|
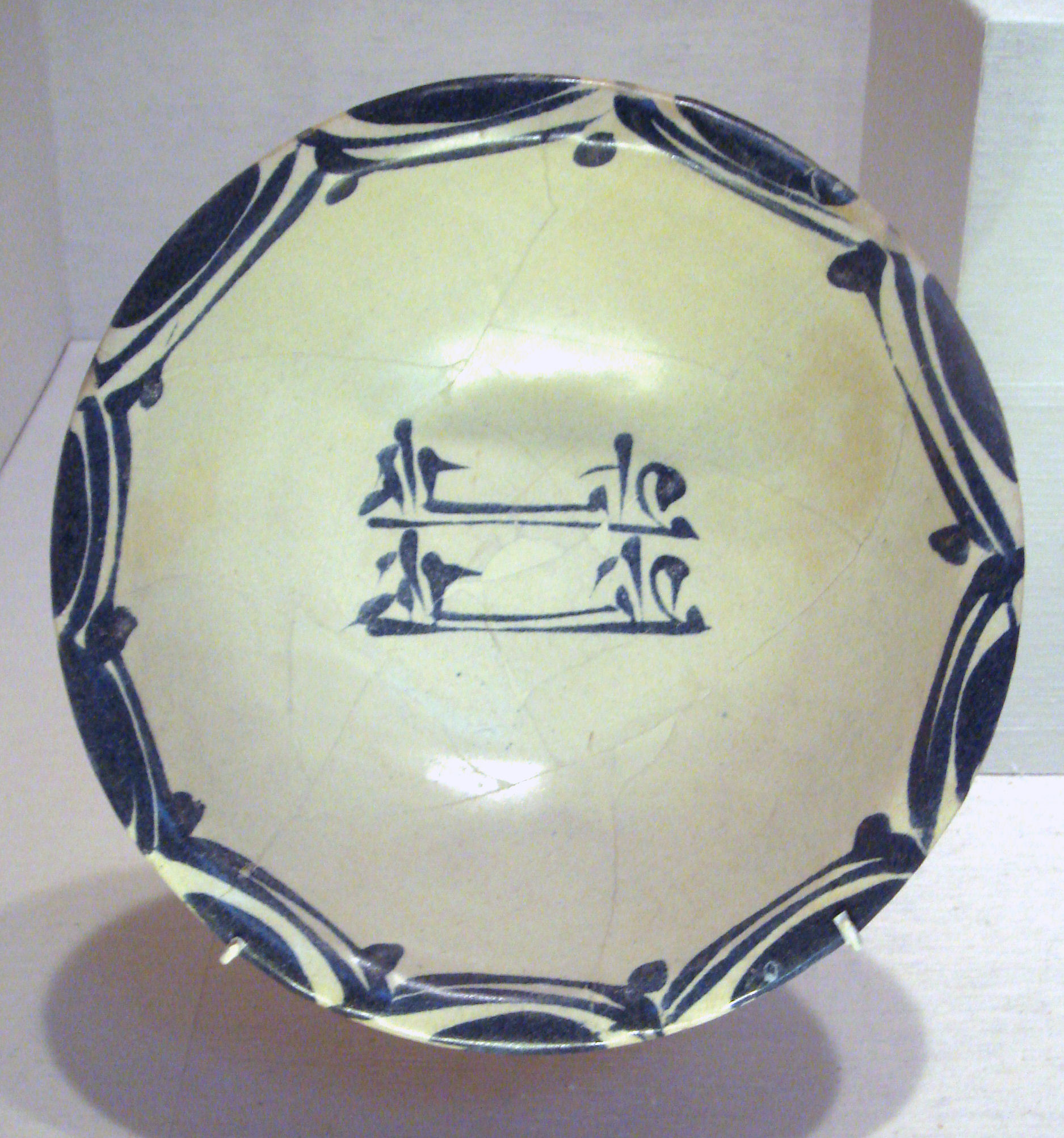
Medici Porcelain
Medici porcelain was the first successful attempt in Europe to make imitations of Chinese porcelain, though it was soft-paste porcelain rather than the hard-paste made in Asia. The experimental manufactory housed in the Casino of San Marco in Florence existed between 1575 and 1587 under the patronage of Francesco I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. Surviving examples are extremely rare, and the great majority of the 60-70 examples are in museums. A painted mark of Brunelleschi's dome and a capital letter F appear on the underside of some pieces; others bear the Medici ''palle'', the balls that are the Medici heraldic charge. Never a commercial venture, Medici porcelains were sometimes given as diplomatic gifts; for example, surviving pieces bear the arms of Philip II of Spain. History and Manufacture Giorgio Vasari reported in the 1568 edition of his ''Vite'' that Bernardo Buontalenti was currently at work on discovering the art of porcelain, but there is no sign that he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medici Porcelain With Surface Detail Florence 1575 1587
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mugello region of Tuscany, and prospered gradually until it was able to fund the Medici Bank. This bank was the largest in Europe during the 15th century and facilitated the Medicis' rise to political power in Florence, although they officially remained citizens rather than monarchs until the 16th century. The Medici produced four popes of the Catholic Church—Pope Leo X (1513–1521), Pope Clement VII (1523–1534), Pope Pius IV (1559–1565) and Pope Leo XI (1605)—and two queens of France—Catherine de' Medici (1547–1559) and Marie de' Medici (1600–1610). In 1532, the family acquired the hereditary title Duke of Florence. In 1569, the duchy was elevated to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany after territorial expansion. The Medici ruled the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around the Indian Ocean by Portuguese explorers, soon after the Cape route was discovered. Nowadays, this term is broadly used to refer to the Malay Archipelago, which today comprises the Philippine Archipelago, Indonesian Archipelago, Malaysian Borneo, and New Guinea. Historically, the term was used in the Age of Discovery to refer to the coasts of the landmasses comprising the Indian subcontinent and the Indochinese Peninsula along with the Malay Archipelago. Overview During the era of European colonization, territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia were known as the Spanish East Indies for 333 years before the American conquest. Dutch occupied colonies in the area were known for about 300 years as the Dutch East Indies till ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiolica
Maiolica is tin-glazed pottery decorated in colours on a white background. Italian maiolica dating from the Renaissance period is the most renowned. When depicting historical and mythical scenes, these works were known as ''istoriato'' wares ("painted with stories"). By the late 15th century, multiple locations,L. Arnoux, 1877, British Manufacturing Industries – Pottery "Most of the Italian towns had their manufactory, each of them possessing a style of its own. Beginning at Caffagiolo and Deruta, they extended rapidly to Gubbio, Ferrara, and Ravenna, to be continued to Casteldurante, Rimini, Urbino, Florence, Venice, and many other places." mainly in northern and central Italy, were producing sophisticated pieces for a luxury market in Italy and beyond. In France maiolica developed as faience, in the Netherlands and England as delftware, and in Spain as talavera. In English the spelling was anglicised to ''majolica'' but the pronunciation usually preserved the vowel with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( , from Low German ''Brunswiek'' , Braunschweig dialect: ''Bronswiek'') is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the North Sea via the rivers Aller and Weser. In 2016, it had a population of 250,704. A powerful and influential centre of commerce in medieval Germany, Brunswick was a member of the Hanseatic League from the 13th until the 17th century. It was the capital city of three successive states: the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1269–1432, 1754–1807, and 1813–1814), the Duchy of Brunswick (1814–1918), and the Free State of Brunswick (1918–1946). Today, Brunswick is the second-largest city in Lower Saxony and a major centre of scientific research and development. History Foundation and early history The date and circumstances of the town's foundation are unknown. Tradition maintains that Brunswick was created through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Gallery Of Art
The National Gallery of Art, and its attached Sculpture Garden, is a national art museum in Washington, D.C., United States, located on the National Mall, between 3rd and 9th Streets, at Constitution Avenue NW. Open to the public and free of charge, the museum was privately established in 1937 for the American people by a joint resolution of the United States Congress. Andrew W. Mellon donated a substantial art collection and funds for construction. The core collection includes major works of art donated by Paul Mellon, Ailsa Mellon Bruce, Lessing J. Rosenwald, Samuel Henry Kress, Rush Harrison Kress, Peter Arrell Browne Widener, Joseph E. Widener, and Chester Dale. The Gallery's collection of paintings, drawings, prints, photographs, sculpture, medals, and decorative arts traces the development of Western Art from the Middle Ages to the present, including the only painting by Leonardo da Vinci in the Americas and the largest mobile created by Alexander Calder. The Gall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue And White Porcelain
"Blue and white pottery" () covers a wide range of white pottery and porcelain decorated underglaze, under the glaze with a blue pigment, generally cobalt(II) oxide, cobalt oxide. The decoration is commonly applied by hand, originally by brush painting, but nowadays by stencilling or by transfer-printing, though other methods of application have also been used. The cobalt pigment is one of the very few that can withstand the highest firing temperatures that are required, in particular for porcelain, which partly accounts for its long-lasting popularity. Historically, many other colours required overglaze decoration and then a second firing at a lower temperature to fix that. The origin of the blue glazes thought to lie in Iraq, when craftsmen in Basra sought to imitate imported white Chinese stoneware with their own tin-glazed, white pottery and added decorative motifs in blue glazes. Such Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid-era pieces have been found in present-day Iraq dating to the 9t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
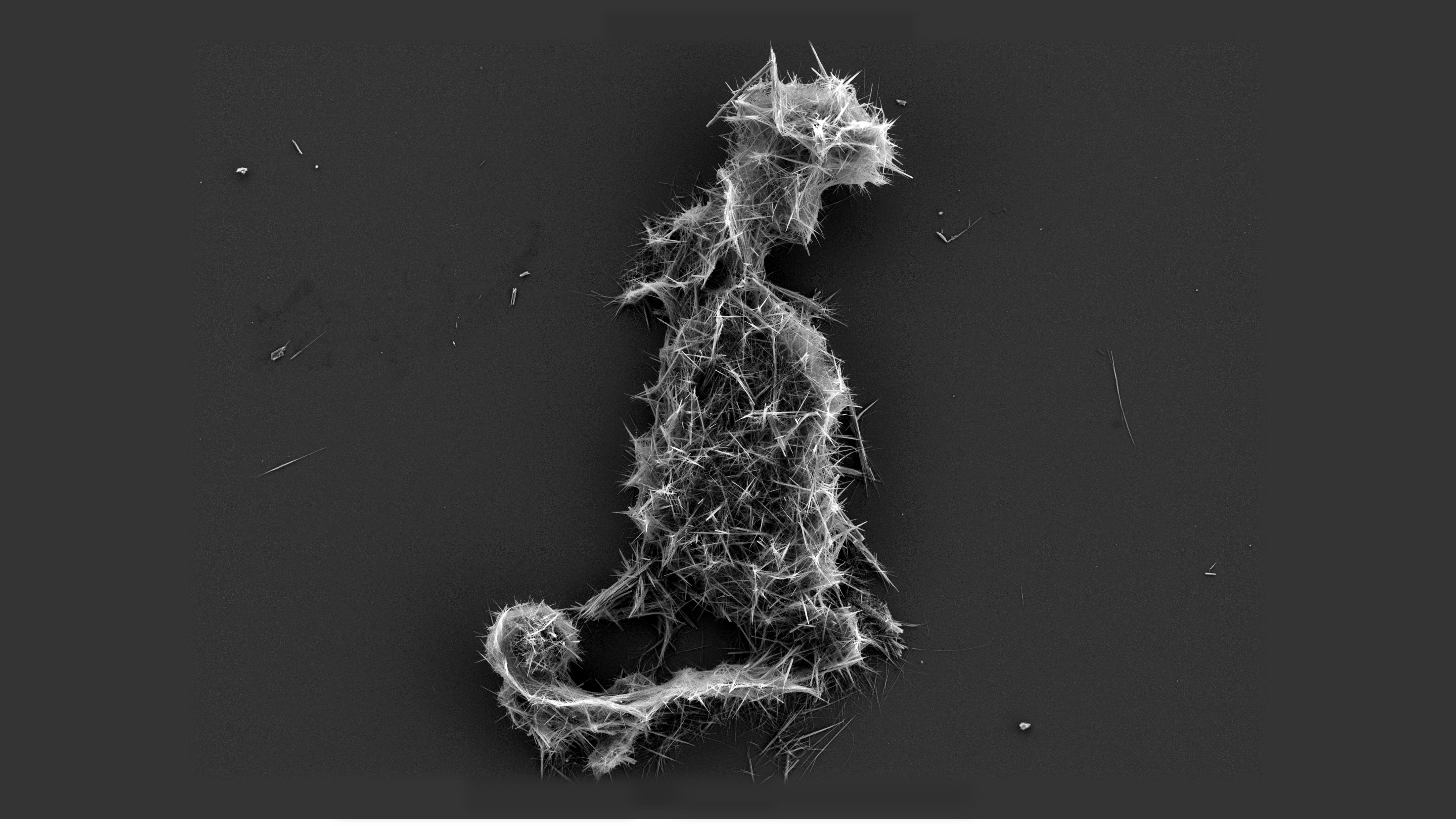
Journal Of Raman Spectroscopy
The ''Journal of Raman Spectroscopy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of Raman spectroscopy, including Higher Order Processes, and Brillouin and Rayleigh scattering. It was established in 1973 and is published by John Wiley & Sons. The editor-in-chief is Laurence A. Nafie (Syracuse University). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.133. Notable papers , the most cited papers published by the journal are: * * * References External links * {{Raman spectroscopy, state=autocollapse Chemistry journals Wiley (publisher) academic journals English-language journals Publications e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral definin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral ( Ca Si O3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone or dolomite is subjected to high temperature and pressure, which sometimes occurs in the presence of silica-bearing fluids as in skarns or in contact with metamorphic rocks. Associated minerals include garnets, vesuvianite, diopside, tremolite, epidote, plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene and calcite. It is named after the English chemist and mineralogist William Hyde Wollaston (1766–1828). Despite its chemical similarity to the compositional spectrum of the pyroxene group of minerals—where magnesium (Mg) and iron (Fe) substitution for calcium ends with diopside and hedenbergite respectively—it is structurally very different, with a third tetrahedron in the linked chain (as opposed to two in the pyroxenes). Production trends Estimated world production of crude wollastonite ore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white solids of nutritious value and are found in many living organisms, e.g., bone mineral and tooth enamel. In milk, it exists in a colloidal form in micelles bound to casein protein with magnesium, zinc, and citrate–collectively referred to as colloidal calcium phosphate (CCP). Various calcium phosphate minerals are used in the production of phosphoric acid and fertilizers. Overuse of certain forms of calcium phosphate can lead to nutrient-containing surface runoff and subsequent adverse effects upon receiving waters such as algal blooms and eutrophication (over-enrichment with nutrients and minerals). Orthophosphates, di- and monohydrogen phosphates These materials contain Ca2+ combined with , , or : * Monocalcium phosphate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |