|
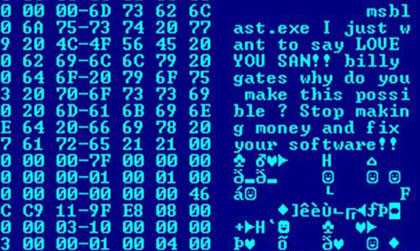
Mebroot
Mebroot is a master boot record based rootkit used by botnets including Torpig. It is a sophisticated Trojan horse that uses stealth techniques to hide itself from the user. The Trojan opens a back door on the victim's computer which allows the attacker complete control over the computer. Payload The Trojan infects the MBR to allow itself to start even before the operating system starts. This allows it to bypass some safeguards and embed itself deep within the operating system. It is known that the Trojan can intercept read/write operations, embed itself deep within network drivers. This allows it the ability to bypass some firewalls and communicate securely, using a custom encrypted tunnel, to the command and control server. This allows the attacker to install other malware, viruses, or other applications. The Trojan most commonly steals information from the victim's computer, in an attempt for small financial gain. Mebroot is linked to Anserin, which is another Trojan that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpig
Torpig, also known as Anserin or Sinowal is a type of botnet spread through systems compromised by the Mebroot rootkit by a variety of trojan horses for the purpose of collecting sensitive personal and corporate data such as bank account and credit card information. It targets computers that use Microsoft Windows, recruiting a network of zombies for the botnet. Torpig circumvents antivirus software through the use of rootkit technology and scans the infected system for credentials, accounts and passwords as well as potentially allowing attackers full access to the computer. It is also purportedly capable of modifying data on the computer, and can perform man-in-the-browser attacks. By November 2008, it was estimated that Torpig had stolen the details of about 500,000 online bank accounts and credit and debit cards and was described as "one of the most advanced pieces of crimeware ever created". History Torpig reportedly began development in 2005, evolving from that point to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Boot Record
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0. The MBR holds the information on how the disc's sectors are divided into partitions, each partition notionally containing a file system. The MBR also contains executable code to function as a loader for the installed operating system—usually by passing control over to the loader's second stage, or in conjunction with each partition's volume boot record (VBR). This MBR code is usually referred to as a boot loader. The organization of the partition table in the MBR limits the maximum addressable storage space of a partitioned disk to 2 TiB . Approaches to slightly raise this limit assuming 32-bit arithmetics or 4096-byte sectors are not officially supported, as they fatally break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keystroke Logging
Keystroke logging, often referred to as keylogging or keyboard capturing, is the action of recording (logging) the keys struck on a keyboard, typically covertly, so that a person using the keyboard is unaware that their actions are being monitored. Data can then be retrieved by the person operating the logging program. A keystroke recorder or keylogger can be either software or hardware. While the programs themselves are legal, with many designed to allow employers to oversee the use of their computers, keyloggers are most often used for stealing passwords and other confidential information. Keylogging can also be used to study keystroke dynamics or human-computer interaction. Numerous keylogging methods exist, ranging from hardware and software-based approaches to acoustic cryptanalysis. Application of keylogger Software-based keyloggers A software-based keylogger is a computer program designed to record any input from the keyboard. Keyloggers are used in IT organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploit (computer Security)
An exploit (from the English verb ''to exploit'', meaning "to use something to one’s own advantage") is a piece of software, a chunk of data, or a sequence of commands that takes advantage of a bug or vulnerability to cause unintended or unanticipated behavior to occur on computer software, hardware, or something electronic (usually computerized). Such behavior frequently includes things like gaining control of a computer system, allowing privilege escalation, or a denial-of-service (DoS or related DDoS) attack. In lay terms, some exploit is akin to a 'hack'. Classification There are several methods of classifying exploits. The most common is by how the exploit communicates to the vulnerable software. A ''remote exploit'' works over a network and exploits the security vulnerability without any prior access to the vulnerable system. A ''local exploit'' requires prior access to the vulnerable system and usually increases the privileges of the person running the exploit past t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Software
Application may refer to: Mathematics and computing * Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks ** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a communications network * Function application, in mathematics and computer science Processes and documents * Application for employment, a form or forms that an individual seeking employment must fill out * College application, the process by which prospective students apply for entry into a college or university * Patent application, a document filed at a patent office to support the grant of a patent Other uses * Application (virtue), a characteristic encapsulated in diligence * Topical application, the spreading or putting of medication to body surfaces See also * * Apply {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive-by Download
Drive-by download is of two types, each concerning the unintended download of computer software from the Internet: # Authorized drive-by downloads are downloads which a person has authorized but without understanding the consequences (e.g. downloads which install an unknown or counterfeit executable program, ActiveX component, or Java applet). # Unauthorized drive-by downloads are downloads which happen without a person's knowledge, often a computer virus, spyware, malware, or crimeware. Drive-by downloads may happen when visiting a website, opening an e-mail attachment or clicking a link, or clicking on a deceptive pop-up window: by clicking on the window in the mistaken belief that, for example, an error report from the computer's operating system itself is being acknowledged or a seemingly innocuous advertisement pop-up is being dismissed. In such cases, the "supplier" may claim that the user "consented" to the download, although the user was in fact unaware of having started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivirus
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware. Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name. However, with the proliferation of other malware, antivirus software started to protect from other computer threats. In particular, modern antivirus software can protect users from malicious browser helper objects (BHOs), browser hijackers, ransomware, keyloggers, backdoors, rootkits, trojan horses, worms, malicious LSPs, dialers, fraud tools, adware, and spyware. Some products also include protection from other computer threats, such as infected and malicious URLs, spam, scam and phishing attacks, online identity (privacy), online banking attacks, social engineering techniques, advanced persistent threat (APT), and botnet DDoS attacks. History 1949–1980 period (pre-antivirus days) Although the roots of the computer vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Registry
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interfaces can all use the registry. The registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance. In other words, the registry or Windows Registry contains information, settings, options, and other values for programs and hardware installed on all versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems. For example, when a program is installed, a new subkey containing settings such as a program's location, its version, and how to start the program, are all added to the Windows Registry. When introduced with Windows 3.1, the Windows Registry primarily stored configuration information for COM-based components. Windows 95 and Windows NT extended its use to rationalize and centralize the information in the profusion of INI fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ntoskrnl
ntoskrnl.exe (short for Windows NT operating system kernel executable), also known as the kernel image, contains the kernel and executive layers of the Microsoft Windows NT kernel, and is responsible for hardware abstraction, process handling, and memory management. In addition to the kernel and executive mentioned earlier, it contains the cache manager, security reference monitor, memory manager, scheduler (Dispatcher), and blue screen of death (the prose and portions of the code).Russinovich, MSystems Internals Tips and Trivia ''SysInternals Information'' Overview ntoskrnl.exe depends on bootvid.dll, hal.dll and kdcom.dll. However, it is not a native application. In other words, it is not linked against ntdll.dll. Instead, ntoskrnl.exe containing a standard "start" entry point that calls the architecture-independent kernel initialization function. Because it requires a static copy of the C Runtime objects, the executable is usually about 10 MB in size. In Windows XP and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATA Packet Interface
ATA Packet Interface (ATAPI) is a protocol that has been added to Parallel ATA and Serial ATA so that a greater variety of devices can be connected to a computer than with the ATA command set alone. It carries SCSI commands and responses through the ATA interface. ATAPI devices include CD-ROM and DVD-ROM drives, tape drives, magneto-optical drives, and large-capacity floppy drives such as the Zip drive and SuperDisk drive. Background ATA was originally designed for, and worked only with hard disks and devices that could emulate them. A group called the Small Form Factor committee (SFF) introduced ATAPI (ATA Packet Interface) ATA to be used for a variety of other devices that require functions beyond those necessary for hard disks. For example, any removable media device needs a "media eject" command, and a way for the host to determine whether the media is present, and these were not provided in the ATA protocol. The Small Form Factor committee approached this problem by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malware
Malware (a portmanteau for ''malicious software'') is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. By contrast, software that causes harm due to some deficiency is typically described as a software bug. Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017, which is twice as many malware variants as in 2016. Cybercrime, which includes malware attacks as well as other crimes committed by computer, was predicted to cost the world economy $6 trillion USD in 2021, and is increasing at a rate of 15% per year. Many types of malware exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |