patients. It is named after Max Wilms, the German surgeon (1867–1918) who first described it. Approximately 650 cases are diagnosed in the U.S. annually. The majority of cases occur in children with no associated genetic syndromes; however, a minority of children with Wilms' tumor have a congenital abnormality. It is highly responsive to treatment, with about 90 percent of children being cured. Signs and symptoms Typical signs and symptoms of Wilms' tumor include the following: * a painless, palpable abdominal mass * loss of appetite * abdominal pain * fever * nausea and vomiting * blood in the urine (in about 20% of cases) * high blood pressure in some cases (especially if synchronous or metachronous bilateral kidney involvement) * Rarely as varicoceleErginel B, Vural S, Akın ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medical imaging. Hydrocephalus is typically treated by the surg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Gene
A fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia. The identification of these fusion genes play a prominent role in being a diagnostic and prognostic marker. History The first fusion gene was described in cancer cells in the early 1980s. The finding was based on the discovery in 1960 by Peter Nowell and David Hungerford in Philadelphia of a small abnormal marker chromosome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia—the first consistent chromosome abnormality detected in a human malignancy, later designated the Philadelphia chromosome. In 1973, Janet Rowley in Chicago showed that the Philadelphia chromosome had originated through a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, and not through a simple deletion of chromosome 22 as was previously thought. Several investigators i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ETV6-NTRK3 Gene Fusion
ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion is the translocation of genetic material between the ''ETV6'' gene located on the short arm (designated p) of chromosome 12 at position p13.2 (i.e. 12p13.2) and the ''NTRK3'' gene located on the long arm (designated q) of chromosome 15 at position q25.3 (i.e. 15q25.3) to create the (12;15)(p13;q25) fusion gene, ''ETV6-NTRK3''. This new gene consists of the 5' end of ''ETV6'' fused to the 3' end of ''NTRK3''. ''ETV6-NTRK3'' therefore codes for a chimeric oncoprotein consisting of the helix-loop-helix (HLH) protein dimerization domain of the ETV6 protein fused to the tyrosine kinase (i.e. PTK) domain of the NTRK3 protein. The ''ETV6'' gene codes for the transcription factor protein, ETV6, which suppresses the expression of, and thereby regulates, various genes that in mice are required for normal hematopoiesis as well as the development and maintenance of the vascular network. ''NTRK3'' codes for Tropomyosin receptor kinase C a NT-3 growth factor receptor cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysts
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrosarcoma
Fibrosarcoma (fibroblastic sarcoma) is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pattern. Fibrosarcomas mainly arise in people between the ages of 25–79 It originates in fibrous tissues of the bone and invades long or flat bones such as the femur, tibia, and mandible. It also involves the periosteum and overlying muscle. Presentation Adult-type Individuals presenting with fibrosarcoma are usually adults thirty to fifty-five years old, often presenting with pain. Among adults, fibrosarcomas develop equally in men and women. Infantile-type In infants, fibrosarcoma (often termed congenital infantile fibrosarcoma) is usually congenital. Infants presenting with this fibrosarcoma usually do so in the first two years of their life. Cytogenetically, congenital infantile fibrosarcoma is characterized by the majority of case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitotic
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), proph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and '' cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |