|
Medial Pontine Reticular Formation
The medial pontine reticular formation (MPRF) is a part of the human brain located in the pons of the brainstem (specifically the central pontine reticular formation). It plays a critical function in the generation of REM sleep. Role in REM sleep GABAergic neurons of the MPRF are activated by Acetylcholine (released by the Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus), and in turn activate cells in the basal forebrain -- namely the Dorsal raphe nucleus (which produces serotonin) and the Locus coeruleus (which produces Norepinephrine). This activation will stimulate cortical activity, which is characteristic of the low amplitude / high frequency EEG Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ... patterns observed during REM sleep. As well, lesions of the MPRF will cause a great decrease of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Structure The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons (ventral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac, and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontine Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts. Neurons of the reticular formation, particularly those of the ascending reticular activating system, play a crucial role in maintaining behavioral arousal and consciousness. The overall functions of the reticular formation are modulatory and premotor, involving somatic motor control, cardiovascular control, pain modulation, sleep and consciousness, and habituation. The modulatory functions are prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPT or PPTg) is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It lies caudal to the substantia nigra and adjacent to the superior cerebellar peduncle. It has two divisions of subnuclei; the pars compacta containing mainly cholinergic neurons, and the pars dissipata containing mainly glutamatergic neurons and some non-cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine nucleus is one of the main components of the reticular activating system. It was first described in 1909 by Louis Jacobsohn-Lask, a German neuroanatomist. Projections Pedunculopontine nucleus neurons project axons to a wide range of areas in the brain, particularly parts of the basal ganglia such as the subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra pars compacta, and globus pallidus internus. It also sends them to targets in the thalamus, cerebellum, basal forebrain, and lower brainstem, and in the cerebral cortex, the supplementary motor ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Raphe Nucleus
The dorsal raphe nucleus is located on the midline of the brainstem and is one of the raphe nuclei. It has rostral and caudal subdivisions. * The rostral aspect of the ''dorsal'' raphe is further divided into interfascicular, ventral, ventrolateral and dorsal subnuclei. * The projections of the ''dorsal'' raphe have been found to vary topographically, and thus the subnuclei differ in their projections. An increased number of cells in the lateral aspects of the dorsal raphe is characteristic of humans and other primates. Serotonin The dorsal raphe is the largest serotonergic nucleus and provides a substantial proportion of the serotonin innervation to the forebrain. Serotonergic neurons are found throughout the dorsal raphe nucleus and tend to be larger than other cells. A substantial population of cells synthesizing substance P are found in the rostral aspects, many of these co-express serotonin and substance P. There is also a population of catecholamine synthesizing neurons i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
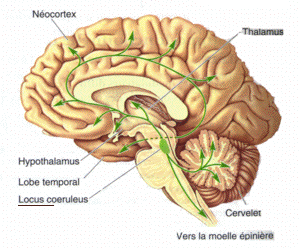
Locus Coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system. The locus coeruleus, which in Latin means "blue spot", is the principal site for brain synthesis of norepinephrine (noradrenaline). The locus coeruleus and the areas of the body affected by the norepinephrine it produces are described collectively as the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system or LC-NA system. Norepinephrine may also be released directly into the blood from the adrenal medulla. Anatomy The locus coeruleus (LC) is located in the posterior area of the rostral pons in the lateral floor of the fourth ventricle. It is composed of mostly medium-size neurons. Melanin granules inside the neurons of the LC contribute to its blue colour. Thus, it is also known as the nucleus pigmentosus pontis, meaning "heavily pigmented nucleus of the pons." The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |