|
Megalograptid
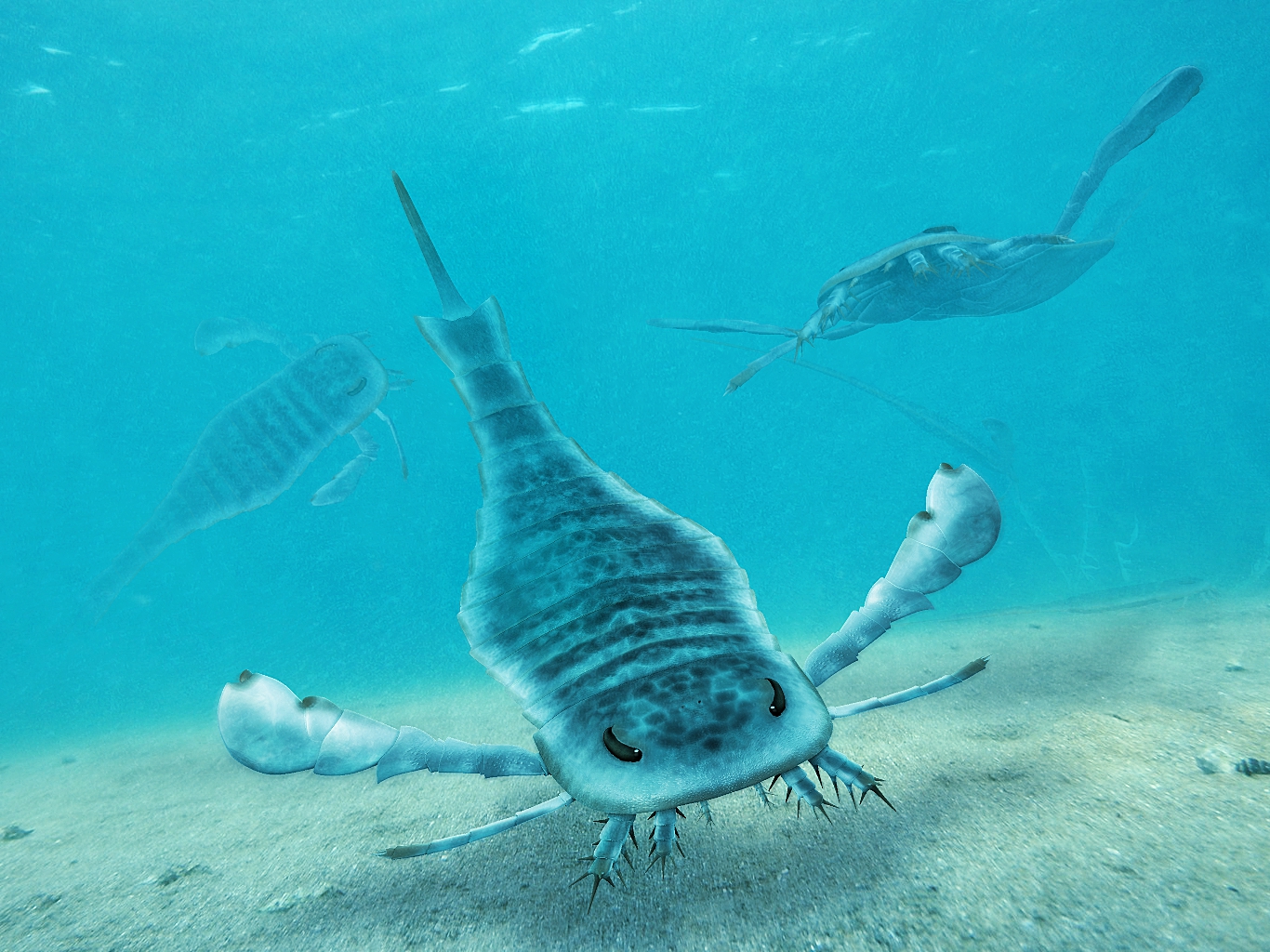
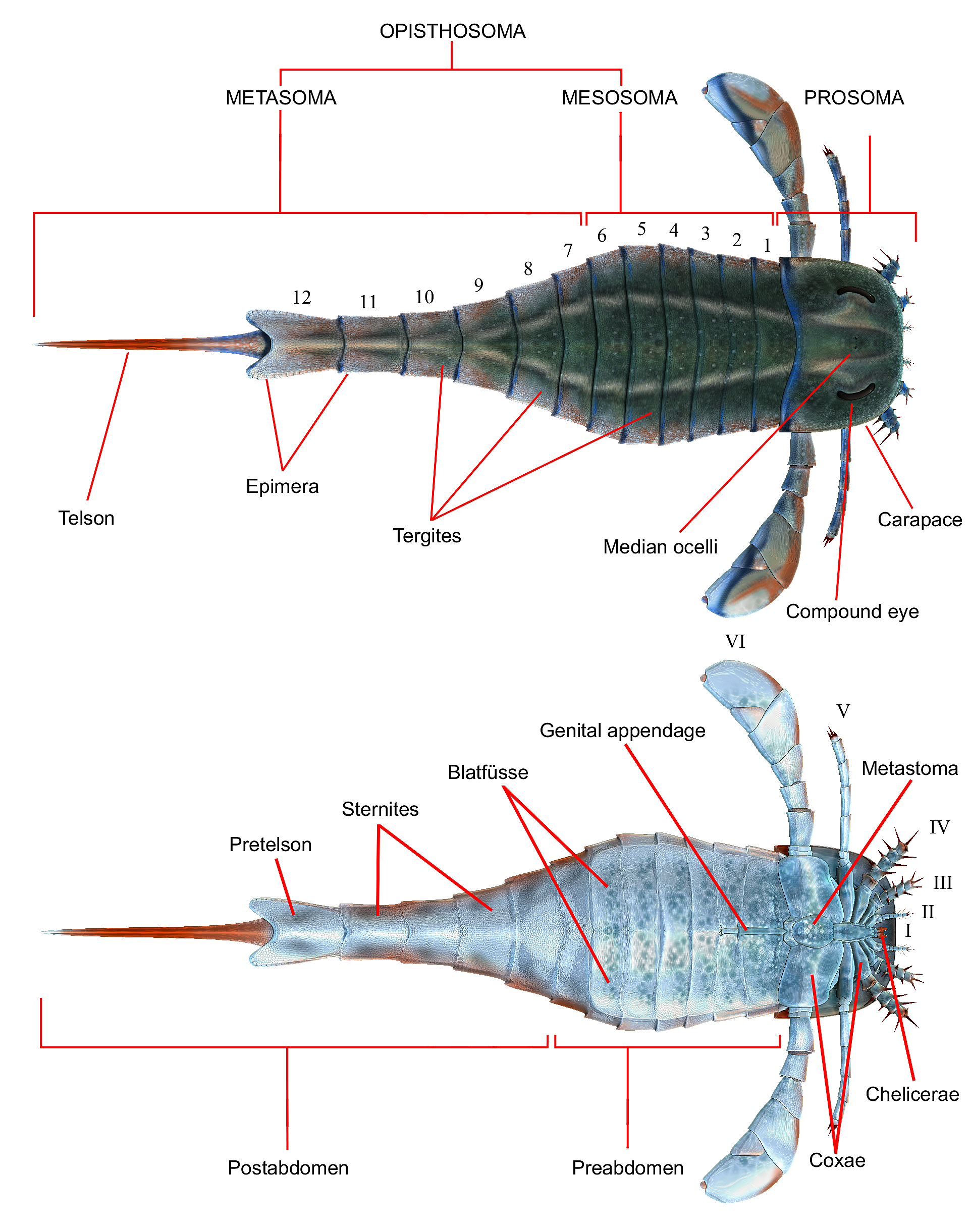
Megalograptidae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The megalograptids were likely the first major successful group of eurypterids, evidenced by a Late Ordovician radiation. All known members of the Megalograptidea are from the Late Ordovician of Laurentia with the exception of the large ''Pentecopterus'' from the Middle Ordovician. Description Megalograptids are characterized by large exoskeletons with ovate to triangular scales. The prosoma (head) is subquadrate, with a tonguelike anterior process bearing marginal spines, and compound eyes on the top front of the head. The chelicerae (claws in front of the mouth) are small and short. The first and third pairs of walking legs are short, with diverging or closely spaced spines. The second pair of walking legs is enormously developed, with long paired spines. The fourth pair of walking legs are nearly spineless. The preabdomen, the front portion of the body, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalograptus
''Megalograptus'' is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of ''Megalograptus'' have been recovered in deposits of Katian (Late Ordovician) age in North America. The genus contains five species: ''M. alveolatus'', ''M. ohioensis'', ''M. shideleri'', ''M. welchi'' and ''M. williamsae'', all based on fossil material found in the United States. Fossils unassigned to any particular species have also been found in Canada. The generic name translates to "great writing" and originates from the mistaken original belief that ''Megalograptus'' was a type of graptolite, often given names ending with -''graptus'' (meaning 'writing'). ''Megalograptus'' was a large predatory megalograptid eurypterid, with the largest and best known species, ''M. ohioensis'', reaching body lengths of . Some species were substantially smaller, with the smallest, belonging to a hitherto undetermined species, only growing to about in length. Morphologically, ''Megalograptus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinognathus
''Echinognathus'' is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. The type and only species of ''Echinognathus'', ''E. clevelandi'', is known from deposits of Late Ordovician age in the United States. The generic name is derived from the New Latin ''echino''- ("spiny") and the Greek ''gnáthos'' ("jaw"), in reference to a spiny endognathary (used to handle food) appendage part of the fossil type material. ''Echinognathus'' is only known from fragmentary fossil material, consisting of body segments, an appendage used to handle food and possibly other body segments. The genus is distinguished from other eurypterids by the large number of elongated and curved spines, blade-like in life, on its limbs. Initially assumed to represent a species of ''Eurypterus'', these distinguishing features were quickly noticed and deemed important enough to designate ''Echinognathus'' as its own genus. With some additional fossil assigned to ''Echinognathus'' in the early 20th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentecopterus
''Pentecopterus'' is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils have been registered from the Darriwilian age of the Middle Ordovician period, as early as 467.3 million years ago. The genus contains only one species, ''P. decorahensis'', that is the oldest known eurypterid, surpassing other Ordovician eurypterids, such as ''Brachyopterus'', in age by almost 9 million years. The generic name derives from the penteconter, a warship from ancient Greece, and the suffix -''pterus'', which means "wing" and is often used in other genus of eurypterids. The specific name refers to Decorah, Iowa, where ''Pentecopterus'' was discovered. The genus is classified as part of the Megalograptidae family of eurypterids, a family differentiated from other eurypterids by the possession of two or more pairs of spines per podomere on prosomal appendage IV, a reduction of almost all spines and the large exoskeletons with ovate to triangular scales. It is estimated that '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
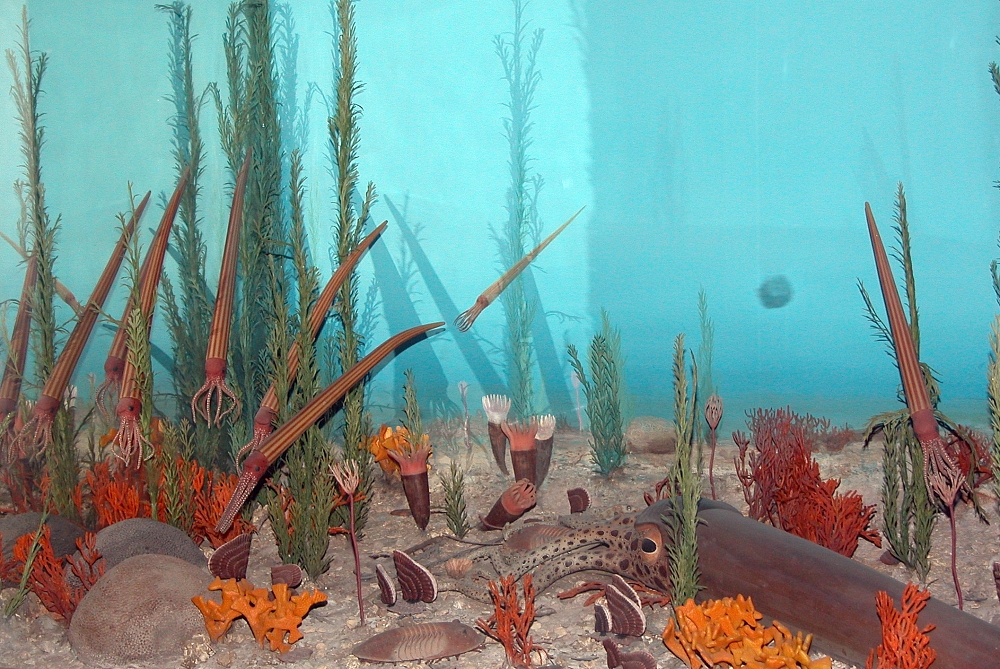
Eurypterid
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 Myr, million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic Chelicerata, chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinosomatoidea
Carcinosomatoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of the superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Eurypterina. Some carcinosomatoid genera have been suggested to have been fully marine as opposed to living in near-shore brackish or hypersaline environments. The majority of carcinosomatoid taxa are known from the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia. Isolated and fragmentary fossils from the Late Silurian of Vietnam and the Czech Republic show that the terranes of Annamia and Perunica were within the geographical range of the carcinosomatoids. Only a few basal carcinosomatoids (e.g. ''Carcinosoma'' and '' Paracarcinosoma'') have been found in deeper waters whilst the more derived forms, such as '' Mixopterus'' and ''Lanarkopterus'' have not. Basal carcinosomatoids (Carcinosomatidae) are likely responsible for the fossil remains in Vietnam and the Czech Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixopteroidea
Carcinosomatoidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of the superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Eurypterina. Some carcinosomatoid genera have been suggested to have been fully marine as opposed to living in near-shore brackish or hypersaline environments. The majority of carcinosomatoid taxa are known from the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia. Isolated and fragmentary fossils from the Late Silurian of Vietnam and the Czech Republic show that the terranes of Annamia and Perunica were within the geographical range of the carcinosomatoids. Only a few basal carcinosomatoids (e.g. ''Carcinosoma'' and '' Paracarcinosoma'') have been found in deeper waters whilst the more derived forms, such as ''Mixopterus'' and ''Lanarkopterus'' have not. Basal carcinosomatoids (Carcinosomatidae) are likely responsible for the fossil remains in Vietnam and the Czech Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterina
Eurypterina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Eurypterine eurypterids are sometimes informally known as "swimming eurypterids". They are known from fossil deposits worldwide, though primarily in North America and Europe. Seventy-five percent of eurypterid species are eurypterines; this represents 99% of specimens. The superfamily Pterygotioidea is the most species-rich clade, with 56 species, followed by the Adelophthalmoidea with 43 species; as sister taxa, they comprise the most derived eurypterines. Pterygotioidea includes the pterygotids, which are the only eurypterids known to have a cosmopolitan distribution. Though more numerous both in specimens and taxa, the eurypterines have the shorter temporal range of the two eurypterid suborders. They first appeared around the same time as the Stylonurina in the Middle Ordovician. The suborder faced a slow extinction during the Middle and Late Devo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician First Appearances
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Arthropods
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Eurypterids
This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomen dubium''), or were not formally published ('' nomen nudum''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names and genera that are no longer considered eurypterids. The list currently includes 115 names out of which 74 are considered valid eurypterid genera. There are approximately 250 species of eurypterids recognized as valid. Naming conventions and terminology There is no "official" or "canonical" list of eurypterid genera. The closest thing is found contained in the regularly updated ''Summary list'' ''of fossil spiders and their relatives'' in the World Spider Catalog. The vast majority of the content of the list below, including the valid genera, preoccupied names, junior synonyms, taxonomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |