|
Meneage
The Meneage ( kw, Menaghek or ''Manahek'') is a district in west Cornwall, United Kingdom. The nearest large towns are Falmouth and Penryn. (''Note: the coordinates above are the approximate centre of the Meneage district.'') The meaning of the name Meneage is "Monkish (land)" and the probability is that in the post-Roman period the land was in the possession of a confederacy of small Celtic monasteries. These may have been founded by missionaries from Brittany. "The north-eastern half of the Lizard peninsula ... has, for the last 1000 years at least and probably for a considerable time longer, gone by the popular name of Meneage, pronounced Menāgue. This name, like Roseland, has no official significance."—Gilbert H. Doble. The Meneage district is located south of the Helford River and is divided into four parishes and part of a fifth. From west to east these are St Mawgan in Meneage (part), St Martin in Meneage, Manaccan, St Anthony in Meneage, and St Keverne. *St Mawg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Martin-in-Meneage
St Martin-in-Meneage ( kw, Dydemin) is a civil parish and village in the Meneage district of the Lizard Peninsula in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is five miles (8 km) south-southeast of Helston. The population at the 2011 census was 377 The church is dedicated to St Martin of Tours Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as th ... and is a chapelry of Mawgan in Meneage (right of sepulture was granted in 1385). The ancient estates of Barry Mylor and Mathiana adjoin the church and the two names indicate that in early times there were chapels of two Breton saints here, of St Melor at Merther Mylor (Barry Mylor) and St Anou at Merther Anou (the modern forms having been variously corrupted).Henderson, Charles (1925) "Parochial history of Cornwall", in: ''Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mawgan-in-Meneage
Mawgan-in-Meneage is a civil parish in Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is situated in the Meneage district of The Lizard peninsula south of Helston in the former administrative district of Kerrier. The parish population at the 2011 census was 1437. Mawgan-in-Meneage lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). Almost a third of Cornwall has AONB designation. Antiquities Evidence of early medieval habitation at Mawgan is in the form of an inscribed pillar stone, located at the meeting of three roads at the centre of the village; it bears an inscription that is no longer readable, but based on an old drawing and a photograph taken in 1936 it could have been a memorial stone to either 'Cnegumus son of Genaius' or 'Genaius son of Cnegumus'. The date of this inscription is not certain beyond having been carved before the twelfth century. History The name of the manor was given as "scanctus icmawgan" after the dedication of the church, in the Domesday Book. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Anthony-in-Meneage
St Anthony-in-Meneage ( kw, Lannentenin) is a coastal civil parish and village in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The parish is in the Meneage district of the Lizard peninsula. In the 2001 census the parish had a population of 171, decreasing to 168 at the 2011 census. Geography The hamlet is on a peninsula between the Helford River and Gillan Harbour on the west side of Falmouth Bay, five miles (8 km) south of Falmouth and seven miles (11 km) east of Helston at . It largely consists of a church, the former vicarage, a farmhouse, and various converted farm buildings now used as holiday accommodation. The peninsula ends at Dennis Head, the site of an early Celtic fortress. Later it served as a Royalist stronghold during the Civil War, and provided a lookout point for the Home Guard during the Second World War. The parish is divided by the tidal Gillan Creek. The hamlet and parish church are on the north side of the creek. On the south side are the hamlets of Carn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lizard
The Lizard ( kw, An Lysardh) is a peninsula in southern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The most southerly point of the British mainland is near Lizard Point at SW 701115; Lizard village, also known as The Lizard, is the most southerly on the British mainland, and is in the civil parish of Landewednack, the most southerly parish. The valleys of the River Helford and Loe Pool form the northern boundary, with the rest of the peninsula surrounded by sea. The area measures about . The Lizard is one of England's natural regions and has been designated as a National Character Area 157 by Natural England. The peninsula is known for its geology and for its rare plants and lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). The name "Lizard" is most probably a corruption of the Cornish name "Lys Ardh", meaning "high court". The Lizard's coast is particularly hazardous to shipping and the seaways round the peninsula were historically known as the "Graveyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lizard
The Lizard ( kw, An Lysardh) is a peninsula in southern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The most southerly point of the British mainland is near Lizard Point at SW 701115; Lizard village, also known as The Lizard, is the most southerly on the British mainland, and is in the civil parish of Landewednack, the most southerly parish. The valleys of the River Helford and Loe Pool form the northern boundary, with the rest of the peninsula surrounded by sea. The area measures about . The Lizard is one of England's natural regions and has been designated as a National Character Area 157 by Natural England. The peninsula is known for its geology and for its rare plants and lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). The name "Lizard" is most probably a corruption of the Cornish name "Lys Ardh", meaning "high court". The Lizard's coast is particularly hazardous to shipping and the seaways round the peninsula were historically known as the "Graveyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manaccan
Manaccan (; kw, Manahan) is a civil parish and village on the Lizard peninsula in south Cornwall, United Kingdom. The village is about five miles (8 km) south-southwest of Falmouth. The origin of the name Manaccan is probably derived not from a saint but from the Cornish for (church) of the monks. It was also at times called Minster in English because it must once have had a Celtic monastery. " St Manacca" is recorded as the patron saint as early as 1308. The population of Manaccan was 321 in the 2011 census, an increase from 299 in the 2001 census. Manaccan lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). Almost a third of Cornwall has AONB designation, with the same status and protection as a National Park. Governance Manaccan is in the parliamentary constituency of St Ives. Derek Thomas is the Member of Parliament. For local government purposes it is in the ''St Keverne and Meneage'' ward of Cornwall Council, a unitary authority. Manaccan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Keverne
St Keverne ( kw, Pluw Aghevran (parish), Lannaghevran (village)) is a civil parish and village on The Lizard in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. In addition to the parish, an electoral ward exists called ''St Keverne and Meneage''. This stretches to the western Lizard coast at Gunwalloe. The population of the ward at the 2011 election was 5,220. The Cornish rebellion of 1497 started in St Keverne. The leader of the rebellion Michael An Gof ("the smith" in Cornish) was a blacksmith from St Keverne and is commemorated by a statue in the village. Before his execution, An Gof said that he should have "a name perpetual and a fame permanent and immortal". In 1997 a 500th anniversary march, "Keskerdh Kernow 500", celebrating the rebellion, retraced the route of the original march from St Keverne, via Guildford to London. Geography The parish is a large one. It includes some 10 miles of coast from Nare Point at the mouth of the Helford River to Kennack Sands, and the Manacles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizard Complex
The Lizard complex, Cornwall is generally accepted to represent a preserved example of an exposed ophiolite complex in the United Kingdom. The rocks found in The Lizard area are analogous to those found in such famous areas as the Troodos Mountains, Cyprus and the Semail Ophiolite, Oman. Lithologies The Lizard comprises three main units; the serpentinites, the 'oceanic complex' and the metamorphic basement. Since the pioneering work of Bromley and Kirby these suites have been understood to represent a slice through a section of ocean crust, including the upper level of the mantle, thrust onto continental crust. Serpentinites The serpentinites are actually the metamorphosed and deformed remains of the upper layers of the mantle. The metamorphosis has in most cases taken the form of ductile deformation and serpentinisation. In many cases the rocks have also been subject to varying degrees of later brittle deformation. Pre-deformation they would have been a combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''. Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
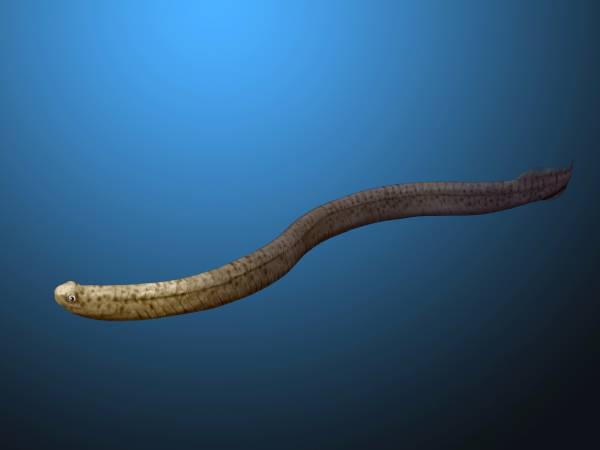
Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', " tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resistant hilltops. The nearly pure silica co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |