|
Mekatelyu
Limonese Creole (also called Limonese, Limón Creole English or ) is a dialect of Jamaican Patois (Jamaican Creole), an English-based creole language, spoken in Limón Province on the Caribbean Sea coast of Costa Rica. The number of native speakers is unknown, but 1986 estimates suggests that there are fewer than 60,000 native and second language speakers combined. Origin and related creoles Limonese is very similar structurally and lexically to the Jamaican Creole spoken in Jamaica and Panama and to a lesser extent other English-based creoles of the region, such as Colón Creole, Mískito Coastal Creole, Belizean Kriol, and San Andrés and Providencia Creole; many of these are also somewhat mutually intelligible to Limonese and each other. Names The name ''Mekatelyu'' is a transliteration of the phrase "make I tell you", or in standard English "let me tell you". In Costa Rica, one common way to refer to Limonese is by the term "patois", a word of French origin used to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
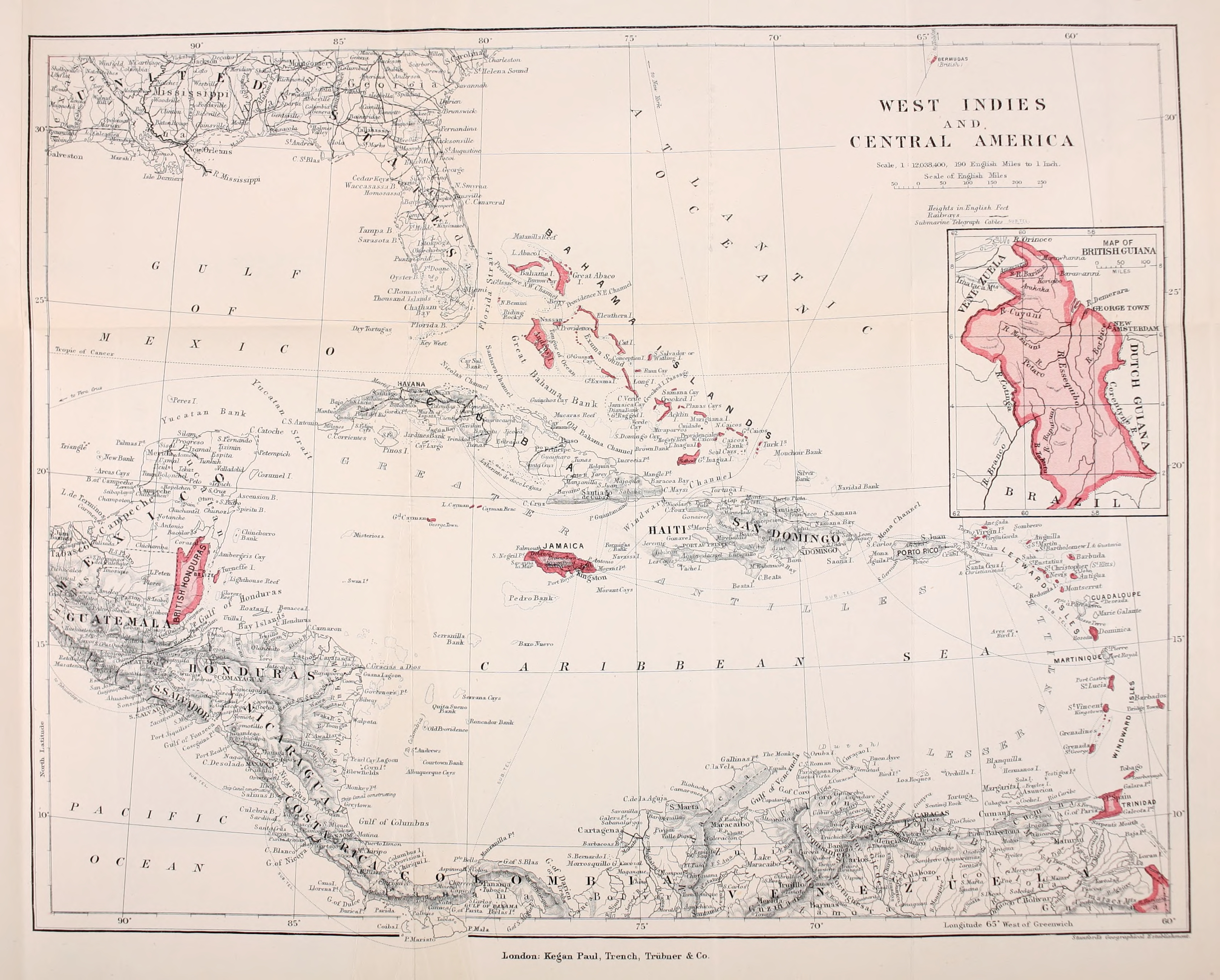
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and Maritime boundary, maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agricultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-based Creole Languages
An English-based creole language (often shortened to English creole) is a creole language for which English was the ''lexifier'', meaning that at the time of its formation the vocabulary of English served as the basis for the majority of the creole's lexicon. Most English creoles were formed in British colonies, following the great expansion of British naval military power and trade in the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. The main categories of English-based creoles are Atlantic (the Americas and Africa) and Pacific (Asia and Oceania). Over 76.5 million people estimated globally speak some form of English-based creole. Sierra Leone, Malaysia, Nigeria, Ghana, Jamaica, and Singapore have the largest concentrations of creole speakers. Origin It is disputed to what extent the various English-based creoles of the world share a common origin. The '' monogenesis hypothesis'' posits that a single language, commonly called ''proto–Pidgin English'', spoken along the West African coast in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Language
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guernésiais: , Jèrriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the Oïl languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to describe not only the Norman language, but also the administrative languages of ''Anglo-Norman'' and ''Law French'' used in England. For the most part, the written forms of Norman and modern French are mutually intelligible. This intelligibility was largely caused by the Norman language's planned adaptation to French orthography (writing). History When Norse Vikings from modern day Scandinavia arrived in Neustria, in the western part of the then Kingdom of the Franks, and settled the land that became known as Normandy, these North-Germanic–speaking people came to live among a local Gallo-Romance–speaking population. In time, the communities converged, so that ''Normandy'' continued to form the name of the region while the original Norse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries. It is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance languages, Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaican English
Jamaican English, including Jamaican Standard English, is a variety of English native to Jamaica and is the official language of the country. A distinction exists between Jamaican English and Jamaican Patois (or Creole), though not entirely a sharp distinction so much as a gradual continuum between two extremes. Jamaican English tends to follow British English spelling conventions. Sociolinguistics Jamaican Standard English is a type of International Standard English ( English language in England). There are several language varieties that have significantly impacted this dialect of English. English was introduced into Jamaica in 1655, because of the colonisation by Britain. British English was spread through post-primary education, and through British teachers that immigrated to Jamaica. Standard English in Jamaica conflated with the British Standard. Individuals who speak the standard variety are often considered to be of a higher social class. Also, American English has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermudian English
Bermudian English is a regional dialect of English found in Bermuda, a British overseas territory in the North Atlantic. Standard English is used in professional settings and in writing, while vernacular Bermudian English is spoken on more casual occasions. The Bermudian dialect began to develop following settlement in the early 17th century and retains traits of Elizabethan English. Casual observers tend to have difficulty in placing the Bermudian dialect, as it differs from those that are clearly British, American, or Caribbean; they also note that the accent tends to vary between individuals. To Americans, it sounds slightly English, while those from the British Isles find it more American. Categorisation Bermudian English has been called "one of the most severely underresearched varieties of English". It primarily shows a mixture of traits typical of British English and American English, and is generally classified as a form of American (rather than Caribbean) English. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbadian English
Barbadian English or Bajan () English is a dialect of the English language as used by Barbadians (Bajans) and by Barbadian diasporas. It should not be confused with Bajan Creole, which is an English-based creole language. Schneider, E.W., and Kortmann, B. " A Handbook of Varieties of English: Morphology and syntax ". Mouton de Gruyter, 2004. In '' Pronunciation Barbadian English is fully rhoticity in English, rhotic and full of glottal stops. One example of Barbadian English would be the pronunciation of ''departments'', which is . It is also notable, in comparison with standard American or British English, for the first vowel in ''price'' or ''prize''. Schneider, E.W., and Kortmann, B. " A Handbook of Varieties of English: Morphology and syntax ". Mouton de Gruyter, 2004. In '' Michelle Straw, Peter L. Patrick. " Dialect acquisition of glottal variation in /t/: Barbadians in Ipswich ". Language Sciences 29 (2007) 385–407. In '' * The realization of the vowel in Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamian Creole
Bahamianese, also described as the Bahamian dialect, is spoken by both Black and white Bahamians, although in slightly different forms. Bahamian dialect also tends to be more prevalent in certain areas of the Bahamas. Islands that were settled earlier or that have a historically large Afro-Bahamian population have a greater concentration of individuals exhibiting creolized speech; the dialect is most prevalent in urban areas. Individual speakers have command of lesser and greater dialect forms. Bahamian dialect shares similar features with other Caribbean English-based creoles, such as those of Jamaica, Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, Turks and Caicos, Saint Lucia, Grenada, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Guyana, and the Virgin Islands. There is also a very significant link between Bahamian and the Gullah language of South Carolina, as many Bahamians are descendants of enslaved Black people brought to the islands from the Gullah region after the American Revolution. In compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decreolization
Decreolization is a postulated phenomenon whereby over time a creole language reconverges with the lexifier from which it originally derived. The notion has attracted criticism from linguists who argue there is little theoretical or empirical basis on which to postulate a process of language change which is particular to creole languages. Overview Decreolization is a process of language change a creole language may undergo when in contact with its lexifier. As languages remain in contact over time, they typically influence one another, especially if one holds higher linguistic prestige. In the context of creole languages, the lexifier tends to have higher prestige (though not always) and will exert a much greater influence on the creole, which has lower prestige. This leads to the reintroduction of linguistic material into the creole from the lexifier. Decreolization predicts that eventually the creole will resemble the lexifier to such a degree that it could then be called a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect Continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of Variety (linguistics), language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated varieties may not be. This is a typical occurrence with widely spread languages and language families around the world, when these languages did not spread recently. Some prominent examples include the Indo-Aryan languages across large parts of India, varieties of Arabic across north Africa and southwest Asia, the Turkic languages, the Varieties of Chinese, Chinese languages or dialects, and subgroups of the Romance languages, Romance, Germanic languages, Germanic and Slavic languages, Slavic families in Europe. Leonard Bloomfield used the name dialect area. Charles F. Hockett used the term L-complex. Dialect continua typically occur in long-settled agrarian populations, as innovations spread from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Register
In sociolinguistics, a register is a variety of language used for a particular purpose or in a particular communicative situation. For example, when speaking officially or in a public setting, an English speaker may be more likely to follow prescriptive norms for formal usage than in a casual setting, for example, by pronouncing words ending in ''-ing'' with a velar nasal instead of an alveolar nasal (e.g., ''walking'' rather than ''walkin'''), choosing words that are considered more "formal" (such as ''father'' vs. ''dad'' or ''child'' vs. ''kid''), and refraining from using words considered nonstandard, such as '' ain't'' and ''y'all''. As with other types of language variation, there tends to be a spectrum of registers rather than a discrete set of obviously distinct varieties—numerous registers can be identified, with no clear boundaries between them. Discourse categorisation is a complex problem, and even in the general definition of ''register'' given above (language va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana (now Guyana) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |