|
Menyuan
Menyuan Hui Autonomous County ( zh, s=éšæșćæèȘæČ»ćż, t=éæșćæèȘæȻ瞣, p=MĂ©nyuĂĄn HuĂzĂș ZĂŹzhĂŹxiĂ n, Xiao'erjing: ; bo, àœŠàœșàœàœŠàŒàœàœČàœàŒàœ§àœŽàœ àœșàŒàœąàœČàœàœŠàŒàœąàœàŒàœŠàŸàŸ±àœŒàœàŒàœàœàŒ) is a county in the northeast of Qinghai Province, China, bordering Gansu Province to the north. It is under the administration of Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Menyuan is situated on the Datong River between the Qilian Mountains and Daban Mountains. Gangshiqia Peak rises dramatically in the north of the county. It used to be called Menyuan () in Chinese, with a different first character from the current name. Climate Transportation * LanzhouâXinjiang High-Speed Railway ( Menyuan railway station) * China National Highway 227 See also * List of administrative divisions of Qinghai Qinghai, a province of the People's Republic of China, is made up of the following administrative divisions. Administrative divisions All of these admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Administrative Divisions Of Qinghai
Qinghai, a province of the People's Republic of China, is made up of the following administrative divisions. Administrative divisions All of these administrative divisions are explained in greater detail at Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China. This chart lists all prefecture-level and county-level divisions of Qinghai. Administrative divisions history Recent changes in administrative divisions Population composition Prefectures Counties Drafted and proposed cities Qinghai is planning to re-organise the following administrative divisions: ;County-level cities * Gonghe â Gonghe County * Guide â Guide County * Haiyan â Haiyan County *Qaidam () â Da Qaidam and Delingha * Maqin â Maqin County See also * List of township-level divisions of Qinghai, for towns and townships References {{authority control Qinghai Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangshiqia Peak
Gangshiqia Peak () is a high mountain peak in the eastern Qilian Mountains of northeastern Qinghai province. The mountain is located within Menyuan Hui Autonomous County of Haibei Prefecture, and is not far from the Gansu border. Ganshiqia is the highest peak in the Lenglong Ling (subrange) of the Qilian Mountains. Its southern slopes are drained by the Datong River and tributaries, while its northern slopes are drained by the Dongda He, an endorheic river terminating in Gansu near Jinchang Jinchang () is a prefecture-level city in the centre of Gansu province, People's Republic of China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the north. Geography Jinchang City is located in central Gansu province, west of the Yellow River, north of the Qi .... The mountain possesses a popular climbing route via its glaciers, although Menyuan County is closed to foreigners without a permit. The nearest town is (), alternately Qingshizui (), in Menyuan County. References {{Reflist Mountains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
Haibei Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (; , , Tib.pin.: ''cojang poirig ranggyong kĂŒ'') is an autonomous prefecture of northeastern Qinghai Province, China. The prefecture has an area of and its seat is Haiyan County. Its name literally means "north of Qinghai Lake." This Tibetan culture area was incorporated into Qinghai province into Qinghai province in the early 1950s, as opposed to being part of the Tibet Autonomous Region. Demographics According to the 2000 census, Haibei has 258,922 inhabitants with a population density of 6.58 inhabitants/km2. The following is a list of ethnic groups in the prefecture, 2000 census. Subdivisions The prefecture is subdivided into 4 county-level divisions: 3 counties and 1 autonomous county Autonomous counties () and autonomous banners () are county-level autonomous administrative divisions of China Chinese autonomous administrative divisions are associated with one or more ethnic minorities that are designated as autonomous w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
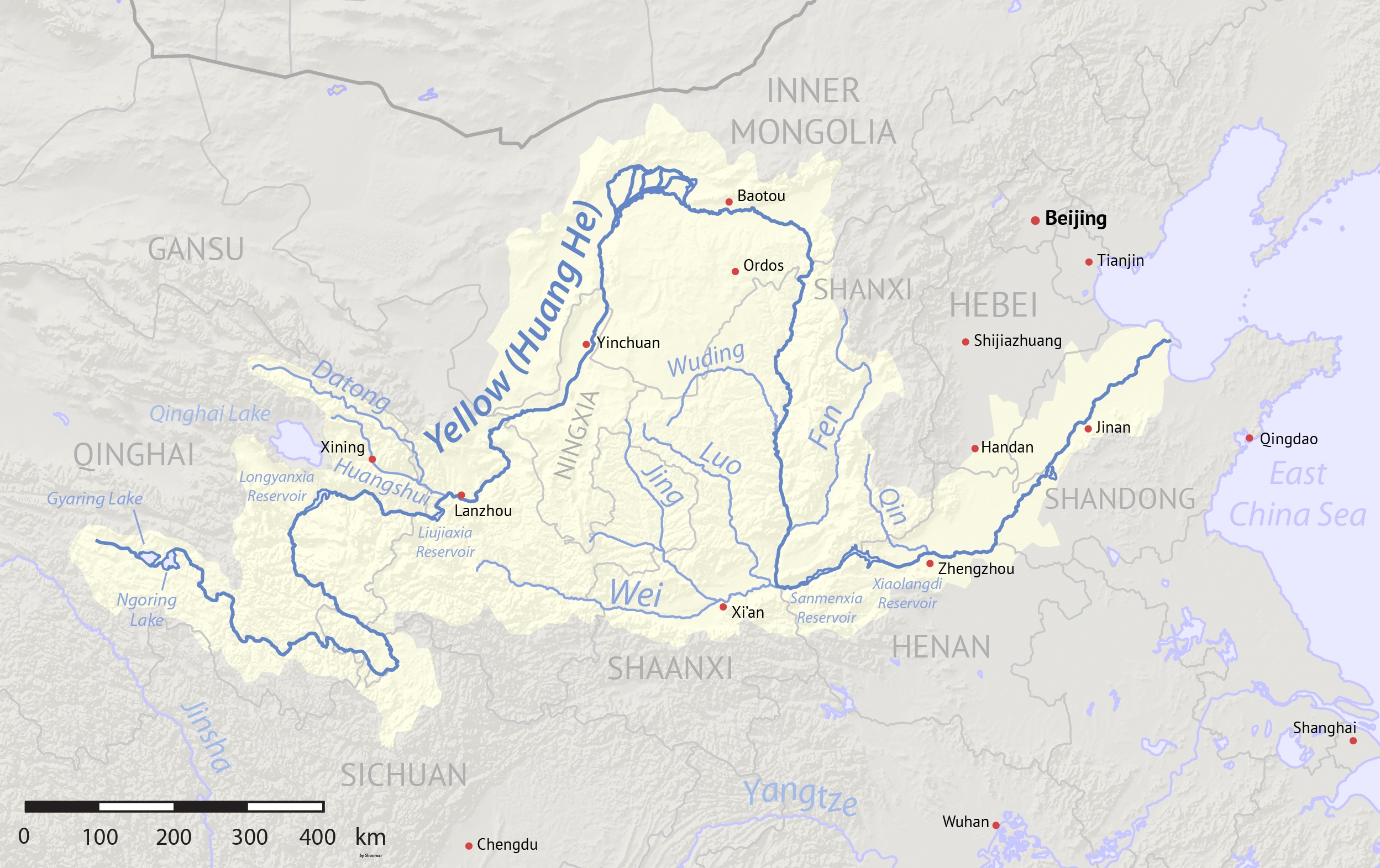
Datong River
The Datong River (), known as the Julak Chu in Amdo Tibetan, is a river in China in the Yellow River basin. It has a total length of , and a basin area of . It has an average annual flow of 90.5 cubic meters per second. It was previously spelled Tatung in English. The river forms in Tianjun County, part of Qinghai Province's Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. It then flows easterly separating the Qilian Mountains The Qilian Mountains (, also romanized as Tsilien; Mongghul: Chileb), together with the Altyn-Tagh (Altun Shan) also known as Nan Shan (, literally "Southern Mountains"), as it is to the south of Hexi Corridor, is a northern outlier of the Kunl ... from the Daban Mountains. The main centre of population along its length here is Menyuan. The Datong meets the Huangshui River at Qinghai's border with Gansu. While it is a tributary of the Huangshui in name, the Datong is actually the main stem of the Huangshui River system and is considerably longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code Of China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures or prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000â009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People's Republic of China. Mail to ROC is treated as international mail, and uses postal codes set forth by Chunghwa Post. Codes starting from 999 are the internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China National Highway 227
China National Highway 227 (G227) runs from Xining, Qinghai to Zhangye, Gansu. It is 347 kilometres in length and runs northwest from Xining towards Zhangye. Route and distance See also * China National Highways External linksOfficial website of Ministry of Transport of PRC 227 Year 227 ( CCXXVII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Senecio and Fulvius (or, less frequently, year 980 ''Ab urbe condi ... Transport in Gansu Transport in Qinghai {{PRChina-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qilian Mountains
The Qilian Mountains (, also romanized as Tsilien; Mongghul: Chileb), together with the Altyn-Tagh (Altun Shan) also known as Nan Shan (, literally "Southern Mountains"), as it is to the south of Hexi Corridor, is a northern outlier of the Kunlun Mountains, forming the border between Qinghai and the Gansu provinces of northern China. Geography The range stretches from the south of Dunhuang some 800 km to the southeast, forming the northeastern escarpment of the Tibetan Plateau and the southwestern border of the Hexi Corridor. The eponymous Qilian Shan peak, situated some 60 km south of Jiuquan, at , rises to 5,547 m. It is the highest peak of the main range, but there are two higher peaks further south, Kangze'gyai at wit5,808 mand Qaidam Shan peak at wit5,759 m Other major peaks include Gangshiqia Peak in the east. The Nan-Shan range continues to the west as Yema Shan (5,250 m) and Altun Shan (Altyn Tagh) (5,798 m). To the east, it passes north of Qinghai L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia (Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of China
Counties ( zh, t=瞣, s=ćż, hp=XiĂ n), formally county-level divisions, are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces and Autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin Dynasty. The number of counties in China proper gradually increased from dynasty to dynasty. As Qin Shi Huang reorganized the counties after his unification, there were about 1,000. Under the Eastern Han Dynasty, the number of counties increased to above 1,000. About 1400 existed when the Sui dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |