|
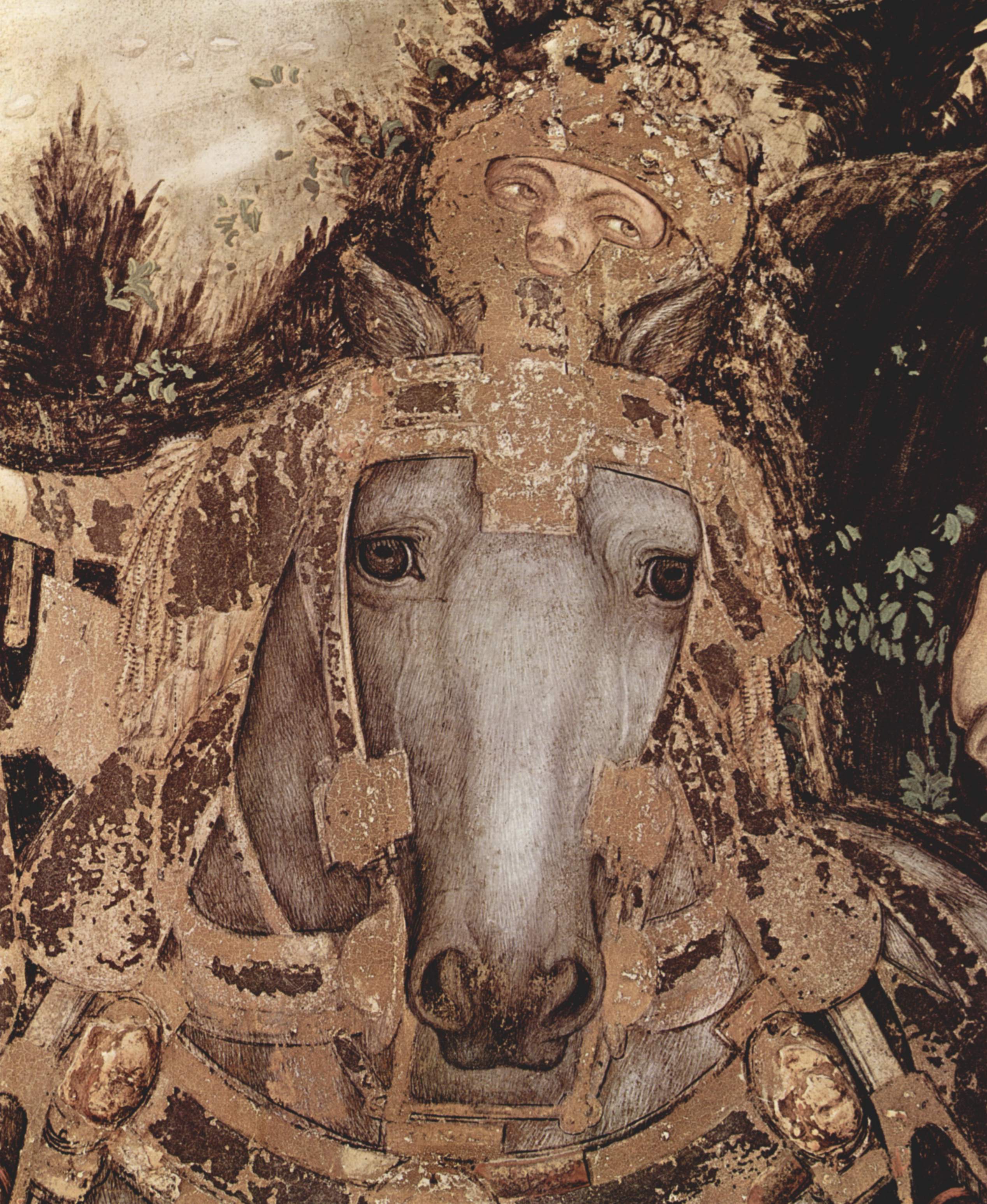
Medal Of John VIII Palaeologus
The medal of John VIII Palaeologus is a portrait medal by the Italian Renaissance artist Pisanello. It is generally considered to be the first portrait medal of the Renaissance. On the obverse of the medal is a profile portrait of the penultimate Byzantine emperor, John VIII Palaeologus; the reverse contains an image of the emperor on horseback before a wayside cross. Although the date of the work is not clear it was likely to have been some time during 1438 and 1439, the years John was in Italy attending the Council of Ferrara (later moved to Florence). It is not known whether the emperor himself or his Italian hosts commissioned Pisanello to make the medal, but Leonello d’Este, the heir apparent to the marquisate of Ferrara, has been suggested as the most likely candidate. Several drawings by Pisanello are closely associated with the medal and these include sketches now held in Paris and Chicago. Its impact on art was significant: it extended beyond numismatics and the prolife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisanello
Pisanello (c. 1380/1395c. 1450/1455), born Antonio di Puccio Pisano or Antonio di Puccio da Cereto, also erroneously called Vittore Pisano by Giorgio Vasari, was one of the most distinguished painters of the early Italian Renaissance and Quattrocento. He was acclaimed by poets such as Guarino da Verona and praised by humanists of his time, who compared him to such illustrious names as Cimabue, Phidias and Praxiteles. Pisanello is known for his resplendent frescoes in large murals, elegant portraits, small easel pictures, and many brilliant drawings such as those in the Codex Vallardi (Louvre). He is the most important commemorative portrait medallist in the first half of the 15th century, and he can claim to have originated this important genre. He was employed by the Doge of Venice, the Pope in the Vatican and the courts of Verona, Ferrara, Mantua, Milan, Rimini, and by the King of Naples. He stood in high esteem in the Gonzaga and Este families. Pisanello had many of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John VIII Palaeologus, Emperor Of Byzantium
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Institute Of Chicago
The Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago's Grant Park, founded in 1879, is one of the oldest and largest art museums in the world. Recognized for its curatorial efforts and popularity among visitors, the museum hosts approximately 1.5 million people annually. Its collection, stewarded by 11 curatorial departments, is encyclopedic, and includes iconic works such as Georges Seurat's ''A Sunday on La Grande Jatte'', Pablo Picasso's ''The Old Guitarist'', Edward Hopper's '' Nighthawks'', and Grant Wood's '' American Gothic''. Its permanent collection of nearly 300,000 works of art is augmented by more than 30 special exhibitions mounted yearly that illuminate aspects of the collection and present cutting-edge curatorial and scientific research. As a research institution, the Art Institute also has a conservation and conservation science department, five conservation laboratories, and one of the largest art history and architecture libraries in the country—the Ryerson and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisanello - Texte ; Description Du Costume ; Jean VIII Paléologue ; Cheval ; Figures, MI 1062, Recto
Pisanello (c. 1380/1395c. 1450/1455), born Antonio di Puccio Pisano or Antonio di Puccio da Cereto, also erroneously called Vittore Pisano by Giorgio Vasari, was one of the most distinguished painters of the early Italian Renaissance and Quattrocento. He was acclaimed by poets such as Guarino da Verona and praised by humanists of his time, who compared him to such illustrious names as Cimabue, Phidias and Praxiteles. Pisanello is known for his resplendent frescoes in large murals, elegant portraits, small easel pictures, and many brilliant drawings such as those in the Codex Vallardi (Louvre). He is the most important commemorative portrait medallist in the first half of the 15th century, and he can claim to have originated this important genre. He was employed by the Doge of Venice, the Pope in the Vatican and the courts of Verona, Ferrara, Mantua, Milan, Rimini, and by the King of Naples. He stood in high esteem in the Gonzaga and Este families. Pisanello had many of his wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central landmark of the city, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement (district or ward). At any given point in time, approximately 38,000 objects from prehistory to the 21st century are being exhibited over an area of 72,735 square meters (782,910 square feet). Attendance in 2021 was 2.8 million due to the COVID-19 pandemic, up five percent from 2020, but far below pre-COVID attendance. Nonetheless, the Louvre still topped the list of most-visited art museums in the world in 2021."The Art Newspaper", 30 March 2021. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard language, Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and ''comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, province of the same name. In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the European Capital of Gastronomy, included in the Eastern Lombardy District (together with the cities of Bergamo, Brescia, and Cremona). In 2008, Mantua's ''centro storico'' (old town) and Sabbioneta were declared by UNESCO to be a World Heritage Site. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family has made it one of the main artistic, culture, cultural, and especially musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole. Having one of the most splendid courts of Europe of the fifteenth, sixteenth, and early seventeenth centuries. Mantua is noted for its significant role in the history of opera; the city is also known for its architectural treasures and artifacts, elegant palaces, and the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a slim majority of Christians worldwide were Eastern Christians comprised; most of the rest were Western Christians. The schism was the culmination of theological and political differences between Eastern and Western Christianity that had developed during the preceding centuries. A series of ecclesiastical differences and theological disputes between the Greek East and Latin West preceded the formal split that occurred in 1054. Prominent among these were the procession of the Holy Spirit (''Filioque''), whether leavened or unleavened bread should be used in the Eucharist, the bishop of Rome's claim to universal jurisdiction, and the place of the See of Constantinople in relation to the pentarchy. In 1053, the first action was taken th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filioque
( ; ) is a Latin term ("and from the Son") added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed (commonly known as the Nicene Creed), and which has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. It is a term that refers to the Son, Jesus Christ, as an additional origin point of the Holy Spirit. It is not in the original text of the Creed, attributed to the First Council of Constantinople (381), which says that the Holy Spirit proceeds "from the Father", without additions of any kind, such as "and the Son" or "alone". In the late 6th century, some Latin Churches added the words "and from the Son" () to the description of the procession of the Holy Spirit, in what many Eastern Orthodox Christians have at a later stage argued is a violation of Canon VII of the Council of Ephesus, since the words were not included in the text by either the First Council of Nicaea or that of Constantinople. The inclusion was incorporated into the liturgical pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosimo De' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derived from his wealth as a banker, and inter-marriage with other powerful and rich families. He was a patron of arts, learning and architecture. He spent over 600,000 gold florins (approx. $500 million inflation adjusted) on art and culture, including Donatello's David, the first freestanding nude male sculpture since antiquity. Despite his influence, his power was not absolute; Florence's legislative councils at times resisted his proposals throughout his life, and he was viewed as first among equals, rather than an autocrat.Martines, Lauro (2011). ''The Social World of the Florentine Humanists, 1390–1460''. University of Toronto Press. p. 8. Biography Early life and family business Cosimo de' Medici was born in Florence to Giovanni di Bicci de' Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarch Sophronius I Of Constantinople
Sophronius I ( el, ), (? – after 1464) was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1463 to 1464. The dates of his reign are disputed by scholars in a range from 1462 to 1464. Life Almost nothing is known about the life and the patriarchate of Sophronius. It is known an act with his name dated August 1464 which certified a cross belonged to Emperor David of Trebizond: the document is probably a forgery, but it confirms us that Sophronius was actually the patriarch. According to Blanchet, who places the reign of Sophronius after Joasaph's, he was Metropolitan of Heraclea before being elected patriarch. One primary source designates Sophronius with the name ''Syropoulos''. Thus it was conjectured, but not proven, that Sophronius was indeed Sylvester Syropoulos, the Orthodox cleric who participated at the Council of Florence and who wrote a chronicle of it. Sylvester Syropoulos belonged to the faction which was in favor of the East-West Union of Churches, and he signed the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borso D'Este, Duke Of Ferrara
Borso d'Este, attributed to Vicino da Ferrara, Pinacoteca of the Castello Sforzesco">Sforza Castle in Milan, Italy. Borso d'Este (1413 – August 20, 1471) was Duke of Ferrara, and the first Duchy of Modena and Reggio, Duke of Modena, which he ruled from 1450 until his death. He was a member of the House of Este. Biography He was an illegitimate son of Niccolò III d'Este, Marquess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio, and his mistress Stella de' Tolomei. Borso succeeded his brother Leonello d'Este in the marquisate on October 1, 1450. left, 220px, A page of Borso d'Este's Bible. On May 18, 1452 he received confirmation over his fiefs, as Duke, by Emperor Frederick III. On April 12, 1471, in St. Peter's Basilica, he was also appointed as Duke of Ferrara by Pope Paul II. Borso followed an expansionist policy for his state, and one of ennobling for his family. He was generally allied with the Republic of Venice, and enemy both to Francesco I Sforza and the Medici family. These rivalri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |