|
Mesangial Proliferative Glomerulonephritis
Mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis (MesPGN) is a morphological pattern characterized by a numerical increase in mesangial cells and expansion of the extracellular matrix within the mesangium of the glomerulus. The increase in the number of mesangial cells can be diffuse or local and immunoglobulin and/or complement deposition can also occur. MesPGN is associated with a variety of disease processes affecting the glomerulus, though can be idiopathic. The clinical presentation of MesPGN usually consists of hematuria or nephrotic syndrome. Treatment is often consistent with the histologic pattern of and/or disease process contributing to mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, and usually involves some form of immunosuppressant. Mechanism MesPGN often occurs as a result of glomerular injury, though can be idiopathic. MesPGN has been associated with disease processes such as: IgA nephropathy, IgM nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematous, Alport's syndrome, resolving post-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesangial Cell
Mesangial cells are specialised cells in the kidney that make up the mesangium of the glomerulus. Together with the mesangial matrix, they form the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle. The mesangial cell population accounts for approximately 30-40% of the total cells in the glomerulus. Mesangial cells can be categorized as either extraglomerular mesangial cells or intraglomerular mesangial cells, based on their relative location to the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are found between the afferent and efferent arterioles towards the vascular pole of the glomerulus. The extraglomerular mesangial cells are adjacent to the intraglomerular mesangial cells that are located inside the glomerulus and in between the capillaries. The primary function of mesangial cells is to remove trapped residues and aggregated protein from the basement membrane thus keeping the filter free of debris. The contractile properties of mesangial cells have been shown to be insignificant in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesangium
The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a ''tuft'', located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule of the nephron. The glomerulus receives its blood supply from an afferent arteriole of the renal arterial circulation. Unlike most capillary beds, the glomerular capillaries exit into efferent arterioles rather than venules. The resistance of the efferent arterioles causes sufficient hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus to provide the force for ultrafiltration. The glomerul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerulus (kidney)
The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a ''tuft'', located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells. The blood is filtered across the capillary walls of this tuft through the glomerular filtration barrier, which yields its filtrate of water and soluble substances to a cup-like sac known as Bowman's capsule. The filtrate then enters the renal tubule of the nephron. The glomerulus receives its blood supply from an afferent arteriole of the renal arterial circulation. Unlike most capillary beds, the glomerular capillaries exit into efferent arterioles rather than venules. The resistance of the efferent arterioles causes sufficient hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus to provide the force for ultrafiltration. The glome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
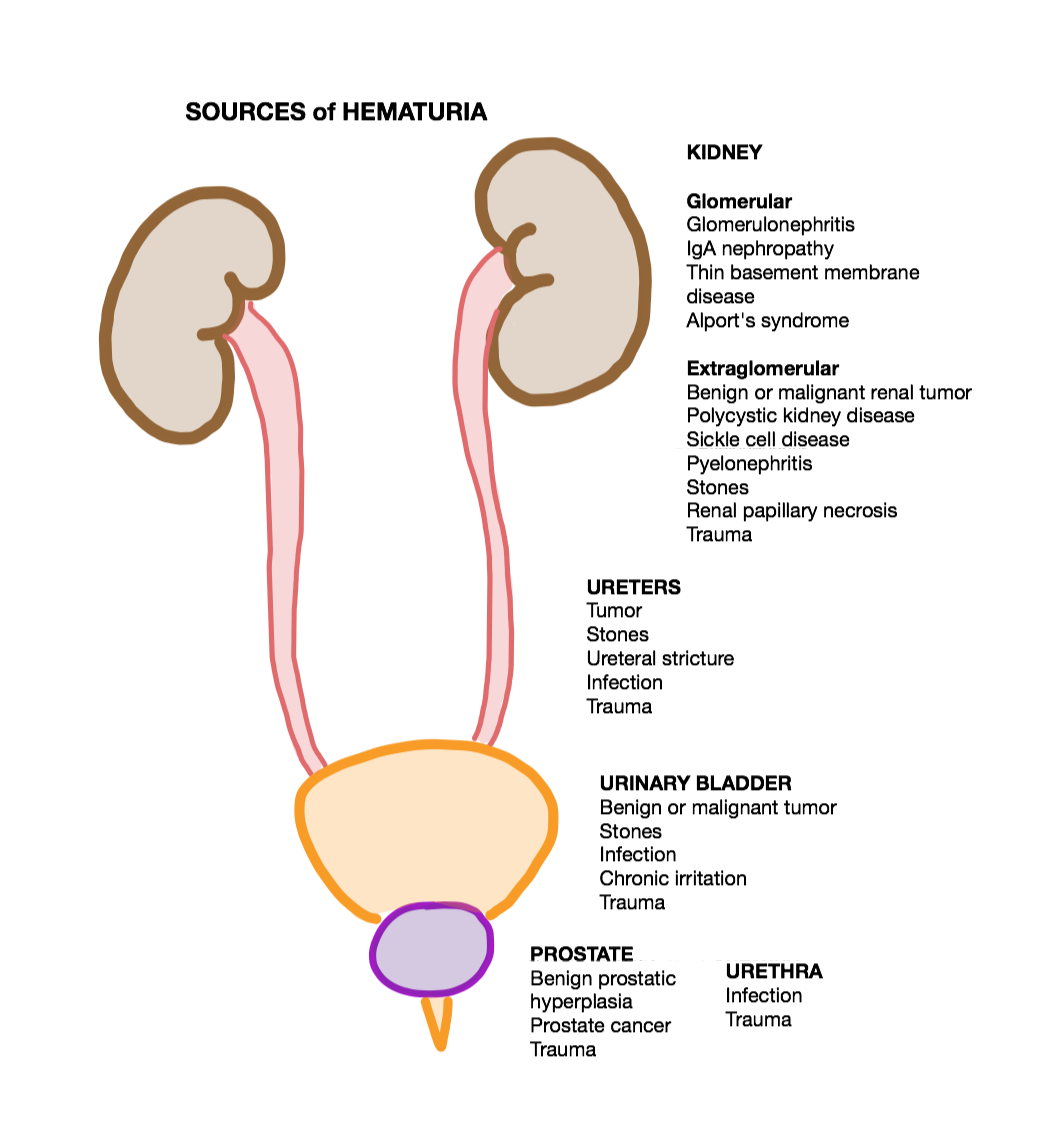
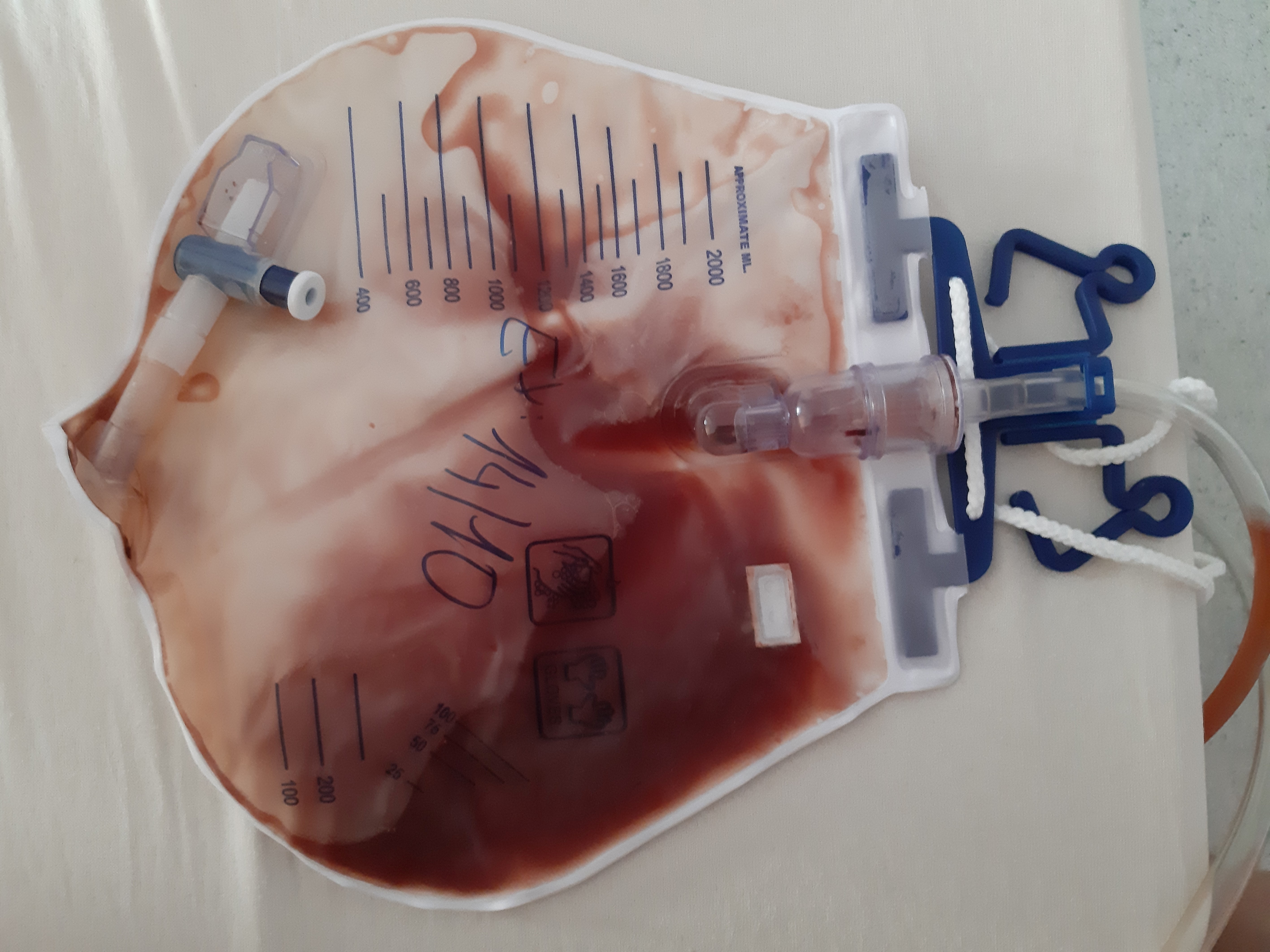
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure. Causes include a number of kidney diseases such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy, and minimal change disease. It may also occur as a complication of diabetes or lupus. The underlying mechanism typically involves damage to the glomeruli of the kidney. Diagnosis is typically based on urine testing and sometimes a kidney biopsy. It differs from nephritic syndrome in that there are no red blood cells in the urine. Treatment is directed at the underlying cause. Other efforts include managing high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and infection risk. A low salt diet and limiting fluids is often recommended. About 5 per 100, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IgA Nephropathy
IgA nephropathy (IgAN), also known as Berger's disease () (and variations), or synpharyngitic glomerulonephritis, is a disease of the kidney (or nephropathy) and the immune system; specifically it is a form of glomerulonephritis or an inflammation of the glomeruli of the kidney. Aggressive Berger's disease (a rarer form of the disease) can attack other major organs, such as the liver, skin and heart. IgA nephropathy is the most common glomerulonephritis worldwide; the global incidence is 2.5/100 000 a year amongst adults. Aggressive Berger's disease is on the NORD list of rare diseases. Primary IgA nephropathy is characterized by deposition of the IgA antibody in the glomerulus. There are other diseases associated with glomerular IgA deposits, the most common being IgA vasculitis (formerly known as Henoch–Schönlein purpura SP, which is considered by many to be a systemic form of IgA nephropathy. IgA vasculitis presents with a characteristic purpuric skin rash, arthritis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomerulonephritis is said to be ''secondary'', and has a different pattern and outcome from conditions with a ''primary'' cause originating in the kidney. The diagnosis of lupus nephritis depends on blood tests, urinalysis, X-rays, ultrasound scans of the kidneys, and a kidney biopsy. On urinalysis, a nephritic picture is found and red blood cell casts, red blood cells and proteinuria is found. Classification The World Health Organization has divided lupus nephritis into five stages based on the biopsy. This classification was defined in 1982 and revised in 1995. Class IV disease (Diffuse proliferative nephritis) is both the most severe, and the most common subtype. Class VI (advanced sclerosing lupus nephritis) is a final class which is inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alport Syndrome
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000-10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect vision, except when changes to the lens occur in later life. Blood in urine is universal. Proteinuria is a feature as kidney disease progresses. The disorder was first identified in a British family by the physician Cecil A. Alport in 1927. Alport syndrome once also had the label hereditary nephritis, but this is misleading as there are many other causes of hereditary kidney disease and 'nephritis'. Alport syndrome is caused by an inherited defect in type IV collagen—a structural material that is needed for the normal function of different parts of the body. Since type IV collagen is found in the ears, eyes, and kidneys, this explains why Alport syndrome affects different seemingly unrelated parts of the body (ears, eyes, kidneys, etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is a disorder of the small blood vessels of the kidney. It is a common complication of bacterial infections, typically skin infection by '' Streptococcus'' bacteria types 12, 4 and 1 ( impetigo) but also after streptococcal pharyngitis, for which it is also known as postinfectious glomerulonephritis (PIGN) or poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN). It can be a risk factor for future albuminuria. In adults, the signs and symptoms of infection may still be present at the time when the kidney problems develop, and the terms ''infection-related glomerulonephritis'' or ''bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis'' are also used. Acute glomerulonephritis resulted in 19,000 deaths in 2013, down from 24,000 deaths in 1990 worldwide. Signs and symptoms Among the signs and symptoms of acute proliferative glomerulonephritis are the following: * Hematuria * Oliguria * Edema * Hypertension * Fever (headache, malaise, anorexia, nausea.) Causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary high blood pressure, defined as high blood pressure due to an identifiable cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both. Causes of AKI are classified as either prerenal (due to decreased blood flow to the kidney), intrinsic renal (due to damage to the kidney itself), or postrenal (due to blockage of urine flow). Prerenal causes of AKI include sepsis, dehydration, excessive blood loss, cardiogenic shock, heart failure, cirrhosis, and certain medications like ACE inhibitors or NSAIDs. Intrinsic renal causes of AKI include glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, acute tubular necrosis, certain antibiotics, and chemotherapeutic agents. Postrenal causes of AKI include kidney stones, bladder cancer, neurogenic bladder, enlargement of the prostate, narrowing of the urethra, and certain medications like anticholinergics. The diagnosis of AKI is made based on a person's signs and sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |