|
McMath–Hulbert Observatory
The McMath-Hulbert Solar Observatory is a solar observatory in Lake Angelus, Michigan, USA. It was established in 1929 as a private observatory by father and son Francis Charles McMath and Robert Raynolds McMath and their friend, Judge Henry Hulbert. In 1932 the observatory was deeded to the University of Michigan which operated it until 1981, at which time it was sold into private ownership again. In 1932 a reflector telescope was added to the observatory as well as a spectroheliokinematograph . This instrument was designed to take motion pictures of the Sun. The McMath-Hulbert Solar Observatory is primarily known for the motion pictures that the McMaths made of various celestial phenomena, including the first movies of solar prominences in motion. Later work involved solar spectroscopy in the near infrared and participation in a solar flare patrol program in the 1950s. Robert McMath and one of the resident astronomers, Keith Pierce, established the McMath–Pierce solar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Angelus, Michigan
Lake Angelus is a city in Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is an affluent suburb of Detroit, with one of the highest per capita incomes of any community in the state. History In the early 1900s, a small community formed around the lake, then called Three Mile Lake. During the 1920s, the lake was renamed Lake Angelus by Mrs. Sollace B. Collidge as the original name stood for the distance from the eastern side of the lake shore to the western shore. The community was under pressure from nearby government establishments to be annexed. In 1929, however, a special state act of legislation was passed, granting Lake Angelus incorporation as a village. Lake Angelus became a city of its own in 1984. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and (34.36%) is water. The city completely surrounds the lake of the same name. The city is bordered: * To the north and east by the city of Auburn Hills * To the south b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMath–Pierce Solar Telescope
McMath–Pierce solar telescope is a 1.6 m f/54 reflecting solar telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States. Built in 1962, the building was designed by American architect Myron Goldsmith and Bangladeshi-American structural engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan. It was the largest solar telescope and the largest unobstructed aperture optical telescope in the world. It is named after the astronomers Robert Raynolds McMath and Keith Pierce. It was originally called the McMath Solar Telescope, and then later renamed the McMath-Pierce Solar Telescope in 1992. Although it is designed for observation of the Sun, it can also be used to view bright objects at night. In 2018, the telescope received a 4.5 million USD grant for an enhanced visitor center and other programs, and to overall revitalize the national icon. Construction The telescope is a triple instrument. In addition to the primary 1.61 m mirror fed by the 2.03 m heliostat, there are a pair of telesco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
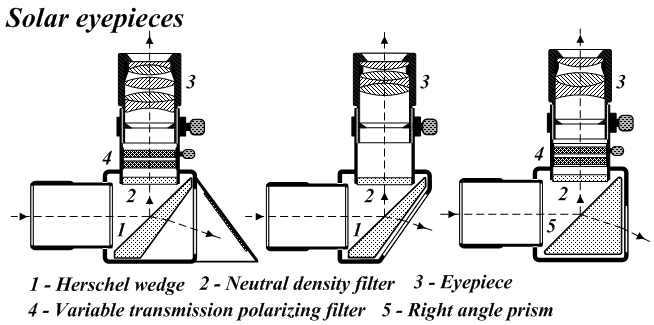
Solar Telescopes
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories In Michigan
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Observatories
This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer in operation. While other sciences, such as volcanology and meteorology, also use facilities called observatories for research and observations, this list is limited to observatories that are used to observe celestial objects. Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Many modern telescopes and observatories are located in space to observe astronomical objects in wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot penetrate the Earth's atmosphere (such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays) and are thus impossible to observe using ground-based telescopes. Being above the atmosphere, these space observatories can also avoid the effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angell Hall Observatory
Angell Hall Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by University of Michigan. It is located on the UM Central Campus on top of Angell Hall in Ann Arbor, Michigan (US). It has a computer-controlled 0.4-m Cassegrain telescope in its single dome, and a small radio telescope on the roof. In the past it has housed a large, clock-driven refracting telescope and a reflecting telescope in side-by-side domes. The current telescope was manufactured by DFM Engineering and installed in December 1994. Other observatories that UM has operated include the Detroit Observatory (1854), the Lamont–Hussey Observatory (South Africa, 1928), the McMath–Hulbert Observatory (Lake Angelus, Michigan, 1930), the Portage Lake Observatory (near Dexter, Michigan, 1948), and the Peach Mountain Observatory (near Dexter, Michigan, 1958). See also *List of observatories References * External links Ann Arbor Clear Sky ClockWeather forecast for observing conditions. Astronomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black [hill]" , nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town" , image_map = , mapsize = 260px , map_caption = Interactive map outlining Tucson , image_map1 = File:Pima County Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Tucson highlighted.svg , mapsize1 = 250px , map_caption1 = Location within Pima County , pushpin_label = Tucson , pushpin_map = USA Arizona#USA , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Arizona##Location within the United States , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State , subdivision_type2 = List of counties in Arizona, County , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_name1 = Arizona , subdivision_name2 = Pima County, Arizona, Pima , established_title = Founded , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitt Peak Observatory
The Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) is a United States astronomical observatory located on Kitt Peak of the Quinlan Mountains in the Arizona-Sonoran Desert on the Tohono Oʼodham Nation, west-southwest of Tucson, Arizona. With more than twenty optical and two radio telescopes, it is one of the largest gatherings of astronomical instruments in the Earth's northern hemisphere. Kitt Peak National Observatory was founded in 1958. It is home to what was the largest solar telescope in the world, and many large astronomical telescopes of the late 20th century in the United States. The observatory was administered by the National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) from the early 1980s until 2019, after which it was overseen by NOIRLab. In June 2022, the Contreras Fire led to the evacuation of Kitt Peak. The fire reached the summit at 2 a.m. on Friday, June 17. Four non-scientific buildings, including a dormitory, were lost in the fire. As of Monday, June 20, the extent of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Pierce
Austin Keith Pierce (October 2, 1918 – March 11, 2005) was an American solar astronomer. Pierce played a key role in the development of the McMath–Pierce solar telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona. Biography Austin Keith Pierce was born October 2, 1918, in Tacoma, Washington. His father, Tracy Pierce, was a mathematician at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln and an amateur astronomer. From 1936 to 1938, he studied at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, before transferring to the University of California, Berkeley where in 1940 he obtained a BSc in astronomy. In 1941 he married Mildred Buell, with whom he went on to have three children. During the Second World War, Pierce worked on uranium isotope separation as part of the Manhattan Project, first at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory and then at Oak Ridge in Tennessee. In 1945 he returned to Berkeley, obtaining his doctorate in 1948 under C. Donald Shane. He then worked at the University of Michigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Observatory
A solar observatory is an observatory that specializes in monitoring the Sun. As such, they usually have one or more solar telescopes. The Einstein Tower was a solar observatory in the Albert Einstein Science Park in Potsdam, Germany. Solar observatories study phenomena associated with the Sun. The Sun, being the closest star to earth, allows a unique chance to study stellar physics with high-resolution. It was, until the 1990s, the only star whose surface had been resolved. General topics that interest a solar astronomer are its 11-year periodicity (i.e., the Solar Cycle), sunspots, magnetic field activity (see solar dynamo), solar flares, coronal mass ejections, differential rotation, and plasma physics. Some examples * Huairou Solar Observing Station * Solar observatories in space * National Solar Observatory See also * Coronagraph * Heliometer * Helioscope * List of solar telescopes This is a list of solar telescopes built in various countries around the world. A so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)