|
Merthyr Alexandra RFC
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydfil, daughter of King Brychan of Brycheiniog, who according to legend was slain at Merthyr by pagans about 480 CE. generally means "martyr" in modern Welsh, but here closer to the Latin : a place of worship built over a martyr's relics. Similar place names in south Wales are Merthyr Cynog, Merthyr Dyfan and Merthyr Mawr. History Pre-history Peoples migrating north from Europe had lived in the area for many thousands of years. The archaeological record starts from about 1000 BC with the Celts. From their language, the Welsh language developed. Hillforts were built during the Iron Age and the tribe that inhabited them in the south of Wales was called the Silures, according to Tacitus, the Roman historian of the Roman invaders. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merthyr Tydfil County Borough
Merthyr Tydfil County Borough ( cy, Bwrdeistref Sirol Merthyr Tudful) is a county borough (since 1908) in the south-east of Wales. In mid 2018, it had an estimated population of 60,183. It is located in the historic county of Glamorgan and takes its name from the town with the same name. The county borough consists of the northern part of the Taff Valley and the smaller neighbouring Taff Bargoed Valley. It borders the counties of Rhondda Cynon Taf to the west, Caerphilly County Borough to the east, and Powys to the north. History Pre-industrial Merthyr What is now Merthyr Tydfil town centre was originally little more than a village. An ironworks existed in the parish in the Elizabethan period, but it did not survive beyond the early 1640s at the latest. In 1754, it was recorded that the valley was almost entirely populated by shepherds. Farm produce was traded at a number of markets and fairs, notably the Waun Fair above Dowlais.The Welsh Academy Encyclopedia of Wales. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare ("hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 (10,000 square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa (1,000 m2) and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Taff
The River Taff ( cy, Afon Taf) is a river in Wales. It rises as two rivers in the Brecon Beacons; the Taf Fechan (''little Taff'') and the Taf Fawr (''great Taff'') before becoming one just north of Merthyr Tydfil. Its confluence with the River Severn estuary is in Cardiff. The river supports several species of migratory fish, including salmon, sewin (sea trout), and eel. Course From its confluence at Cefn-coed-y-cymmer, the river flows south, passing several towns. It picks up a few tributaries, such as the River Cynon, River Rhondda, Bargoed Taf and Nant Clydach. It flows through Pontypridd and through to Taff's Well, the site of Wales' only thermal spring. It flows underneath the M4 Motorway, before turning southeastward and flowing past the Cardiff suburbs of Radyr, Whitchurch, Llandaff, Pontcanna, the city centre and Grangetown, before emptying into Cardiff Bay, near to the mouth of the River Ely. Taf Fawr The Taf Fawr rises below the peak of Corn Du, south- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penydarren
: ''For Trevithick's Pen-y-darren locomotive, see Richard Trevithick#"Pen-y-Darren" locomotive, Richard Trevithick.'' Penydarren is a Community (Wales), community and electoral ward in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough in Wales. Description The area is most notable for being the site of a 1st-century Roman fort, and during the Industrial Revolution it housed Penydarren Ironworks the third largest of the great Merthyr works. Penydarren was also used by Richard Trevithick as the location for his experiments into steam locomotion. The community and ward has a population of 5,253, increasing to 5,419 at the 2011 Census. Penydarren Park, the site of the Roman fort and the football ground, is today outside the community boundary. Roman fort Being located on a spur of land above sea level, just southwest of the River Taff, made Pen-y-Darren an ideal location to build an occupation outpost fort for the Romans in AD75, during the governorship of Sextus Julius Frontinus. It was during this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Auxiliary
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen Roman legion, legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of infantry as the legions and, in addition, provided almost all of the Roman army's Roman cavalry, cavalry (especially light cavalry and horse archer, archers) and more specialised troops. The ''auxilia'' thus represented three-fifths of Rome's regular land forces at that time. Like their legionary counterparts, auxiliary recruits were mostly volunteers, not conscripts. The Auxilia were mainly recruited from the ''peregrinus (Roman), peregrini'', free provincial subjects who did not hold Roman citizenship and constituted the vast majority of the population in the 1st and 2nd centuries (c. 90% in the early 1st century). In contrast to the legions, which only admitted Roman citizenship, Roman citizens, members of the Auxilia could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Fort
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term. In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and plural forms could refer in Latin to either a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". However, scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large legionary fortresses, smaller forts for cohorts or for auxiliary forces, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. For a list of known castra, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
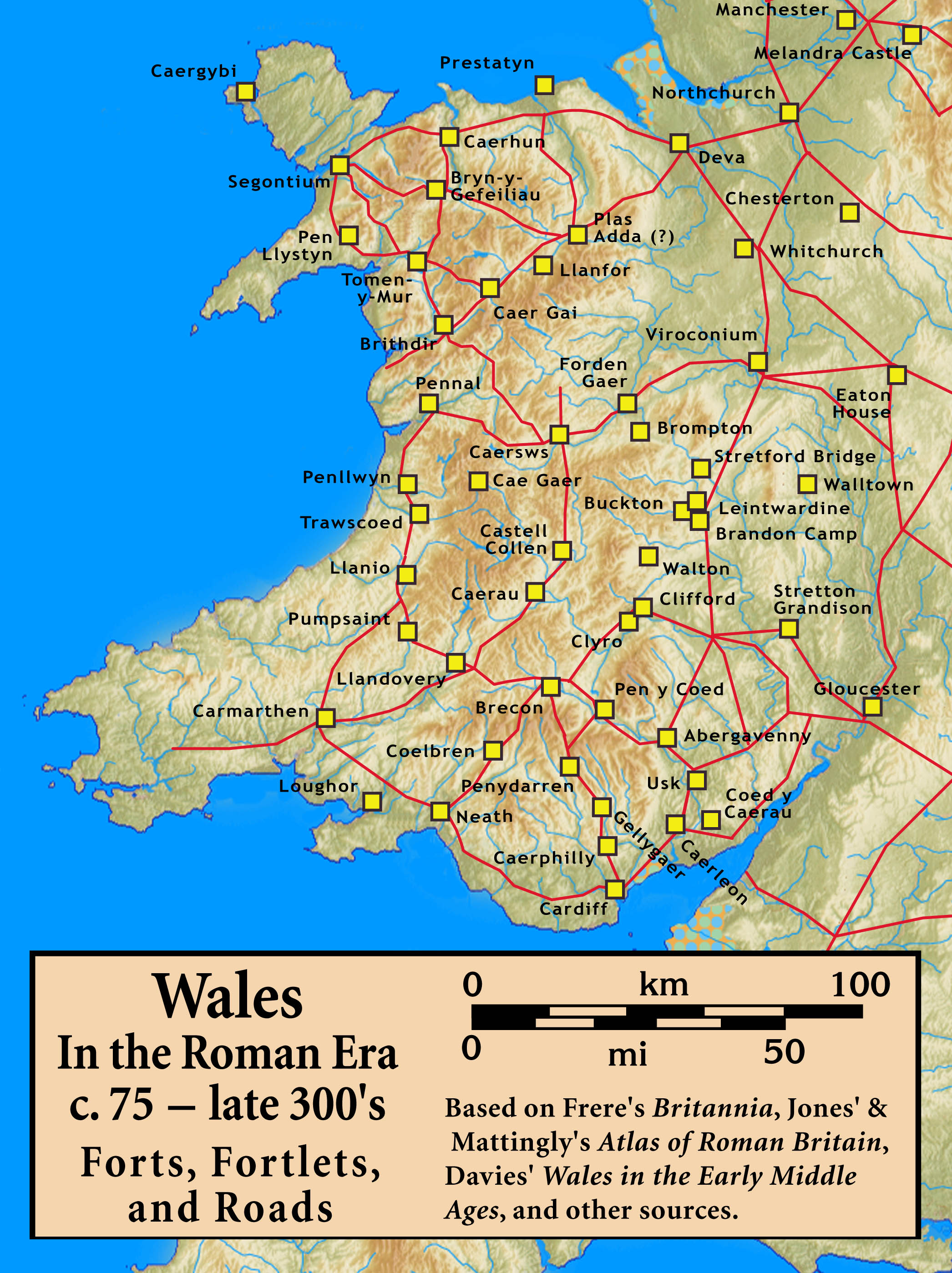
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanisation in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is located in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of mineral wealth, and the Romans used their engineering technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman campaigns of conquest in Wales appear in surviving ancient sources, who record in particular the resistance and ultimate conquest of two of the five na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Invasion Of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Stanegate was established. Conquest of the far north and Scotland took longer with fluctuating success. The Roman army was generally recruited in Italia, Hispania, and Gaul. To control the English Channel they used the newly formed fleet. The Romans under their general Aulus Plautius first forced their way inland in several battles against British tribes, including the Battle of the Medway, the Battle of the Thames, and in later years Caratacus's last battle and the Roman conquest of Anglesey. Following a widespread uprising in AD 60 in which Boudica sacked Camulodunum, VerulamiumChurchill, ''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples'', p. 7 and Londinium, the Romans suppressed the rebellion in the Defeat of Boudica. They went on eventually to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historiography, Roman historians by modern scholars. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals (Tacitus), ''Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales'') and the Histories (Tacitus), ''Histories'' (Latin: ''Historiae'')—examine the reigns of the Roman emperor, emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). These two works span the history of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the death of Domitian (96 AD), although there are substantial Lacuna (manuscripts), lacunae in the surviving texts. Tacitus's other writings discuss Public speaking, oratory (in dialogue format, see ''Dialogus de oratoribus''), Germania (in Germania (book), ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunni; and to the west by the Demetae. Origins According to Tacitus's biography of Agricola, the Silures usually had a dark complexion and curly hair. Due to their appearance, Tacitus believed they had crossed over from Spain at an earlier date."... the swarthy faces of the Silures, the curly quality, in general, of their hair, and the position of Spain opposite their shores, attest to the passage of Iberians in old days and the occupation by them of these districts; ..." (Tacitus Annales Xi.ii, translated by M. Hutton) Jordanes, in his Origins and Deeds of the Goths, describes the Silures. "The Silures have swarthy features and are usually born with curly black hair, but the inhabitants of Caledonia have reddish hair and large loose-joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)