|
Melingoi
The Melingoi or Milingoi ( el, Μηλιγγοί) were a Slavic tribe that settled in the Peloponnese in southern Greece during the Middle Ages. In the early decades of the 7th century, Slavic tribes (Sclaveni) settled throughout the Balkans following the collapse of the Byzantine Empire's defense of the Danube frontier with some groups reaching as far south as the Peloponnese. The Sclaveni often settled in small groups (i.e., families and clans) and their demographic impact in mainland Greece was both weak and diffuse. Of these, two groups are known by name from later sources, the Melingoi and the Ezeritai, of whom the Melingoi settled on the western slopes of Mount Taygetos. The origin and etymology of the name ''Melingoi'' is unknown. History Like the Ezeritai, the Melingoi are first mentioned in the ''De administrando imperio'', a manual on statecraft written by the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos (r. 945–959). The emperor records that in his time they pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William II Of Villehardouin
William of Villehardouin (french: Guillaume de Villehardouin; Kalamata, 1211 – 1 May 1278) was the fourth prince of Achaea in Frankish Greece, from 1246 to 1278. The younger son of Prince Geoffrey I, he held the Barony of Kalamata in fief during the reign of his elder brother Geoffrey II. William ruled Achaea as regent for his brother during Geoffrey's military campaigns against the Greeks of Nicaea, who were the principal enemies of his overlord, the Latin Emperor of Constantinople Baldwin II. William succeeded his childless brother in the summer of 1246. Conflicts between Nicaea and Epirus enabled him to complete the conquest of the Morea in about three years. He captured Monemvasia and built three new fortresses, forcing two previously autonomous tribes, the Tzakones and Melingoi, into submission. He participated in the unsuccessful Egyptian crusade of Louis IX of France, who rewarded him with the right to issue currency in the style of French ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krinites Arotras
Krinites or Krenites Arotras ( el, Κρινίτης or Κρηνίτης Ἀροτρᾶς) was a Byzantine aristocrat and military governor in southern Greece. He is most notable for suppressing a Slavic revolt in the Peloponnese in 921/22. Origin and appointment to the Peloponnese Arotras was a scion of the Krenites family, an aristocratic clan present in Byzantium since the early 9th century. Peter Charanis speculates that the family was of Armenian origin, however his methods of identifying Armenians in the Byzantine Empire are questionable, and have been criticized by historians such as Anthony Kaldellis who are hesitant to accept them. Nevertheless, in early 921 or 922 (earlier scholars dated this event to ), when he held the rank of ''protospatharios'', he was appointed as military governor ('' strategos'') of the theme of the Peloponnese and tasked with suppressing the revolt of the Slavic tribes of the Melingoi and Ezeritai. The two tribes had rebelled in the past, in 84 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezeritai
The Ezeritai ( el, ) were a Slavic tribe that settled in the Peloponnese in southern Greece during the Middle Ages. In the early decades of the 7th century, Slavic tribes (Sclaveni) settled throughout the Balkans following the collapse of the Byzantine Empire's defense of the Danube frontier with some groups reaching as far south as the Peloponnese. The Sclaveni often settled in small groups (i.e., families and clans) and their demographic impact in mainland Greece was both weak and diffuse. Of these, two groups are known by name from later sources, the Ezeritai and the Melingoi, both having settled on the slopes of Mount Taygetos. Etymology The Ezeritai apparently settled in the area known as ''Helos'' (Greek for "swamp"), from which their name derives ( South Slavic ''ezero'' meaning "lake").. History The Ezeritai are mentioned in the '' De administrando imperio'' of Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos (r. 945–959), who records that they paid a tribute of 300 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese Middle Ages Map-en
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic Greek, demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions of Greece, administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica (region), Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
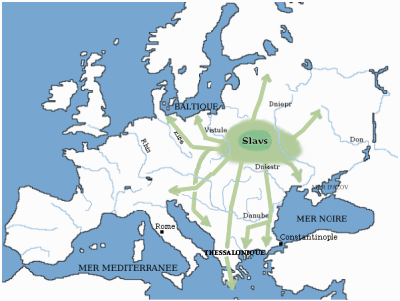
Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin) or ' (various forms in Greek, see below) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byzantine chroniclers as barbarians having appeared at the Byzantine borders along with the Antes (East Slavs), another Slavic group. The Sclaveni were differentiated from the Antes and Wends (West Slavs); however, they were described as kin. Eventually, most South Slavic tribes accepted Byzantine or Frankish suzerainty, and came under their cultural influences and Chalcedonian Christianity. The term was widely used as general catch-all term until the emergence of separate tribal names by the 10th century. Customs The Sclaveni had similar if not identical customs and culture as the Antes. They were carefully described by chroniclers such as Procopius and Maurice, whose works contribute greatly to our understanding of these two Early Slavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzaousios
The ''tzaousios'' ( gr, τζαούσιος) was a late Byzantine military office, whose exact functions and role are somewhat unclear.. The term is derived from the Turkish '' çavuş'', meaning "courier" or "messenger", and was in use by the Byzantines perhaps as early as the late 11th century.. In the 13th–15th centuries, it became applied to officers serving in provincial posts. A ''tzaousios'' could serve as commander of the garrison of a ''kastron'' (a fortified administrative center run by a '' kephale''), possibly combining the military and administrative roles, or as an officer to the '' megala allagia'' of the imperial field army. Most of the ''tzaousioi'' mentioned in the sources came from the Byzantine Morea, where they played an important role in provincial administration. In Macedonia and Thrace by contrast, they seem to have been limited to a purely military role within the ''megala allagia''. The variant ''megas tzaousios'' (μέγας τζαούσιος, "grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks. Geography Laconia is bordered by Messenia to the west and Arcadia to the north and is surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea to the east and by the Laconian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It encompasses Cape Malea and Cape Tainaron and a large part of the Mani Peninsula. The Mani Peninsula is in the west region of Laconia. The islands of Kythira and Antikythera lie to the south, but they administratively belong to the Attica regional unit of islands. The island, Elafonisos, situated between the Laconian mainland and Kythira, is part of Laconia. The Eurotas is the lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droungos
''Droungos'' (Greek: , sometimes δρόγγος, ''drongos'') or ''drungus'' is a late Roman and Byzantine term for a battalion-sized military unit, and later for a local command guarding mountain districts. Its commander was a "" or "" (δρουγγάριος), anglicized as "Drungary". History and functions The term is first attested in Latin in the late 4th century AD. It derives from Gaulish * (see Old Irish ; Old Breton or ), meaning "tribe", "group", "throng" or "crowd". An alternative Germanic etymology () cited by some historians,. originates in 17th-century guesswork which has been rejected by the overwhelming majority of philologists. The earliest usage of in Latin is non-technical and similarly signifies a generic "band" or "troop", which Vegetius equates to Latin . The term first occurs in Greek as () or (δρόγγος), with the same meaning, in the early 5th century. In the late 6th century, the Emperor Maurice (r. 582–602) applies to a specific tactical depl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (Byzantine District)
The themes or ( el, θέματα, , singular: , ) were the main military/administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle Of The Morea
The ''Chronicle of the Morea'' ( el, Τὸ χρονικὸν τοῦ Μορέως) is a long 14th-century history text, of which four versions are extant: in French, Greek (in verse), Italian and Aragonese. More than 9,000 lines long, the ''Chronicle'' narrates events of the Franks' establishment of feudalism in mainland Greece. West European Crusaders settled in the Peloponnese (called Morea at the time) following the Fourth Crusade. The period covered in the ''Chronicle'' was 1204 to 1292 (or later, depending on the version). It gives significant details on the civic organization of the Principality of Achaia. The extant texts of the ''Chronicle of the Morea'' The Greek text is the only text written in verse. The French, Italian and Aragonese texts are written in prose.Jean-Claude Polet, ''Patrimoine littéraire européen'', De Boeck Université, 1995, Greek text The verses of the Greek text are written in a 15-syllable political verse. The verses are accented but not r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Despotate Of The Morea
The Despotate of the Morea ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μορέως) or Despotate of Mystras ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μυστρᾶ) was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centuries. Its territory varied in size during its existence but eventually grew to include almost all the southern Greek peninsula now known as the Peloponnese, which was known as the Morea during the medieval and early modern periods. The territory was usually ruled by one or more sons of the current Byzantine emperor, who were given the title of ''despotes'' (in this context it should not be confused with despotism). Its capital was the fortified city of Mystras, near ancient Sparta, which became an important centre of the Palaiologan Renaissance. History The Despotate of the Morea was created out of territory seized from the Frankish Principality of Achaea. This had been organized from former Byzantine territory after the Fourth Crusade (12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |