|
Me-1 Road (Spain)
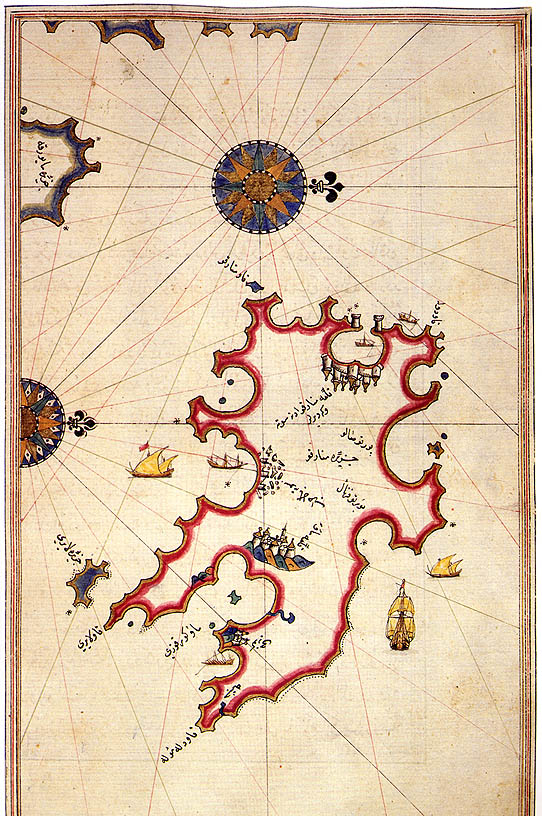
The Me-1 road (previously known as the C-721 road) is situated on the island of Menorca, Balearic Islands, Spain. It connects the two main cities of the island, Mahón and Ciutadella. In 2001 improvements were made to the road; the lanes were widened and the road was diverted from the urban centres of Alayor and Ferreries. It has a total length of 45 kilometres. History The origins of the road date back to the 2nd century BC, when the Roman Empire conquered the Balearic Islands, Quintus Caecilius Metellus Balearicus ordered for a Roman road to be built which united the cities of Magonis (now Mahón) and Jamma (now Ciudadella). Since then route of the road has changed very little. Name Former name Before the improvements in 2001 the road was called the C-721. This name was formed using a combination of the letter ''C'', identifying that the road is regional (Spanish: ''comarcal''), with the following three numbers: * Firstly: ''7'', indicating that the road is situated on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alayor
Alaior (, , ; previously in Spanish, ''Alayor'') is a municipality on the island of Menorca, in the Balearic Islands, Spain. It is situated 12 km from the capital, Maó. In 2005 it had a population of 8,671 and it covers an area of 109.77 km². The principal activities are tourism, shoemaking, cheese, and construction materials. The patron saint of the municipality is Saint Lawrence Saint Lawrence or Laurence ( la, Laurentius, lit. "Laurel wreath, laurelled"; 31 December AD 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, perse ... and Saint Eulalia. For this reason, the patron festivals are celebrated the weekend after August 10, the saint's festival day, with ''jaleo'' dance. The principal tourist centers are Son Bou, Sant Jaume, Torre Solí, Cala'n Porter, and Cales Coves. References External linksTown GuideTown council webpage [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Es Mercadal
Es Mercadal is a town and municipality in northern Menorca in the Spanish Balearic Islands. Etymology The name "Mercadal" derives from the Latin language ''mercatum'', meaning "market". In 1301, King James II of Majorca decreed the establishment of a public center of commerce in Menorca, and the bustling open-air marketplace remains a principal attraction of the island to this day. Features Mercadal is dominated by Mount Toro (El Toro El Toro, Spanish for "the bull", may refer to: Geography * El Toro (Mallorca), a neighbourhood in the municipality of Calvià on the island of Mallorca * El Toro, Castellón, a town in Castellón, Spain * El Toro (Jujuy), a rural municipality and ...), the highest point on the island. In mid-July, Mercadal is the site of traditional Menorcan festivities dedicated to the Roman Catholic saint Martin (Sant Martí). References External links Mercadal's Town Hall Web page Municipalities in Menorca Populated places in Menorca {{Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferreries
Ferreries is a municipality on the island of Menorca, in the Spanish autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. Its name is derived from the Catalan word ''ferrer'' ("blacksmith"), which in turn, comes from Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ... word ''ferrum''. At an elevation of 150 metres it is the island's highest town. Plaça Espanya Phil Lee ''The Rough Guide to Menorca'' 1858287081- 2001 Page 154 "Tucked into a hollow beneath a steep hill, 8km from Es Mercadal on the C721 and 7km from Es Migjorn Gran, lies FERRERIES, with its narrow, sloping streets, framed by terraced fields. A surprise here is the pagoda-like piece of modern sculpture in the main square, the Plaça Espanya, while just up the hill at the back of the plaça – along c/Fred – stands th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
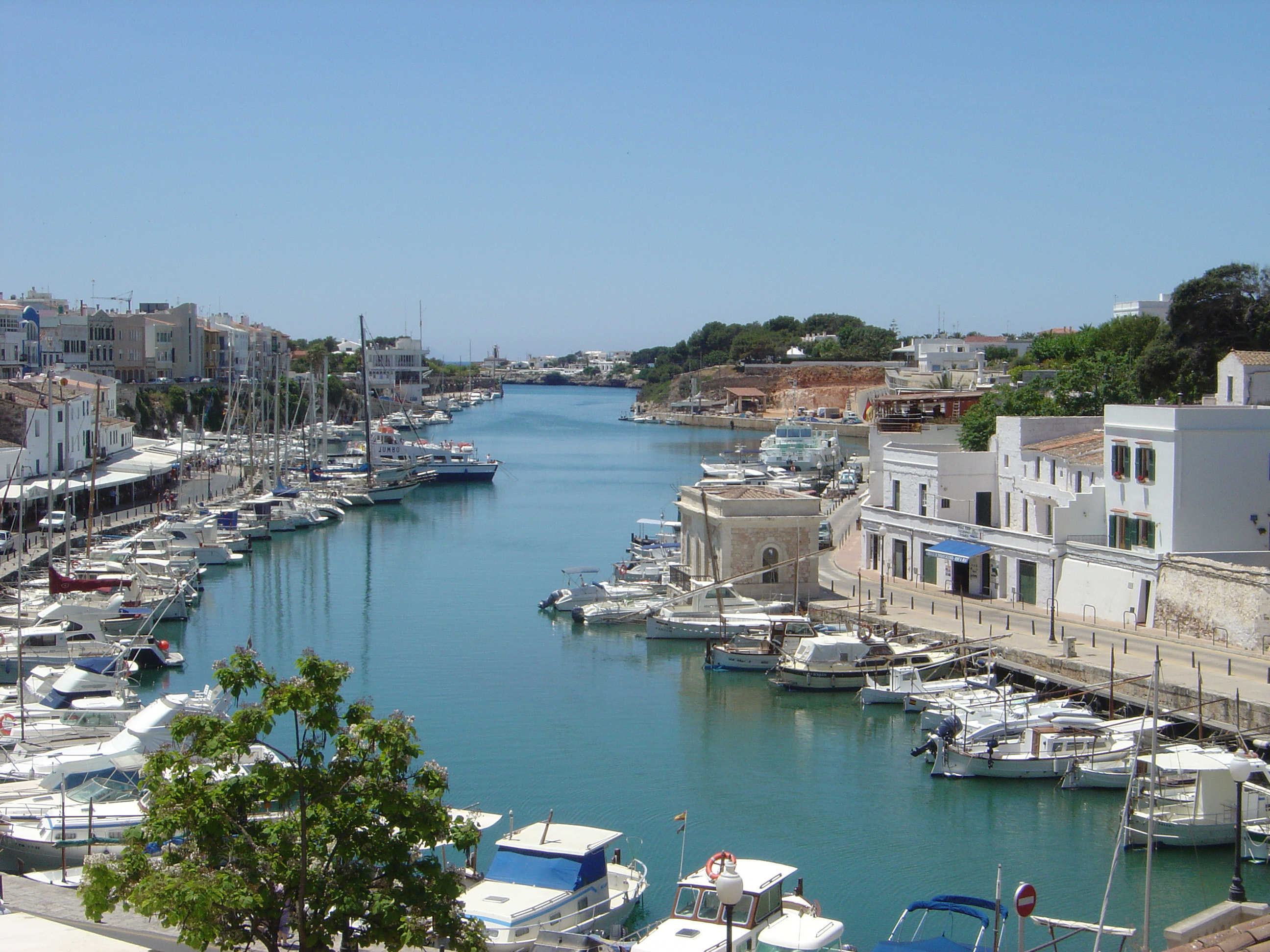
Mahón
Mahón (), officially Maó (), and also written as Mahon or Port Mahon in English, is the capital and second largest city of Menorca. The city is located on the eastern coast of the island, which is part of the archipelago and autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. Mahón has one of the longest natural harbours in the world: long and up to wide. The water is deep but remains mostly clear due to the port's enclosed nature. Mayonnaise is considered to have originated in Mahón. Its population in 2021 was estimated to be 29,125. History The name's origin is attributed to the Carthaginian general Mago Barca, brother to Hannibal, who is thought to have taken refuge there in 205 BC. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, it became part of the Eastern Roman Empire; it suffered raids from Vikings and Arabs until the Islamic Caliphate of Córdoba conquered it in 903. Mahón was captured in 1287 from the Moors by Alfonso III of Aragon and incorporated into the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciutadella De Menorca
Ciutadella de Menorca () or simply Ciutadella is a town and a municipality in the western end of Menorca, one of the Balearic Islands (Spain). It is one of the two primary cities in the island, along with Maó. History It was founded by the Carthaginians, and became the seat of a bishop in the 4th century. After being governed by the Moors under the names of ''Medīna el Jezīra'' ( ar, مدينة الجزيرة) and ''Medīna Menūrqa'' (مدينة منورقة) for several centuries, Ciutadella was recaptured during the reconquista by men serving Alfonso III and became part of the Crown of Aragon. During the Middle Ages, it became an important trading center. On 9 July 1558, the Turks under Piyale Pasha and Turgut Reis with a powerful Turkish Armada of 140 ships and 15,000 soldiers, put the town under siege for eight days entered and decimated the town. The town was defended by only a few hundred men. All of Ciutadella's 3,099 inhabitants who survived the siege were taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capital is Mahón ( ca, Maó), situated on the island's eastern end, although Menorca is not a province and forms a political union with the other islands in the archipelago. Ciutadella and Mahon are the main ports and largest towns. The port of Mahon is the second biggest natural port in the world. Menorca has a population of approximately 93,397 (at 1 January 2019). It is located 39°47' to 40°00'N, 3°52' to 4°24'E. Its highest point, called El Toro (from Catalan "''turó''" meaning ''hill''), is above sea level. History The island is known for its collection of megalithic stone monuments: ''navetes'', ''taules'' and ''talaiots'', which indicate very early prehistoric human activity. Some of the earliest culture on Menorca was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is Palma. The 2007 Statute of Autonomy designates the Balearic Islands as one of the ''nationalities'' of Spain. The official languages of the Balearic Islands are Catalan and Spanish. Its four largest islands are Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza, and Formentera. Many of its minor islands and islets are close to the larger islands, including Cabrera, Dragonera, and S'Espalmador. The islands have a Mediterranean climate, and the four major islands are all popular tourist destinations. Ibiza, in particular, is known as an international party destination, attracting many of the world's most popular DJs to its nightclubs. The islands' culture and cuisine are similar to those of the rest of Spain but have their own distinctive features. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Balearicus
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Balearicus (born c. 170 BC) was a Roman statesman and general who was elected consul for the year 123 BC. Career Quintus Caecilius Metellus was the eldest son of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus, the Roman consul of 143 BC, and a member of the plebeian '' gens Caecilia''. It is suspected that he served under his father in Hispania Citerior during 143-142 BC. By 126 BC, he had been elected to the office of Praetor. He was then elected to the consulship in 123 BC, serving alongside Titus Quinctius Flamininus. During his consulship, he was awarded the command of the campaign against the pirates of the Balearic Islands. His campaign continued into 122 BC, and when his consulship ended, he was granted a proconsular command. By 121 BC, he had defeated the pirates and conquered Mallorca and Menorca, the Balearics, for which he earned his cognomen ''Balearicus'' and the honours of a Triumph. In the aftermath of the victory, he established at Palma and Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
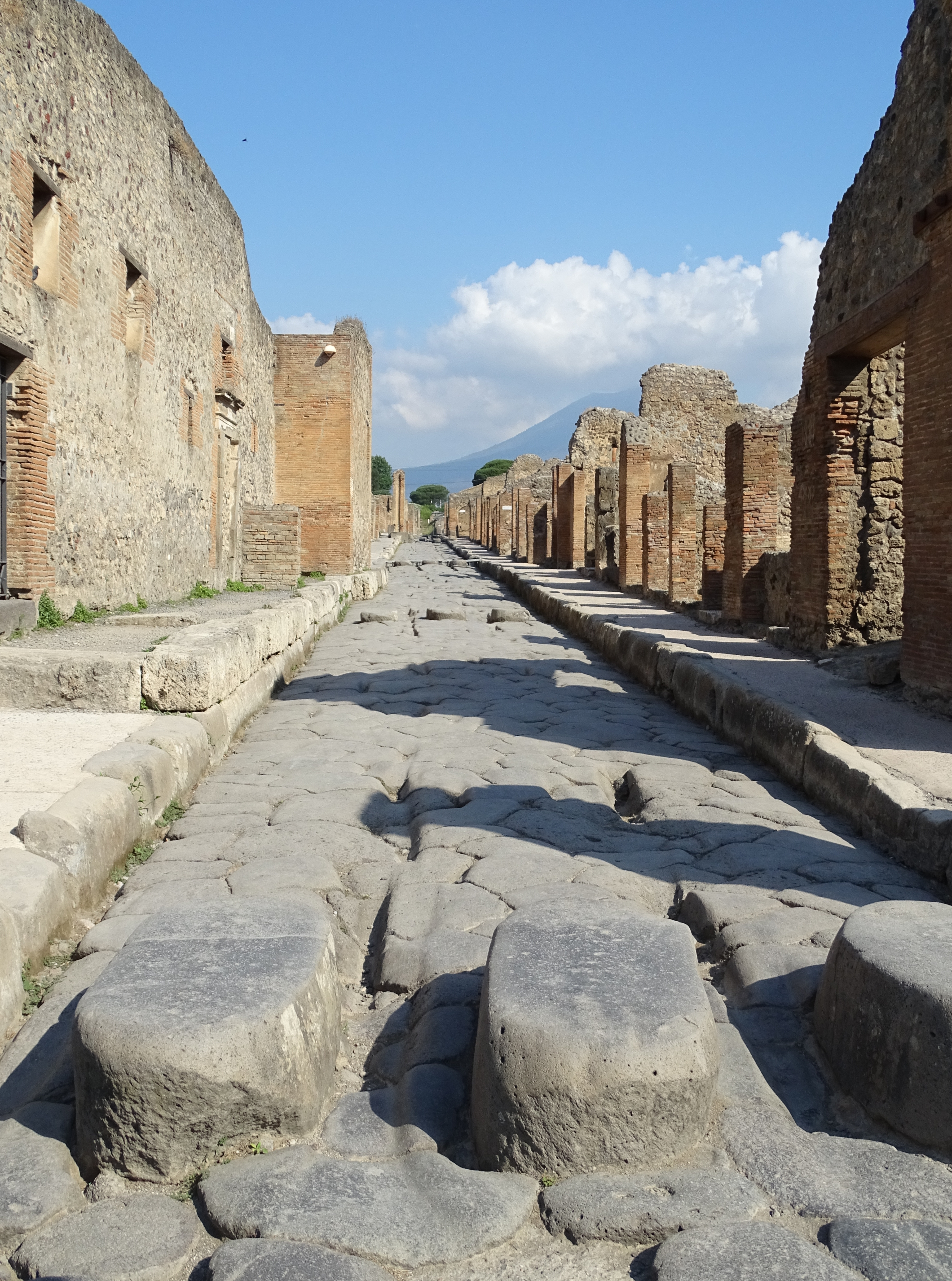
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |