|
Mehetweret
Mehet-Weret or Mehturt ( egy, mḥt-wrt) is an ancient Egyptian deity of the sky in ancient Egyptian religion. Her name means "Great Flood". She was mentioned in the Pyramid Texts. In ancient Egyptian creation myths, she gives birth to the sun at the beginning of time, and in art she is portrayed as a cow with a sun disk between her horns. She is associated with the goddesses Neith, Hathor, and Isis, all of whom have similar characteristics, and like them she could be called the "Eye of Ra". Mehet-Weret is primarily known as being the "Celestial Cow" or "Cow Goddess" because of her physical characteristics, but she contributes to the world in more ways than that. She is also the Goddess of Water, Creation, and Rebirth; in Egyptian mythology, Mehet-Weret is one of the main components in the making and survival of life.Seawright, Caroline. "Mehet-Weret, Ancient Egyptian Goddess of Creation." Egyptology & Archaeology Essays, November 16, 2003. http://www.thekeep.org/~kunoichi/kunoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir El-Medina
Deir el-Medina ( arz, دير المدينة), or Dayr al-Madīnah, is an ancient Egyptian workmen's village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th Dynasties of the New Kingdom of Egypt (ca. 1550–1080 BCE)Oakes, p. 110 The settlement's ancient name was ''wikt:st#Etymology 2 2, Set wikt:mꜣꜥt#Egyptian, maat'' ("Place of Truth"), and the workmen who lived there were called "Servants in the Place of Truth". During the Christian era, the temple of Hathor was converted into a church from which the Egyptian Arabic name ''Deir el-Medina'' ("Monastery of the City") is derived. At the time when the world's press was concentrating on Howard Carter's discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamun in 1922, a team led by Bernard Bruyère began to excavate the site."Pharaoh’s Workers: How the Israelites Lived in Egypt", Leonard and Barbara Lesko, Biblical Archaeological Review, Jan/Feb 1999 This work has resulted in one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patricia Monaghan
Patricia Monaghan (February 15, 1946, – November 11, 2012) was a poet, a writer, a spiritual activist, and an influential figure in the contemporary women's spirituality movement. Monaghan wrote over 20 books on a range of topics including Goddess spirituality, earth spirituality, Celtic mythology, the landscape of Ireland, and techniques of meditation. In 1979, she published the first encyclopedia of female divinities, a book which has remained steadily in print since then and was republished in 2009 in a two volume set as ''The Encyclopedia of Goddesses and Heroines''. She was a mentor to many scholars and writers including biologist Cristina Eisenberg, poet Annie Finch, theologian Charlene Spretnak, and anthropologist Dawn Work-MaKinne, and was the founding member of the Association for the Study of Women and Mythology, which brought together artists, scholars, and researchers of women-centered mythology and Goddess spirituality for the first time in a national academic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky And Weather Goddesses
The sky is an unobstructed view upward from the surface of the Earth. It includes the atmosphere and outer space. It may also be considered a place between the ground and outer space, thus distinct from outer space. In the field of astronomy, the sky is also called the celestial sphere. This is an abstract sphere, concentric to the Earth, on which the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars appear to be drifting. The celestial sphere is conventionally divided into designated areas called constellations. Usually, the term ''sky'' informally refers to a perspective from the Earth's surface; however, the meaning and usage can vary. An observer on the surface of the Earth can see a small part of the sky, which resembles a dome (sometimes called the ''sky bowl'') appearing flatter during the day than at night. In some cases, such as in discussing the weather, the sky refers to only the lower, denser layers of the atmosphere. The daytime sky appears blue because air molecules scatter shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Goddesses
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to ''maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art—as animals, humans, objects, and combinations of different forms—also alluded, through symbolism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
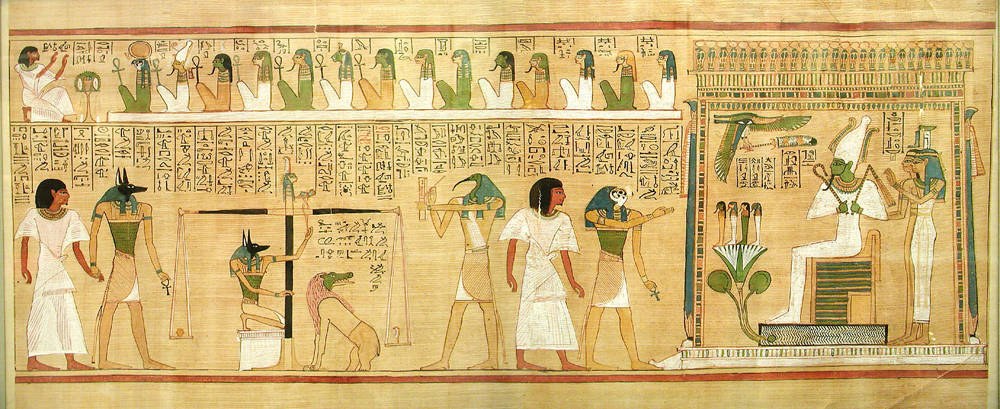
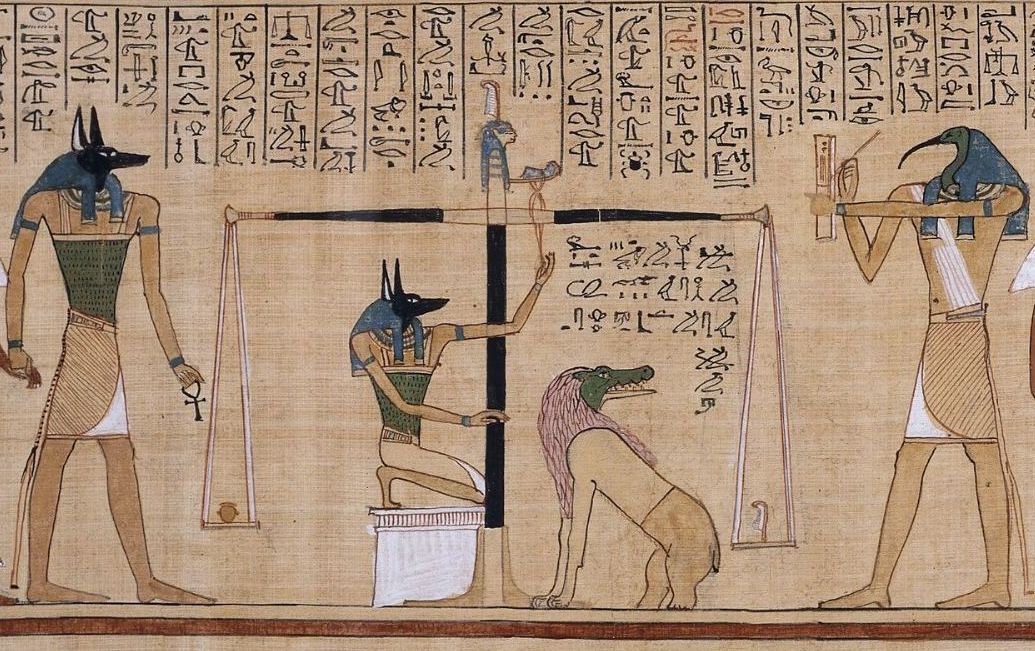
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sennedjem
Sennedjem was an Ancient Egyptian artisan. Sennedjem lived in Set Maat (translated as "The Place of Truth"), contemporary Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reigns of Seti I and Ramesses II. Sennedjem had the title "Servant in the Place of Truth". He was buried along with his wife, Iyneferti, and family in a tomb in the village necropolis. His tomb was discovered January 31, 1886. When Sennedjem's tomb was found, in it there was regular furniture from his home, including a stool and a bed, which he actually used when he was alive. His titles included Servant in the Place of Truth, Ushabti of Sennedjem from The Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco meaning that he worked on the excavation and decoration of the nearby royal tombs. See also *TT1 The Theban Tomb TT1 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official, Sennedjem a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' ( λίθος σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C. The Hagia Triada sarcophagus is a stone sarcophagus elaborately painted in fresco; one style of later A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geraldine Pinch
Geraldine Harris (born 1951), aka Geraldine Harris Pinch, is an author (of both fiction and non-fiction) and Egyptologist. She is a member of the Faculty of Oriental Studies at the University of Oxford. Her works include the Seven Citadels quartet and numerous information text books about Egypt. Partial bibliography *''White Cranes Castle'', illustrated by Lisa Jensen, Macmillan (London), 1979. *"Seven Citadels" series **''Prince of the Godborn'', Greenwillow (New York City), 1982. **''The Children of the Wind'', Greenwillow, 1982. **''The Dead Kingdom'', Greenwillow, 1983. **'' The Seventh Gate'', Greenwillow, 1983. *''Gods and Pharaohs from Egyptian Mythology'', illustrated by John Sibbick and David O'Connor, Lowe (London), 1982, Schocken (New York City), 1983, reprinted, P. Bedrick (New York City), 1996. *''The Junior Atlas of Ancient Egypt'', Lionheart (London), 1989. *''New Kingdom Votive Offerings to Hathor'', Griffith Institute (Oxford), 1989. *''Isis and Osiris'', NTC P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile River
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its covers eleven countries: the |