|
Mennonites In Paraguay
Mennonites in Paraguay are either ethnic Mennonites with mostly Flemish, Frisian and Prussian ancestry and who speak Plautdietsch or of mixed (southern European/Amerindian) or Amerindian ancestry like the vast majority of Paraguayans. Ethnic Mennonites contribute heavily to the agricultural and dairy output of Paraguay. History In the 1760s,Catherine the Great of Russia invited Mennonites from Prussia to settle north of the Black Sea in exchange for religious freedom and exemption from military service, a precondition founded in their commitment to non-violence. After Russia introduced the general conscription in 1874, many Mennonites migrated to the US and Canada. The members of the Menno Colony moved to Paraguay from Canada when universal, secular compulsory education was implemented in 1917 that required the use of the English language. More conservative Mennonites saw this as a threat to the religious basis of their community. In 1927, 1743 pioneers came from Canada to Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan Bautista, Paraguay
San Juan Bautista (), capital of the Department of Misiones, Paraguay, is considered the cradle of the religious mission culture. The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of San Juan Bautista de las Misiones. Geography San Juan Bautista Misiones is located 196 kilometers south of Asunción. One can travel to the city by following the Route 1st “Mcal. Francisco Solano López”. Climate In summer, the maximum temperature is 42 degrees Celsius. The minimum temperature in winter is zero degrees Celsius. The annual average is 21 degrees Celsius. Demography With a total area of 2,300 square kilometers, San Juan Bautista has a population of 18,441 inhabitants, 9,281 male and 9,161 female, according to projections of the General Office of Statistics, Surveys and Censuses. The city is the third most populated one in Misiones, after San Ignacio and Ayolas. History This city was established during the government of Carlos Antonio López, declared a small town in 1893, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Mennonite
The term ethnic Mennonite refers to Mennonites of Central European ancestry and culture who are considered to be members of a Mennonite ethnic or ethnoreligious group. The term is also used for aspects of their culture, such as language, dress, and Mennonite food.Voth, Norma Jost, "Mennonite Foods & Folkways from South Russia, Volumes I", pp. 35-55. Good Books, 1990. History The most prominent ethnic Mennonite groups are Russian Mennonites (German: ''Russland-Mennoniten''), who formed as an ethnic group in Prussia and South Russia (now Ukraine), but who are of Dutch (both Flemish and Frisian) ancestry and speak Plautdietsch and Mennonites of Pennsylvania Dutch heritage who formed as an ethnic group in North America and who are of Swiss-German and German ancestry. Because Mennonites for centuries almost only married inside their churches, they developed into ethnic groups in Russia since 1789 and in North America since the 1730s, where for a long time almost all of them kept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Order Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churches, another Anabaptist denomination. The Amish are known for simple living, plain dress, Christian pacifism, and slowness to adopt many conveniences of modern technology, with a view neither to interrupt family time, nor replace face-to-face conversations whenever possible, and a view to maintain self-sufficiency. The Amish value rural life, manual labor, humility and '' Gelassenheit'' (submission to God's will). The history of the Amish church began with a schism in Switzerland within a group of Swiss and Alsatian Mennonite Anabaptists in 1693 led by Jakob Ammann. Those who followed Ammann became known as Amish. In the second half of the 19th century, the Amish divided into Old Order Amish and Amish Mennonites; the latter do not abstai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Labor Of Germans In The Soviet Union
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union was considered by the Soviet Union to be part of German war reparations for the damage inflicted by Nazi Germany on the Soviet Union during the Axis-Soviet campaigns (1941-1945) of World War II. Soviet authorities deported German civilians from Germany and Eastern Europe to the USSR after World War II as forced laborers, while ethnic Germans living in the USSR were deported during World War II and conscripted for forced labor. German prisoners of war were also used as a source of forced labor during and after the war by the Soviet Union and by the Western Allies. Nazi Germany had used forced labour of people in the occupied territories since the beginning of World War II. In 1940 it initiated a massive project of enslaving the populations of Eastern European countries to use as forced labour in German factories and agricultural facilities. The Soviet government proposed the use of German labor as reparations in 1943, and raised the iss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organised Persecution Of Ethnic Germans
The persecution of Germans based on their ethnicity has occurred at various points throughout history. These instances have been due to either one of two reasons: 1. The German populations in the area were considered, correctly or not, linked with German nationalist regimes (e.x. Imperial Germany or Nazi Germany) 2. The German people were seen as foreigners ''lacking properties'' in the country in which they resided. An example of the first case can be found in both the World War I era persecution of Germans in the United States and of those in Eastern and Central Europe following the end of World War II. While many victims of these persecutions did not have any connection to those regimes, cooperation between German minority organizations and the Nazi regime did occur, for example in Selbstschutz organizations. This was used as a justification for hostility against both Germans directly involved in these organizations, and those uninvolved. After World War II, many Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close-cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
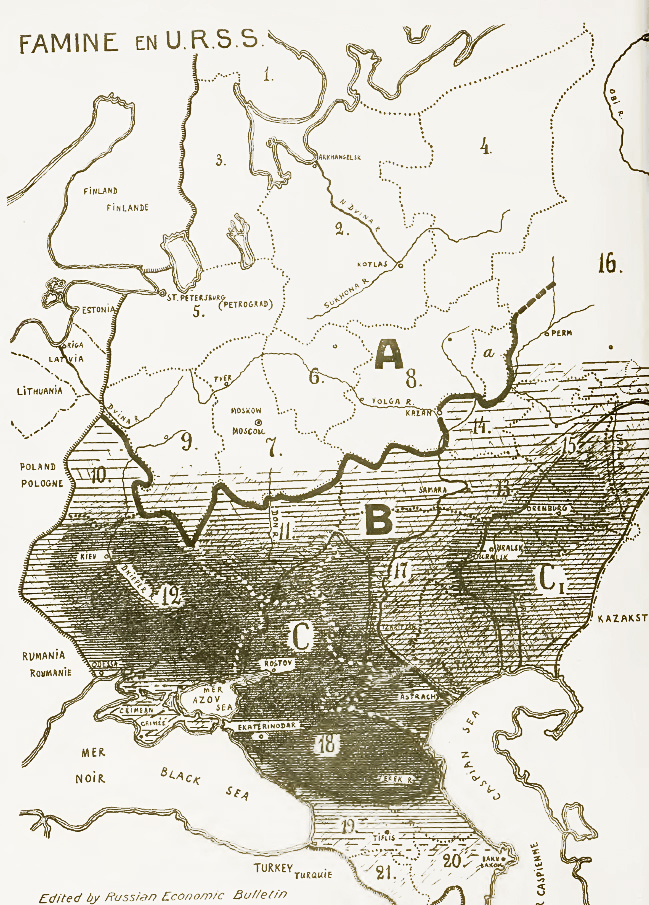
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject to unre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collectivization In The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union introduced the collectivization (russian: Коллективизация) of its agricultural sector between 1928 and 1940 during the ascension of Joseph Stalin. It began during and was part of the first five-year plan. The policy aimed to integrate individual landholdings and labour into collectively-controlled and state-controlled farms: ''Kolkhozes'' and ''Sovkhozes'' accordingly. The Soviet leadership confidently expected that the replacement of individual peasant farms by collective ones would immediately increase the food supply for the urban population, the supply of raw materials for the processing industry, and agricultural exports via state-imposed quotas on individuals working on collective farms. Planners regarded collectivization as the solution to the crisis of agricultural distribution (mainly in grain deliveries) that had developed from 1927. This problem became more acute as the Soviet Union pressed ahead with its ambitious industrializati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persecution Of Christians In The Soviet Union
Throughout the history of the Soviet Union (1917–1991), there were periods when Soviet authorities brutally suppressed and persecuted various forms of Christianity to different extents depending on State interests. Soviet Marxist-Leninist policy consistently advocated the control, suppression, and ultimately, the elimination of religious beliefs, and it actively encouraged the propagation of Marxist-Leninist atheism in the Soviet Union. However, most religions were never officially outlawed. The state advocated the destruction of religion, and to achieve this goal, it officially denounced religious beliefs as superstitious and backward. Froese, Paul. "'I am an atheist and a Muslim': Islam, communism, and ideological competition." Journal of Church and State 47.3 (2005) The Communist Party destroyed churches, synagogues, and mosques, ridiculed, harassed, incarcerated and executed religious leaders, flooded the schools and media with anti-religious teachings, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernheim Colony
The Fernheim Colony is a Plautdietsch-speaking settlement of Russian Mennonite, Mennonites originally from Russia of about 5000 in the Gran Chaco, Chaco of Paraguay. Mennonites from the Soviet Union founded it between 1930 and 1932. Filadelfia is the administrative center of the colony, seat of Boquerón department and is considered the 'Capital of the Chaco'. In the late 1920s, some Mennonite refugees tried to escape persecution of "Kulaks" in Stalinism, Stalinist Russia, which meant the total destruction of the Mennonite religious and cultural life. They left their home villages and gathered in Moscow. For humanitarian reasons they were admitted into Germany, because they were believed to have German ethnicity, though most would be more accurately described as Dutch people, Dutch. Because there was no place in Germany where they could settle together as a community, they moved to Paraguay a year later. There already was a large settlements of Mennonites with the same Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |