|
Merge (software)
Merge is a software system which allows a user to run DOS/ Windows 3.1 on SCO UNIX, in an 8086 virtual machine. History Merge was originally developed to run DOS under UNIX System V Release 2 on an AT&T 6300 Plus personal computer. Development of the virtual machine began in late 1984, and AT&T announced the availability of the machine on 9 October 1985, referring to the bundled Merge software as Simultask. (The PC 6300 Plus shipped with MS-DOS in 1985 though, because its Unix System V distribution was not ready until the end March 1986.) Merge was developed by engineers at Locus Computing Corporation, with collaboration from AT&T hardware and software engineers, particularly on aspects of the system that were specific to the 6300 Plus (in contrast to a standard IBM PC/AT). The AT&T 6300 Plus contained an Intel 80286 processor, which did not include the support for 8086 virtual machines (virtual 8086 mode) found in the 80386 and later processors in the x86 family. On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus Computing Corporation
Locus Computing Corporation was formed in 1982 by Gerald J. Popek, Charles S. Kline and Gregory I. Thiel to commercialize the technologies developed for the LOCUS distributed operating system at UCLA. Locus was notable for commercializing single-system image software and producing the Merge package which allowed the use of DOS and Windows 3.1 software on Unix systems. Locus was acquired by Platinum Technology Inc in 1995. Products AIX for IBM PS/2 and System/370 Locus was commissioned by IBM to produce a version of the AIX UNIX based operating system for the PS/2 and System/370 ranges. The single-system image capabilities of LOCUS were incorporated under the name of AIX TCF (transparent computing facility). OSF/1 AD for the Intel Paragon Locus was commissioned by Intel to produce a multiprocessor version of OSF/1 for the Intel Paragon a massively parallel NORMA (No Remote Memory Access) system. The system was known as OSF/1 AD, where AD stood for "Advanced Developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
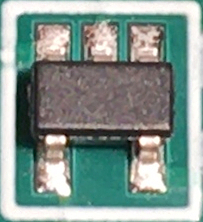
Watchdog Timer
A watchdog timer (sometimes called a ''computer operating properly'' or ''COP'' timer, or simply a ''watchdog'') is an electronic or software timer that is used to detect and recover from computer malfunctions. Watchdog timers are widely used in computers to facilitate automatic correction of temporary hardware faults, and to prevent errant or malevolent software from disrupting system operation. During normal operation, the computer regularly restarts the watchdog timer to prevent it from elapsing, or "timing out". If, due to a hardware fault or program error, the computer fails to restart the watchdog, the timer will elapse and generate a timeout signal. The timeout signal is used to initiate corrective actions. The corrective actions typically include placing the computer and associated hardware in a safe state and invoking a computer reboot. Microcontrollers often include an integrated, on-chip watchdog. In other computers the watchdog may reside in a nearby chip that connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Interface Source Environment
Windows Interface Source Environment (or WISE) was a licensing program from Microsoft which allowed developers to recompile and run Windows-based applications on UNIX and Macintosh platforms. WISE SDKs were based on an emulation of the Windows API which could run on Unix and Macintosh platforms. History WISE was issued in 1994. WISE software development kits were not directly provided by Microsoft. Instead, Microsoft established partnerships with several software providers (which needed to have access to Windows internals source code), which in turn sold WISE SDKs to end-users. A few software providers provided WISE SDKs or emulators, mainly: * Mainsoft developed a product called Mainwin, which provided an implementation of MFC on Unix platforms. * Bristol Technology Inc. developed Wind/U, which ran on top of Motif. * Insignia Solutions provided an emulator called '' Softwindows.'' * Locus Computing Corporation provided an emulator called ''Merge.'' Unfair use of Microsoft domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Microsoft Windows, Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office Productivity software#Office suite, suite, and the Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's List of the largest software companies, largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Tech, Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR DOS 6
DR-DOS (written as DR DOS, without a hyphen, in versions up to and including 6.0) is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS attempting to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-DOS (which were the same product sold under different names). DR-DOS was developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. As ownership changed, various later versions were produced with names including Novell DOS and Caldera OpenDOS. History Origins in CP/M Digital Research's original CP/M for the 8-bit Intel 8080- and Z-80-based systems spawned numerous spin-off versions, most notably CP/M-86 for the Intel 8086/8088 family of processors. Although CP/M had dominated the market since the mid-1970s, and was shipped with the vast majority of non-proprietary-architecture personal computers, the IBM PC in 1981 brought the beginning of what was eventuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novell
Novell, Inc. was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi- platform network operating system known as Novell NetWare. Under the leadership of chief executive Ray Noorda, NetWare became the dominant form of personal computer networking during the second half of the 1980s and first half of the 1990s. At its high point, NetWare had a 63 percent share of the market for network operating systems and by the early 1990s there were over half a million NetWare-based networks installed worldwide encompassing more than 50 million users. Novell technology contributed to the emergence of local area networks, which displaced the dominant mainframe computing model and changed computing worldwide. Novell was the second-largest maker of software for personal computers, trailing only Microsoft Corporation, and became instrumental in making Utah Valley a focus for technology and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Univel
Univel, Inc. was a joint venture of Novell and AT&T's Unix System Laboratories (USL) that was formed in December 1991 to develop and market the Destiny desktop Unix operating system, which was released in 1992 as UnixWare 1.0. Univel existed only briefly in the period between AT&T initially divesting parts of USL in 1991, and its eventual outright purchase by Novell, which completed in June 1993, thereby acquiring rights to the Unix operating system. Novell merged USL and Univel into their new Unix Systems Group (USG). Beginning Novell was the leader in network operating system software, with its product NetWare, while Unix System Laboratories was an AT&T majority-owned entity responsible for the development and maintenance of one of the main branches of the Unix operating system, the UNIX System V Release 4 source code product. The idea to combine forces originated during 1991, with USL chief Roel Pieper believing that the advent of 32-bit applications and workgroup comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix Technologies
Phoenix Technologies Ltd is an American company that designs, develops and supports core system software for personal computers and other computing devices. The company's products commonly referred to as BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or firmware support and enable the compatibility, connectivity, security and management of the various components and technologies used in such devices. Phoenix Technologies and IBM developed the El Torito standard. Phoenix was incorporated in Massachusetts in September 1979, and its headquarters are in Campbell, California. History In 1979, Neil Colvin formed what was then called Phoenix Software Associates after his prior employer, Xitan, went out of business. Neil hired Dave Hirschman, a former Xitan employee. During 1980–1981, they rented office space for the first official Phoenix location at 151 Franklin Street, Boston, Massachusetts. In this same time period Phoenix purchased a non-exclusive license for Seattle Computer Products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactive Systems Corporation
Interactive Systems Corporation (styled INTERACTIVE Systems Corporation, abbreviated ISC) was a US-based software company and the first vendor of the Unix operating system outside AT&T, operating from Santa Monica, California. It was founded in 1977 by Peter G. Weiner, a RAND Corporation researcher who had previously founded the Yale University computer science department and had been the Ph. D. advisor to Brian Kernighan, one of Unix's developers at AT&T. Weiner was joined by Heinz Lycklama, also a veteran of AT&T and previously the author of a Version 6 Unix port to the LSI-11 computer. ISC was acquired by the Eastman Kodak Company in 1988, which sold its ISC Unix operating system assets to Sun Microsystems on September 26, 1991. Kodak sold the remaining parts of ISC to SHL Systemhouse Inc in 1993. Several former ISC staff founded Segue Software which partnered with Lotus Development to develop the Unix version of Lotus 1-2-3 and with Peter Norton Computing to develop the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Flight Simulator
''Microsoft Flight Simulator'' is a series of amateur flight simulator programs for Microsoft Windows operating systems, and earlier for MS-DOS and Classic Mac OS. It was an early product in the Microsoft application portfolio and differed significantly from Microsoft's other software, which was largely business-oriented. In November 2022, ''Microsoft Flight Simulator'' is the longest-running software product line for Microsoft, predating Windows by three years. ''Microsoft Flight Simulator'' is one of the longest-running PC video game series of all time. Bruce Artwick began the development of ''Flight Simulator'' in 1977. His company, Sublogic, initially distributed it for various personal computers. In 1981, Artwick was approached by Microsoft's Alan M. Boyd who was interested in creating a "definitive game" that would graphically demonstrate the difference between older 8-bit computers, such as the Apple II, and the new 16-bit computers, such as the IBM PC, still in dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |