|
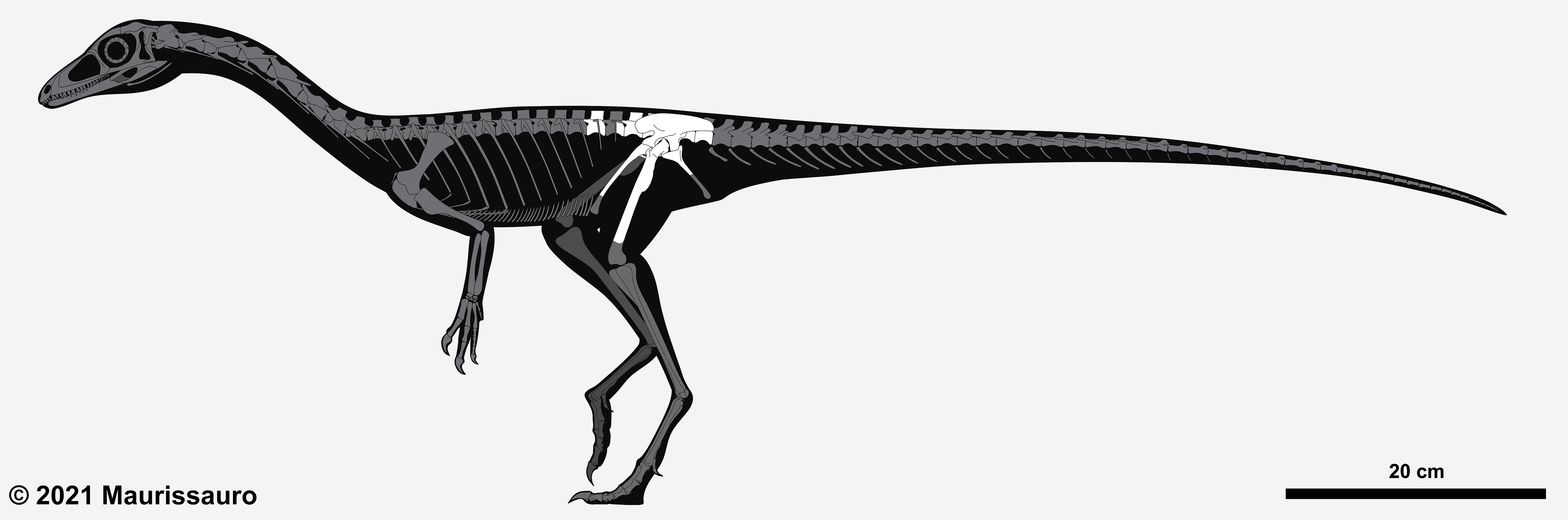
Megapnosaurus
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Africa. The species was a small to medium-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to long and weigh up to . It was originally given the genus name ''Syntarsus'', but that name was later determined to be preoccupied by a beetle. The species was subsequently given a new genus name, ''Megapnosaurus,'' by Ivie, Ślipiński & Węgrzynowicz in 2001. Some studies have classified it as a species within the genus ''Coelophysis,'' but this interpretation has been challenged by more subsequent studies and the genus is now considered valid. Discovery and history The first fossils of ''Megapnosaurus'' were found in 1963 by a group of students from Northle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period from the Carnian and Rhaetian faunal stages in what is now the southwestern United States. '' Megapnosaurus'' was once considered a species within this genus,Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Jurassic, Africa)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 535–536. but this interpretation has been challenged since 2017 and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. ''Coelophysis'' was a small, slenderly-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore that could grow up to long. It is one of the earliest known dinosaur genera. Scattered material representing similar animals has been found worldwide in some Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis? Kayentakatae
''Coelophysis''? ''kayentakatae'' is an extinct species of neotheropod dinosaur that lived approximately 200 - 196 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now the southwestern United States. While originally assigned to the genus '' Syntarsus'' as ''Syntarsus kayentakatae'', that genus name was found to be preoccupied by a Colydiine beetle, so it was moved to the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' as ''Megapnosaurus kayentakatae''. Later it was moved again to ''Coelophysis'', however the species still possesses no definite genus assignment. Discovery The holotype of ''C.''? ''kayentakatae'' (MNA V2623) was recovered in the Silty Facies Member of the Kayenta Formation in Arizona. This material was collected in 1977 from carbonaceous sandstone deposited during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages of the Jurassic period.Padian, K (1997) Glen Canyon Group In: Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs, edited by Currie, P. J., and Padian, K., Academic Press. Specimen UCM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysid
Coelophysidae is a family of primitive carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Most species were relatively small in size. The family flourished in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, and has been found on numerous continents. Many members of Coelophysidae are characterized by long, slender skulls and light skeletons built for speed. One member genus, ''Coelophysis'', displays the earliest known furcula in a dinosaur. Under cladistic analysis, Coelophysidae was first defined by Paul Sereno in 1998 as the most recent common ancestor of '' Coelophysis bauri'' and ''Procompsognathus triassicus'', and all of that common ancestor's descendants. However, Tykoski (2005) has advocated for the definition to change to include the additional taxa of "Syntarsus" ''kayentakatae'' and ''Segisaurus halli''. Coelophysidae is part of the superfamily Coelophysoidea, which in turn is a subset of the larger Neotheropoda clade. As part of Coelophysoidea, Coelophysidae is often placed as sister to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysoidea
Coelophysoidea were common dinosaurs of the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivore, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the coelurosaurs, with which they were formerly classified, and some species had delicate cranium, cranial crests. Sizes range from about 1 to 6 m in length. It is unknown what kind of external covering coelophysoids had, and various artists have portrayed them as either scaly or feathered dinosaurs, feathered. Some species may have lived in packs, as inferred from sites where numerous individuals have been found together. Examples of coelophysoids include ''Coelophysis'', ''Procompsognathus'' and ''Liliensternus''. Most dinosaurs formerly referred to as being in the dubious taxon "Podokesauridae" are now classified as coelophysoids. Classification Despite their very early occurrence in the fossil record, coelophysoids have a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, southern Free State, and in the eastern KwaZulu-Natal provinces of South Africa. Outcrops and exposures are also found in several localities in Lesotho such as Qacha's Neck, Hill Top, Quthing, and near the capital, Maseru. The Elliot Formation is further divided into the lower (LEF) and upper (UEF) Elliot formations to differentiate significant sedimentological differences between these layers. The LEF is dominantly Late Triassic (Norian-Hettangian) in age while the UEF is mainly Early Jurassic (Sinemurian-Pliensbachian) and is tentatively regarded to preserve a continental record of the Triassic-Jurassic boundary in southern Africa. This geological formation is named after the town of Elliot in the Eastern Cape, and its stratotype locality i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Sandstone
The Forest Sandstone is a geological formation in southern Africa, dating to roughly between 200 and 190 million years ago and covering the Hettangian to Sinemurian stages of the Jurassic Period in the Mesozoic Era. As its name suggests, it consists mainly of sandstone. Fossils of the prosauropod dinosaur '' Massospondylus'' and the primitive sauropod '' Vulcanodon'' have been recovered from the Forest Sandstone. Geology Description The formation is a sedimentary unit, consisting mainly of aeolian sands and silts with interbedded fluvial sediments, laid down during a period of increasing aridity. Extent The Forest Sandstone is found in Botswana, Zambia and Zimbabwe, in the Mid-Zambezi, Mana Pools, Cabora Bassa and Limpopo Basins, with its greatest thickness in the Cabora Bassa Basin. Deposition Age The formation is dated at 200 to 190 Ma. Stratigraphy The Forest Sandstone is the penultimate formation in the Upper Karoo Group of the Karoo Supergroup, lying above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lufeng Formation
The Lufeng Formation (formerly Lower Lufeng Series) is a Lower Jurassic sedimentary rock formation found in Yunnan, China. It has two units: the lower Dull Purplish Beds/Shawan Member are of Hettangian age, and Dark Red Beds/Zhangjia'ao Member are of Sinemurian age.Luo, Z., and X.-C. Wu. 1994. The small tetrapods of the Lower Lufeng Formation, Yunnan, China; pp. 251–270 in N. C. Fraser and H.-D.Sues (eds.), In the Shadow of the Dinosaurs. Cambridge University Press, New York It is known for its fossils of early dinosaurs. The Dull Purplish Beds have yielded the possible therizinosaur '' Eshanosaurus'', the possible theropod ''Lukousaurus'', and the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus" ''sinensis'', '' Lufengosaurus'', '' Jingshanosaurus'', and '' Yunnanosaurus''. Dinosaurs discovered in the Dark Red Beds include the theropod ''Sinosaurus triassicus'', the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus", ''Lufengosaurus'', and ''Yunnanosaurus'', indeterminate remains of sauropods, and the early arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendraig
''Pendraig'' (meaning "chief dragon" in Middle Welsh) is a genus of coelophysoid theropod dinosaur from South Wales. It contains one species, ''Pendraig milnerae'', named after Angela Milner. The specimen was discovered in the Pant-y-Ffynnon quarry. In life it would have measured in length. History The holotype of ''Pendraig'' were found in the Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in Wales in 1952 by Kermack and Robinson along with the holotypes of '' Pantydraco'' and '' Terrestrisuchus'', and were subsequently lost in the collections of the Natural History Museum, London. The fossils were originally thought to belong to a " coelurosaur" (in the outdated sense of the word) and even subsequently classified as a species of "''Syntarsus''" (now ''Megapnosaurus'' or ''Coelophysis''). Recently Angela Milner and Susannah Maidment rediscovered the fossils stored with some crocodile bones (likely '' Terrestrisuchus''). The fossils were named as representing a new genus of theropod in 2021. Descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayenta Formation
The Kayenta Formation is a geological formation in the Glen Canyon Group that is spread across the Colorado Plateau province of the United States, including northern Arizona, northwest Colorado, Nevada, and Utah. Traditionally has been suggested as Sinemurian-Pliensbachian, but more recent dating of detrital zircons has yielded a depositional age of 183.7 ± 2.7 Ma, thus a Pliensbachian-Toarcian age is more likely A previous depth work recovered a solid Lower-Middle Pliensbachian age from measurements done in the Tenney Canyon. This rock formation is particularly prominent in southeastern Utah, where it is seen in the main attractions of a number of national parks and monuments. These include Zion National Park, Capitol Reef National Park, the San Rafael Swell, and Canyonlands National Park. The Kayenta Formation frequently appears as a thinner dark broken layer below Navajo Sandstone and above Wingate Sandstone (all three formations are in the same group). Together, these thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massospondylus
''Massospondylus'' ( ; from Greek, (massōn, "longer") and (spondylos, "vertebra")) is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. (Hettangian to Pliensbachian ages, ca. 200–183 million years ago). It was described by Sir Richard Owen in 1854 from remains discovered in South Africa, and is thus one of the first dinosaurs to have been named. Fossils have since been found at other locations in South Africa, Lesotho, and Zimbabwe. Material from Arizona's Kayenta Formation, India, and Argentina has been assigned to the genus at various times, but the Arizonan and Argentinian material are now assigned to other genera. The type species is ''M. carinatus''; seven other species have been named during the past 150 years, but only ''M. kaalae'' is still considered valid. Early sauropodomorph systematics have undergone numerous revisions during the last several years, and many scientists disagree where exactly ''Massospondylus'' lies on the dinosaur evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitake River
The Chitake River flows through the Mana Pools National Park, Zimbabwe, and has its source in the Zambezi Escarpment. The source is a perennial spring at the foothills, which flows for 1 kilometre within the canyon walls. The river discharges into the Rukomechi River. There is a major fossil site on the Chitake River, where large numbers of Syntarsus rhodesiensis ''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago duri ... have been found. Source: Mouth: Rivers of Zimbabwe {{Zimbabwe-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
