|
Mellrichstadt–Fladungen Railway
The Mellrichstadt–Fladungen railway, also called the Streu Valley Line (), is a Bavarian branch line that connects Mellrichstadt in Lower Franconia () with the town of Fladungen, which nestles in the Rhön mountains. History Public transport arrived in the Streu Valley in 1838, but only a few of the local inhabitants could afford the luxury of travelling by post coach. Ostheim, an enclave of the Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach pressed for a railway link as early as 1853. But it was only in 1866 that Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria decided to extend the railway network into the remote and poorly served Rhön mountains in the north of the state. In 1871 the line from Schweinfurt to Bad Kissingen was opened, but it was another 18 years before the Lokalbahn AG was initially tasked with building a line from Mellrichstadt to Ostheim, only for it to be cancelled. Finally, in 1897, work began, and the line was completed on 20 December 1898. The early years were d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except High-speed rail in Russia, those in Russia, High-speed rail in Finland, Finland, High-speed rail in Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in High-speed rail in Spain, Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in Imperial and US customary measurement systems, U.S. customary/Imperial units, British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Museums In Bavaria
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage Railways In Germany
Heritage may refer to: History and society * A heritage asset is a preexisting thing of value today ** Cultural heritage is created by humans ** Natural heritage is not * Heritage language Biology * Heredity, biological inheritance of physical characteristics * Kinship, the relationship between entities that share a genealogical origin Arts and media Music * ''Heritage'' (Earth, Wind & Fire album), 1990 * ''Heritage'' (Eddie Henderson album), 1976 * ''Heritage'' (Opeth album), 2011, and the title song * Heritage Records (England), a British independent record label * "Heritage" (song), a 1990 song by Earth, Wind & Fire Other uses in arts and media * ''Heritage'' (1919), Vita Sackville-West's first novel * ''Heritage'' (1935 film), a 1935 Australian film directed by Charles Chauvel * ''Heritage'' (1984 film), a 1984 Slovenian film directed by Matjaž Klopčič * ''Heritage'' (2019 film), a 2019 Cameroonian film by Yolande Welimoum * ''Heritage'' (novel), 2002 ''Doctor Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard-gauge Railways In Germany
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/ British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the inner sides of the rail heads) to be used, as the wheels of the rolling stock (locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after the end of World War I from the regional railways of the individual states of the German Empire. The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' has been described as "the largest enterprise in the capitalist world in the years between 1920 and 1932"; nevertheless, its importance "arises primarily from the fact that the Reichsbahn was at the center of events in a period of great turmoil in German history". Overview The company was founded on 1 April 1920 as the ("German Imperial Railways") when the Weimar Republic, which still used the nation-state term of the previous monarchy, (German Reich, hence the usage of the in the name of the railway; the monarchical term was ), took national control of the German railways, which had previously been run by the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Bavarian State Railways
The Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königliche Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen'' or ''K.Bay.Sts.B.'') was the state railway company for the Kingdom of Bavaria. It was founded in 1844. The organisation grew into the second largest of the German state railways (after that of the Prussian state railways) with a railway network of 8,526 kilometres (including the Palatinate Railway or ''Pfalzbahn'') by the end of the First World War. Following the abdication of the Bavarian monarchy at the end of the First World War, the 'Royal' title was dropped and on 24 April 1920 the Bavarian State Railway (''Bayerische Staatseisenbahn''), as it was then called, was merged into the newly formed German Reich Railways Authority or Deutsche Reichseisenbahnen as the Bavarian Group Administration (''Gruppenverwaltung Bayern''). The management of the Bavarian railway network was divided into four Reichsbahn divisions: Reichsbahndirektion Augsburg, Augsburg, Reichsbahndirektion München, Munich, Reichs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
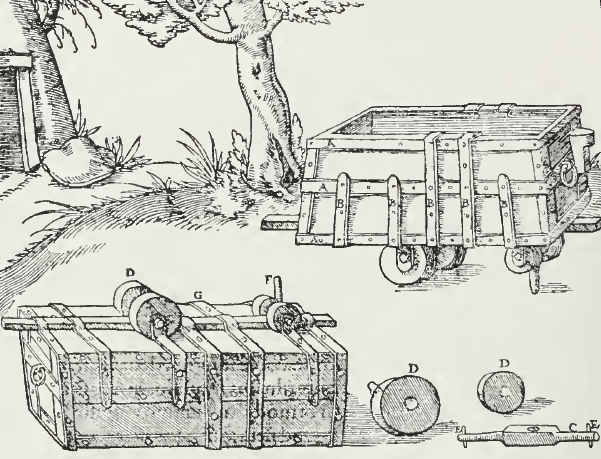
History Of Rail Transport In Germany
The history of rail transport in Germany can be traced back to the 16th century. The earliest form of railways, wagonways, were developed in Germany in the 16th century. Modern German rail history officially began with the opening of the steam-powered Bavarian Ludwig Railway between Nuremberg and Fürth on 7 December 1835. This had been preceded by the opening of the horse-drawn Prince William Railway on 20 September 1831. The first long-distance railway was the Leipzig-Dresden railway, completed on 7 April 1839. Forerunners The forerunner of the railway in Germany, as in England, was to be found mainly in association with the mining industry. Mine carts were used below ground for transportation, initially using wooden rails, and were steered either by a guide pin between the rails or by flanges on the wheels. A wagonway operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola (image right) in his work '' De re metallica''. This line used "Hund" carts with unflanged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconian Open Air Museum
{{disambig ...
Franconian may refer to: *anything related to Franconia (German ''Franken''), a historic region in Germany, now part of Bavaria, Thuringia and Baden-Württemberg *East Franconian German, a dialect spoken in Franconia *Franconian languages *Franconian (stage), a stage in North American stratigraphy named for the Franconia Formation, near the town of Franconia in eastern Minnesota *Franconian notation, mensural musical notation as formulated by Franco of Cologne in the 13th century See also * Name of the Franks *Frankish (other) *Franks (other) Frank, FRANK, or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a Germanic people in late Roman times * Franks, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian GtL 4/4
The Bavarian Class GtL 4/4 engines were superheated steam locomotives in service with the Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königlich Bayerische Staats-Eisenbahnen'') for duties on branch lines (''Lokalbahnen''). History Bavarian GtL 4/4 locomotives were supplied by Krauss to the state railway. In 1911, two were delivered and, in 1914, they were followed by a further eleven engines. As a result of their positive experience with the GtL 4/4 the Bavarian Group Administration (''Gruppenverwaltung Bayern'') of the Deutsche Reichsbahn decided to procure more examples of this locomotive. From 1921 to 1927 Krauss supplied another 108 engines that were somewhat heavier and differed from the original versions in the design of the driver's cab. The last 17 locomotives from 1927 were even heavier than the previous engines, which was due to the increased size of water and coal tanks. Boiler, drive and power remained unchanged over the entire procurement period. The locomotives were des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Bundesbahn
Deutsche Bundesbahn (, ) or DB () was formed as the state railway of the newly established West Germany (FRG) on 7 September 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). The DB remained the state railway of West Germany until after German reunification, when it was merged with the former East German Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR) to form Deutsche Bahn, which came into existence on 1 January 1994. Background After World War II, each of the military governments of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany were ''de facto'' in charge of the German railways in their respective territories. On 10 October 1946, the railways in the British and American occupation zones formed the ''Deutsche Reichsbahn im Vereinigten Wirtschaftsgebiet'' (German Imperial Railway in the united economic area), while on 25 June 1947, the provinces under French occupation formed the Südwestdeutsche Eisenbahn. With the formation of the FRG these successor organisations of the DRG were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |