|
Meso-hexestrol
Hexestrol, sold under the brand name Synestrol among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen which was previously used for estrogen replacement therapy and in the treatment of certain hormone-dependent cancers as well as gynecological disorders but is mostly no longer marketed. It has also been used in the form of esters such as hexestrol diacetate (brand name Sintestrol) and hexestrol dipropionate (brand name Hexanoestrol). Hexestrol and its esters are taken by mouth, held under the tongue, or via injection into muscle. Medical uses Hexestrol has been used in estrogen replacement therapy, for the treatment of breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men, and for the treatment of certain gynecological disorders. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Hexestrol has approximately 302% and 234% of the affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptors (ERs) ERα and ERβ, respectively. The affinity of hexestrol for the ERs is said to be similar to or slightly higher than that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERα
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 1), is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor (mainly found as a chromatin-binding protein) that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ''ESR1'' (EStrogen Receptor 1). Structure The estrogen receptor (ER) is a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. Alternative splicing results in several ESR1 mRNA transcripts, which differ primarily in their 5-prime untranslated regions. The translated receptors show less variability. Ligands Agonists Non-selective * Endogenous estrogens (e.g., estradiol, estrone, estriol, estetrol) * Natural estrogens (e.g., conjugated equine estrogens) * Synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol) Selective Agonists of ERα selective over ERβ include: * Propylp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. (See also Solvent and Inorganic nonaqueous solvent.) Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are ''hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution (pharmacology)
Distribution in pharmacology is a branch of pharmacokinetics which describes the reversible transfer of a drug from one location to another within the body. Once a drug enters into systemic circulation by absorption or direct administration, it must be distributed into interstitial and intracellular fluids. Each organ or tissue can receive different doses of the drug and the drug can remain in the different organs or tissues for a varying amount of time.Carmine Pascuzzo Lima. ''Farmacocinética III:Distribución'' Available o (in Spanish). Visited 10 January 2009 The distribution of a drug between tissues is dependent on vascular permeability, regional blood flow, cardiac output and perfusion rate of the tissue and the ability of the drug to bind tissue and plasma proteins and its lipid solubility. pH partition plays a major role as well. The drug is easily distributed in highly perfused organs such as the liver, heart and kidney. It is distributed in small quantities through less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models. Overview Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Of Hexestrol Radioactivity After A Subcutaneous Injection Of Tritiated Hexestrol In Oil Solution In Female Goats
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Development
Breast development, also known as mammogenesis, is a complex biological process in primates that takes place throughout a female's life. It occurs across several phases, including prenatal development, puberty, and pregnancy. At menopause, breast development ceases and the breasts atrophy. Breast development results in prominent and developed structures on the chest known as breasts in primates, which serve primarily as mammary glands. The process is mediated by an assortment of hormones (and growth factors), the most important of which include estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and growth hormone. Biochemistry Hormones The master regulators of breast development are the steroid hormones, estrogen and progesterone, growth hormone (GH), mostly via its secretory product, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and prolactin. These regulators induce the expression of growth factors, such as amphiregulin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), IGF-1, and fibroblast growth factor (FGF), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
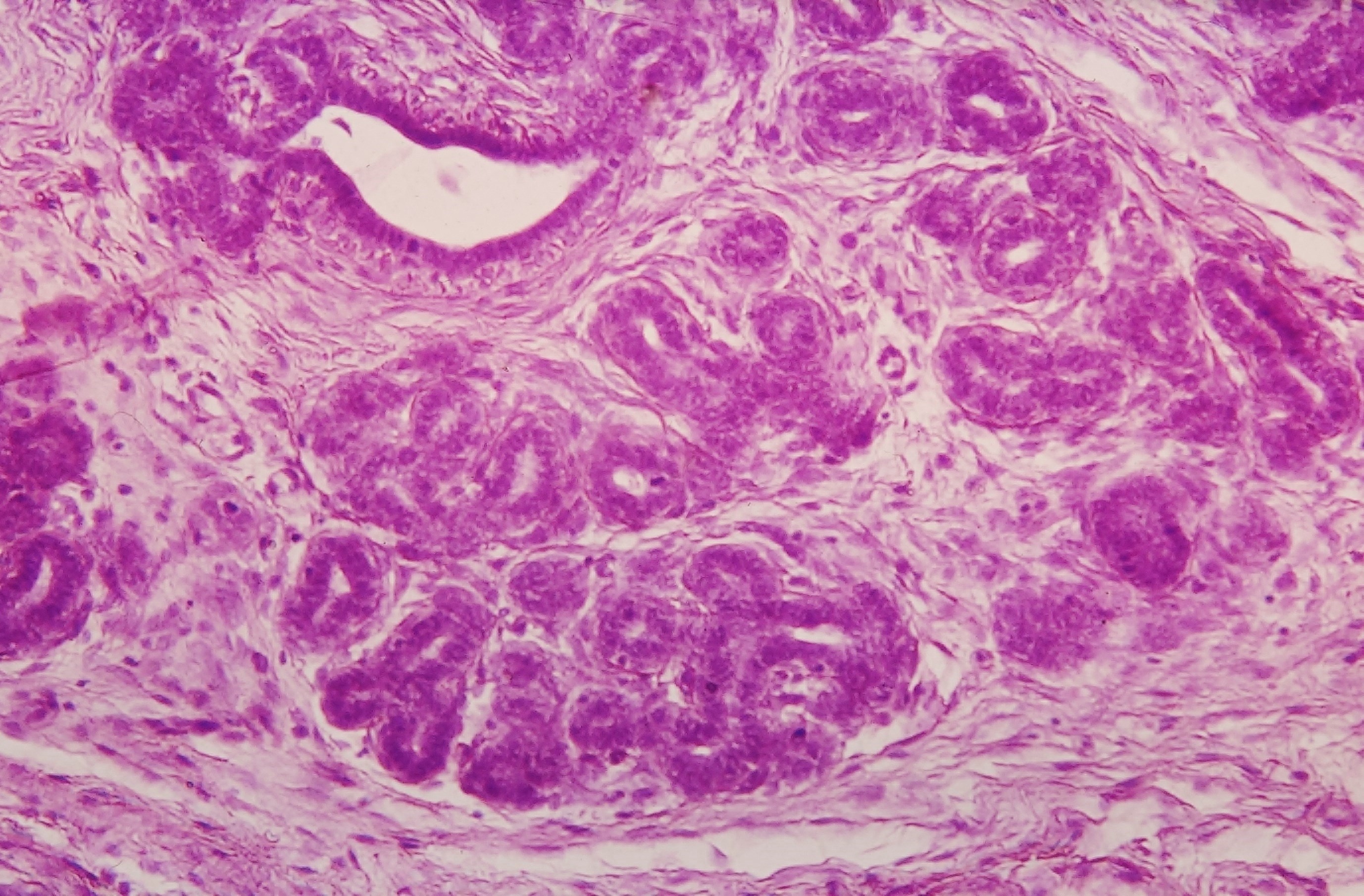
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats). Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: prototherians, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of prototherians, both males and females have functional mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite the fact that these terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
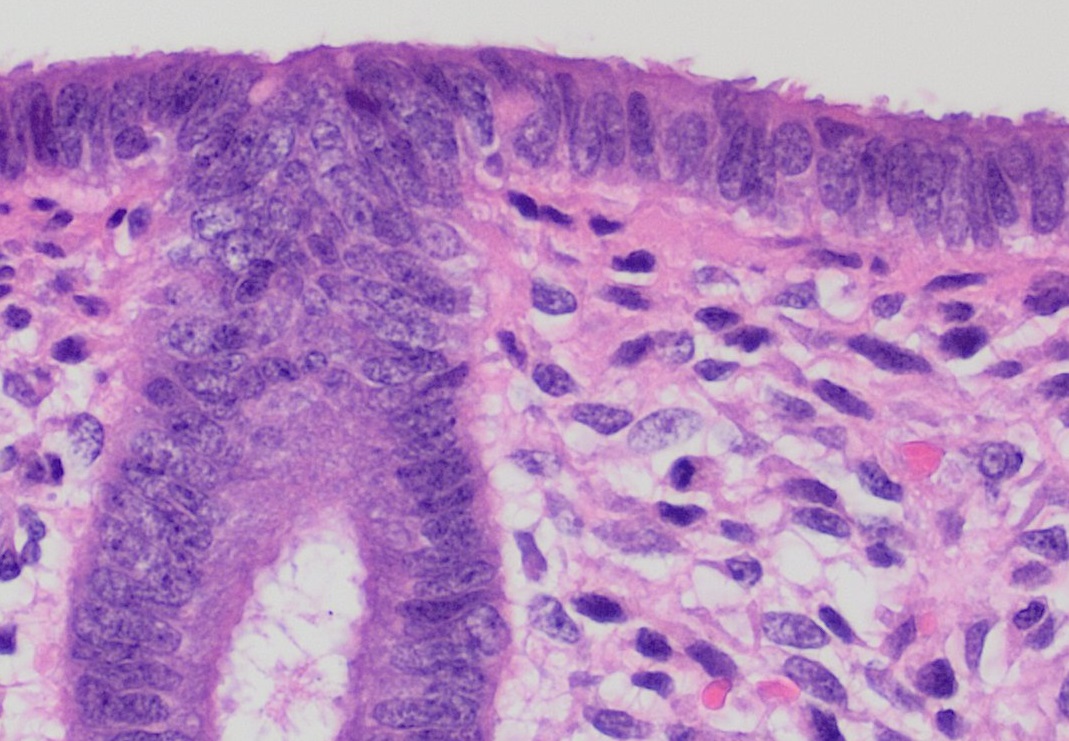
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
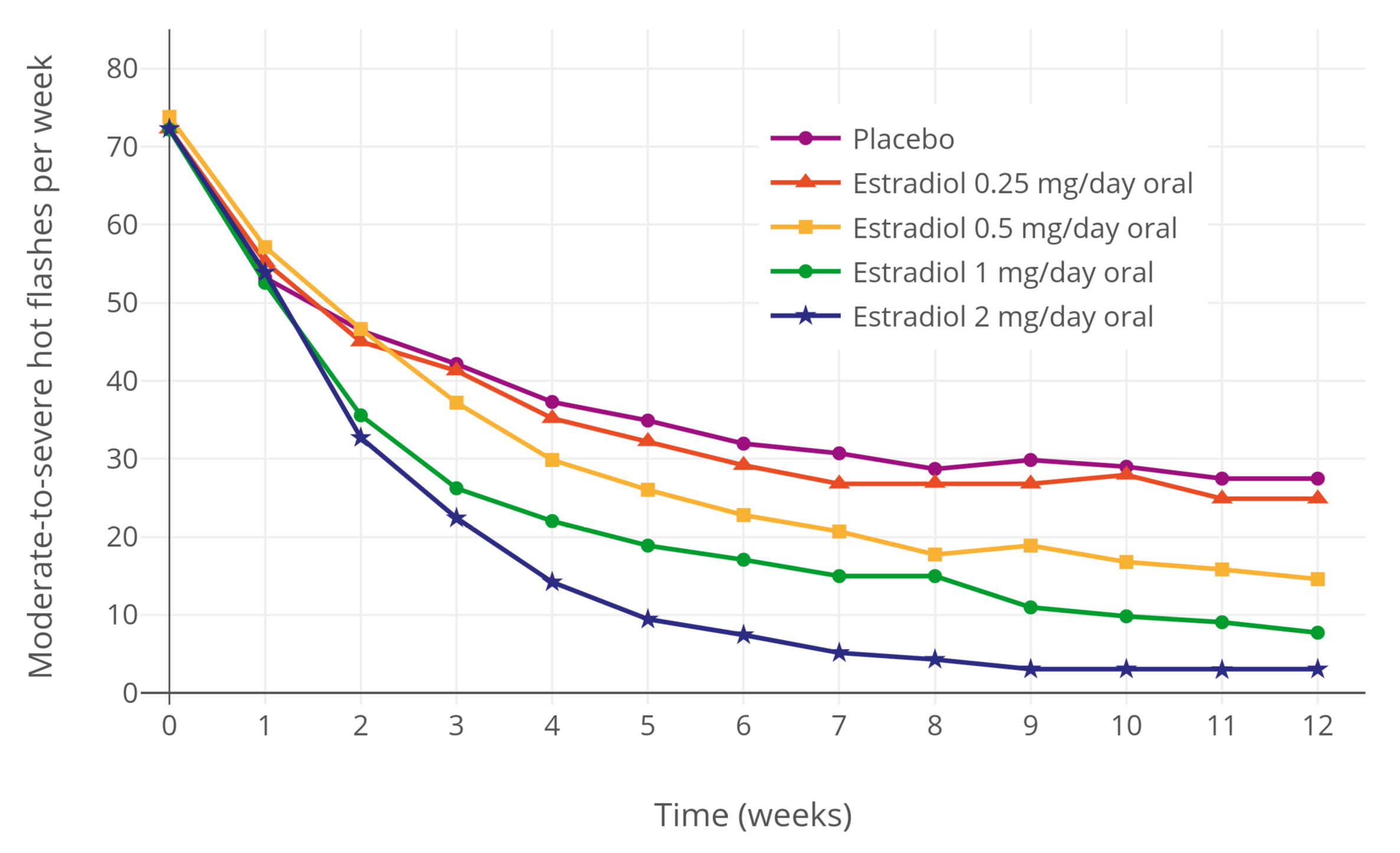
Estrogen (medication)
An estrogen (E) is a type of medication which is used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy, and as part of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. They can also be used in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer and for various other indications. Estrogens are used alone or in combination with progestogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of estrogens include bioidentical estradiol, natural conjugated estrogens, synthetic steroidal estrogens like ethinylestradiol, and synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Estrogens are one of three types of sex hormone agonists, the others being androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone and progestogens like progesterone. Side effects of estrogens include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, headache, nausea, fluid retention, and edema among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |