|
Memory Rank
A memory rank is a set of DRAM chips connected to the same chip select, which are therefore accessed simultaneously. In practice all DRAM chips share all of the other command and control signals, and only the chip select pins for each rank are separate (the data pins are shared across ranks). Details The term ''rank'' was created and defined by JEDEC, the memory industry standards group. On a DDR, DDR2, or DDR3 memory module, each rank has a 64-bit-wide data bus (72 bits wide on DIMMs that support ECC). The number of physical DRAMs depends on their individual widths. For example, a rank of ×8 (8-bit wide) DRAMs would consist of eight physical chips (nine if ECC is supported), but a rank of ×4 (4-bit wide) DRAMs would consist of 16 physical chips (18, if ECC is supported). Multiple ranks can coexist on a single DIMM. Modern DIMMs can for example feature one rank (single rank), two ranks (dual rank), four ranks (quad rank), or eight ranks (octal rank). There is only a little di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRAM
Dram, DRAM, or drams may refer to: Technology and engineering * Dram (unit), a unit of mass and volume, and an informal name for a small amount of liquor, especially whisky or whiskey * Dynamic random-access memory, a type of electronic semiconductor memory * Dram, Welsh term for a minecart, a small railway cargo truck used in a mine railway Currency and geography * Dram, Armenian for "money" ** Armenian dram, a monetary unit ** Artsakh dram (formerly ''Nagorno-Karabakh dram''), a monetary unit * Dram, the Tibetan name for the town of Zhangmu on the Nepal-Tibet border * Historic English name for Drammen, Norway Music * DRAM (musician) (Shelley Marshaun Massenburg-Smith, born 1988), American rapper and actor * Database of Recorded American Music, an online resource * The Drams, an American band made up of members of Slobberbone See also * Dram shop, a bar, tavern or similar commercial establishment where alcoholic beverages are sold * Dirham The dirham, dirhem or drah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) Chemical milling, etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. PCBs are used to connect or Electrical wiring, "wire" Electronic component, components to one another in an electronic circuit. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers, generally by soldering, which both electrically connects and mechanically fastens the components to the board. Another manufacturing process adds Via (electronics), vias, metal-lined drilled holes that enable electrical interconnections between conductive layers, to boards with more than a single side. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Geometry
In the design of modern computers, memory geometry describes the internal structure of random-access memory. Memory geometry is of concern to consumers upgrading their computers, since older memory controllers may not be compatible with later products. Memory geometry terminology can be confusing because of the number of overlapping terms. The geometry of a memory system can be thought of as a multi-dimensional array. Each dimension has its own characteristics and physical realization. For example, the number of data pins on a memory module is one dimension. Physical features Memory geometry describes the logical configuration of a RAM module, but consumers will always find it easiest to grasp the physical configuration. Much of the confusion surrounding memory geometry occurs when the physical configuration obfuscates the logical configuration. The first defining feature of RAM is form factor. RAM modules can be in compact SO-DIMM form for space constrained applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble (computing)
In the design of pipelined computer processors, a pipeline stall is a delay in execution of an instruction in order to resolve a hazard. Details In a standard five-stage pipeline, during the decoding stage, the control unit will determine whether the decoded instruction reads from a register to which the currently executed instruction writes. If this condition holds, the control unit will stall the instruction by one clock cycle. It also stalls the instruction in the fetch stage, to prevent the instruction in that stage from being overwritten by the next instruction in the program. In a Von Neumann architecture which uses the program counter (PC) register to determine the current instruction being fetched in the pipeline, to prevent new instructions from being fetched when an instruction in the decoding stage has been stalled, the value in the PC register and the instruction in the fetch stage are preserved to prevent changes. The values are preserved until the instruction c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
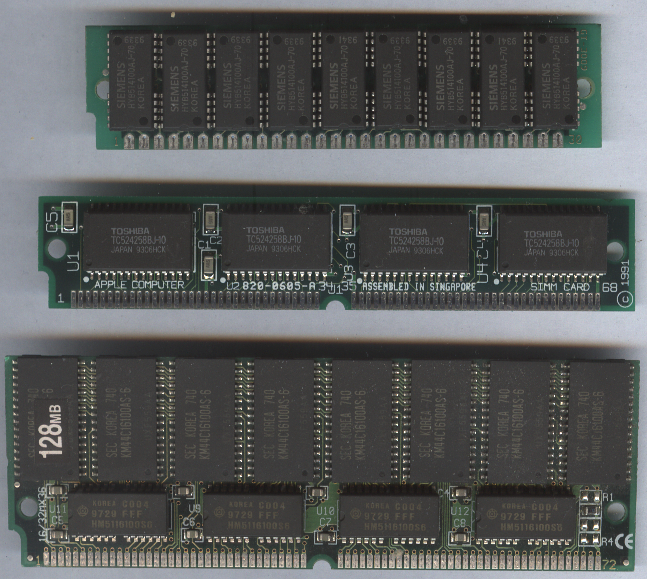
SIMM
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It is a printed circuit board upon which multiple random-access memory Integrated circuit chips are attached to one or both sides. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards ( 8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1983 by James E. ClaytonClayton, James E. (1983)Low-cost, high-density memory packaging: A 64K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Module
In computing, a memory module or RAM stick is a printed circuit board on which Computer memory, memory integrated circuits are mounted. Memory modules permit easy installation and replacement in electronic systems, especially computers such as personal computers, workstations, and Server (computing), servers. The first memory modules were proprietary designs that were specific to a model of computer from a specific manufacturer. Later, memory modules were standardized by organizations such as JEDEC and could be used in any system designed to use them. Distinguishing characteristics of computer memory modules include voltage, capacity, speed (i.e., bit rate), and computer form factor, form factor. Overview Types of memory module include: * TransFlash Memory Module * SIMM, a single in-line memory module * DIMM, dual in-line memory module ** Rambus memory modules are a subset of DIMMs, but are normally referred to as RIMMs ** SO-DIMM, small outline DIMM, a smaller version of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Memory
Registered memory (also called buffered memory) is computer memory that has a register between the DRAM modules and the system's memory controller. A registered memory module places less electrical load on a memory controller than an unregistered one. Registered memory allows a computer system to remain stable with more memory modules than it would have otherwise. When conventional memory is compared with registered memory, conventional memory is usually referred to as unbuffered memory or unregistered memory. When registered memory is manufactured as a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), it is called an RDIMM. Similarly, an unregistered DIMM is called a UDIMM or simply "DIMM". Registered memory is often more expensive because of the additional circuitry required and lower number of units sold, so it is usually found only in applications where the need for scalability and robustness outweighs the need for a low price for example, registered memory is usually used in server ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Controller
A memory controller, also known as memory chip controller (MCC) or a memory controller unit (MCU), is a digital circuit that manages the flow of data going to and from a computer's main memory. When a memory controller is integrated into another chip, such as an integral part of a microprocessor, it is usually called an integrated memory controller (IMC). Memory controllers contain the logic necessary to read and write to dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), and to provide the critical memory refresh and other functions. Reading and writing to DRAM is performed by selecting the row and column data addresses of the DRAM as the inputs to the multiplexer circuit, where the demultiplexer on the DRAM uses the converted inputs to select the correct memory location and return the data, which is then passed back through a multiplexer to consolidate the data in order to reduce the required bus width for the operation. Memory controllers' bus widths range from 8-bit in earlier systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unbuffered Memory
Registered memory (also called buffered memory) is computer memory that has a register between the DRAM modules and the system's memory controller. A registered memory module places less electrical load on a memory controller than an unregistered one. Registered memory allows a computer system to remain stable with more memory modules than it would have otherwise. When conventional memory is compared with registered memory, conventional memory is usually referred to as unbuffered memory or unregistered memory. When registered memory is manufactured as a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), it is called an RDIMM. Similarly, an unregistered DIMM is called a UDIMM or simply "DIMM". Registered memory is often more expensive because of the additional circuitry required and lower number of units sold, so it is usually found only in applications where the need for scalability and robustness outweighs the need for a low price for example, registered memory is usually used in servers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chip Select
Chip select (CS) or slave select (SS) is the name of a control line in digital electronics used to select one (or a set) of integrated circuit An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...s (commonly called "chips") out of several connected to the same computer bus, usually utilizing the three-state logic. One bus that uses the chip/slave select is the Serial Peripheral Interface Bus (SPI bus). When an engineer needs to connect several devices to the same set of input wires (e.g., a computer bus), but retain the ability to send and receive data or commands to each device independently of the others on the bus, they can use a chip select. The chip select is a command pin on many integrated circuits which connects the I/O pins on the device to the internal circuitry of tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECC RAM
Error correction code memory (ECC memory) is a type of computer data storage that uses an error correction code (ECC) to detect and correct ''n''-bit data corruption which occurs in memory. Typically, ECC memory maintains a memory system immune to single-bit errors: the data that is read from each word is always the same as the data that had been written to it, even if one of the bits actually stored has been flipped to the wrong state. Most non-ECC memory cannot detect errors, although some non-ECC memory with parity support allows detection but not correction. ECC memory is used in most computers where data corruption cannot be tolerated, like industrial control applications, critical databases, and infrastructural memory caches. Concept Error correction codes protect against undetected data corruption and are used in computers where such corruption is unacceptable, examples being scientific and financial computing applications, or in database and file servers. ECC can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIMM
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM chips and pins. The vast majority of DIMMs are manufactured in compliance with JEDEC memory standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and capacities, and are generally one of two lengths: PC, which are , and laptop (SO-DIMM), which are about half the length at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs were introduced to eliminate this disadvantage. The contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant, while DIMMs have separate electrical contacts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |