|
Melica Montezumae
''Melica montezumae'', Montezuma melicgrass, is a grass species in the family Poaceae that can be found in Texas and Mexico. Description The plant is perennial and is caespitose as well. The culms are long while the leaf-sheaths scaberulous and tubular. Eciliate membrane is long. Leaf-blades are either flat or involute and are wide. Their panicle is open and is in length. The main panicle branches are ascended or spreadout, while spikelets are pendulous and solitary. Fertile spikelets have filiformed pedicels, are cuneate and are long. They have 1 fertile floret which is diminished. Fertile lemma is chartaceous and elliptic and is long. Palea is 2 veined and have scaberulous keels as well. Sterile florets are barren, cuneated, and grow in a clump. Both upper and lower glumes are oblong, scarious and keelless, but the lower one is in length while the upper one is long. Flowers are fleshy, oblong, truncate, and are growing side by side with 3 anthers. Fruits are caryop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Piper
Charles Vancouver Piper (16 June 1867 – 11 February 1926) was an American botanist and agriculturalist. Born in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, he spent his youth in Seattle, Washington Territory and graduated from the University of Washington Territory in 1885. He taught botany and zoology in 1892 at the Washington Agricultural College (now Washington State University) in Pullman, Washington, Pullman. He earned a master's degree in botany in 1900 from Harvard University. Piper compiled the first authoritative guides to flora in the northwestern United States. With his collaborator, R. Kent Beattie, he surveyed the Palouse area of southeastern Washington, and expanded the study to the entire state in 1906. That year, The Smithsonian Institution published his catalo''Flora of the State of Washington'' He also publishe''Flora of Southeast Washington and Adjacent Idaho''(1914) an''Flora of the Northwest Coast''(1915). These works established him as an authority on the plants of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
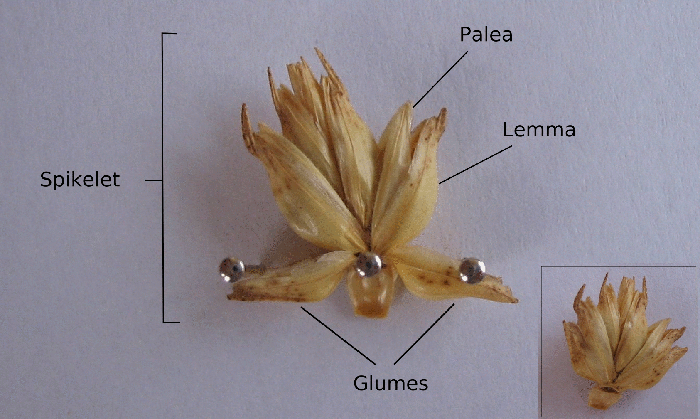
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lowermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melica
''Melica'' is a genus of perennial Poaceae, grasses known generally as melic or melic grass. They are found in most temperate regions of the world. Melic grasses are clumping to short-rhizome, rhizomatous Poaceae, grasses. They have culm (botany), flowering culms up to tall bearing spikelets of papery flowers. The spikelets have between one and seven fertile flowers with a rudimentary structure at the distal end composed of one to four sterile florets. Some species of melic have corms, lending them the name oniongrass. The genus is most diverse in South America and temperate Asia. Eight species are endemic to China. In North America, most species occur west of the Mississippi River, with exceptions being ''Melica mutica'' and Melica nitens, ''M. nitens'' which occur throughout much of the southeast and lower Midwest respectively. Species Species and hybrids include: * ''Melica altissima'' L. – Siberian melic grass * ''Melica amethystina'' Pourr. * ''Melica animarum'' Muj. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the oldest university in the English-speaking world; it has buildings in every style of English architecture since late Anglo-Saxon. Oxford's industries include motor manufacturing, education, publishing, information technology and science. History The history of Oxford in England dates back to its original settlement in the Saxon period. Originally of strategic significance due to its controlling location on the upper reaches of the River Thames at its junction with the River Cherwell, the town grew in national importance during the early Norman period, and in the late 12th century became home to the fledgling University of Oxford. The city was besieged during The Anarchy in 1142. The university rose to dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of North America
The ''Flora of North America North of Mexico'' (usually referred to as ''FNA'') is a multivolume work describing the native plants and naturalized plants of North America, including the United States, Canada, St. Pierre and Miquelon, and Greenland. It includes bryophytes and vascular plants. All taxa are described and included in dichotomous keys, distributions of all species and infraspecific taxa are mapped, and about 20% of species are illustrated with line drawings prepared specifically for FNA. It is expected to fill 30 volumes when completed and will be the first work to treat all of the known flora north of Mexico; in 2015 it was expected tha the series would conclude in 2017. Twenty-nine of the volumes have been published as of 2022. Soon after publication, the contents are made available online. FNA is a collaboration of about 1,000 authors, artists, reviewers, and editors from throughout the world. Reception The series has been praised for "the comprehensive treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett. The organisation manages botanic gardens at Kew in Richmond upon Thames in south-west London, and at Wakehurst, a National Trust property in Sussex which is home to the internationally important Millennium Seed Bank, whose scientists work with partner organisations in more than 95 countries. Kew, jointly with the Forestry Commission, founded Bedgebury National Pinetum in Kent in 1923, specialising in growing conifers. In 1994, the Castle Howard Arboretum Trust, which runs the Yorkshire Arboretum, was formed as a partnership between Kew and the Castle Howard Estate. In 2019, the organisation had 2,316,699 public visitors at Kew, and 312,813 at Wakehurst. Its site at Kew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caryopsis
In botany, a caryopsis (plural caryopses) is a type of simple fruit—one that is monocarpellate (formed from a single carpel) and indehiscent (not opening at maturity) and resembles an achene, except that in a caryopsis the pericarp is fused with the thin seed coat. The caryopsis is popularly called a grain and is the fruit typical of the family Poaceae (or Gramineae), which includes wheat, rice, and corn. The term ''grain'' is also used in a more general sense as synonymous with cereal (as in "cereal grains", which include some non-Poaceae). Considering that the fruit wall and the seed are intimately fused into a single unit, and the caryopsis or grain is a dry fruit, little concern is given to technically separating the terms ''fruit'' and ''seed'' in these plant structures. In many grains, the " hulls" to be separated before processing are flower bracts. Etymology The name "caryopsis" is derived from the Greek words ''karyon'' and ''-opsis'', meaning "nut" and "havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains ''sporangium, microsporangia''. Most commonly anthers are two-lobed and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile tissue between the lobes is called the connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The stamens in a flower are collectively called the androecium. The androecium can consist of as few as one-half stamen (i.e. a single locule) as in ''Canna (plant), Canna'' species or as many as 3,482 stamens which have been counted in the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaff
Chaff (; ) is the dry, scaly protective casing of the seeds of cereal grains or similar fine, dry, scaly plant material (such as scaly parts of flowers or finely chopped straw). Chaff is indigestible by humans, but livestock can eat it. In agriculture it is used as livestock fodder, or is a waste material ploughed into the soil or burned. Etymology "Chaff" comes from Middle English ''chaf'', from Old English , related to Old High German ''cheva'', "husk". Grain chaff In grasses (including cereals such as rice, barley, oats, and wheat), the ripe seed is surrounded by thin, dry, scaly bracts (called glumes, lemmas and paleas), forming a dry husk (or hull) around the grain. Once it is removed it is often referred to as chaff. In wild cereals and in the primitive domesticated einkorn,Potts, D. T. (1996) ''Mesopotamia Civilization: The Material Foundations'' Cornell University Press. p. 62. . emmer and spelt wheats, the husks enclose each seed tightly. Before the grain can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (zoology)
Sessility is the biological property of an organism describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile organisms for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile organisms can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other sessile organisms grow from a solid such as a rock, dead tree trunk, or a man-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floret
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_(255_31)_Cross-section.jpg)


