|
McIntosh Apple
The McIntosh ( ), McIntosh Red, or colloquially the Mac, is an apple cultivar, the national apple of Canada. The fruit has red and green skin, a tart flavour, and tender white flesh, which ripens in late September. In the 20th century it was the most popular cultivar in Eastern Canada and New England, and is considered an all-purpose apple, suitable both for cooking and eating raw. John McIntosh (farmer), John McIntosh discovered the original McIntosh sapling on his South Dundas, Ontario, Dundela farm in Upper Canada in 1811. He and his wife cultivated it, and the family started grafting the tree and selling the fruit in 1835. In 1870, it entered commercial production, and became common in northeastern North America after 1900. While still important in production, the fruit's popularity fell in the early 21st century in the face of competition from varieties such as the Gala (apple), Gala. According to the US Apple Association website it is one of the fifteen most popular app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Dundas, Ontario
South Dundas is a municipality in eastern Ontario, Canada, in the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry along the north shore of the St. Lawrence River. It is located approximately 100 kilometres (60 miles) south of Ottawa and is midway between Kingston and Montreal, Quebec. Communities The Municipality of South Dundas comprises a number of villages and hamlets, including the following communities: * The western portion, in the former Matilda Township: Brinston, Dixons Corners, Dundela, Glen Stewart, Hanesville, Hulbert, Irena, Iroquois, Stampville; ''Haddo'', ''Pleasant Valley'', ''Rowena'', ''Toyes Hill''; ''Iroquois Beach'', ''New Ross'', ''Oak Valley'' (partially), ''Pinetree Point'', ''Rapide Plat Point'', ''Robertson Point'', ''Straders Hill'' * The eastern portion, in the former Williamsburg Township: Dunbar, Elma, Glen Becker, Morrisburg, Riverside Heights, Williamsburg, Winchester Springs (partially); ''Archer'', ''Beckstead'', ''Boucks Hill'', ''Colquhoust' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
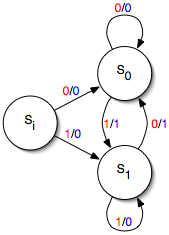
Mealy
In the theory of computation, a Mealy machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined both by its current state and the current inputs. This is in contrast to a Moore machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state. A Mealy machine is a deterministic finite-state transducer: for each state and input, at most one transition is possible. History The Mealy machine is named after George H. Mealy, who presented the concept in a 1955 paper, "A Method for Synthesizing Sequential Circuits". Formal definition A Mealy machine is a 6-tuple (S, S_0, \Sigma, \Lambda, T, G) consisting of the following: * a finite set of states S * a start state (also called initial state) S_0 which is an element of S * a finite set called the input alphabet \Sigma * a finite set called the output alphabet \Lambda * a transition function T : S \times \Sigma \rightarrow S mapping pairs of a state and an input symbol to the corresponding next state. * an output funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Delicious
'Golden Delicious' is a cultivar of apple. It is one of the 15 most popular apple cultivars in the United States. It is not closely related to 'Red Delicious'. History Golden Delicious arose from a chance seedling, possibly a hybrid of 'Grimes Golden' and 'Golden Reinette'. The original tree was found on the Mullins' family farm in Clay County, West Virginia, United States, and was locally known as Mullin's Yellow Seedling and Annit apple. In Clay County, George Deems was instrumental in preserving and perpetuating the original Stark's Golden delicious apple tree on A. H. Mullins property back in 1938. The famed tree came to the attention of the Stark Brothers a number of years before, when Mr. Mullins sent three apples to Mr. Stark one fine April. The Golden Delicious' long keeping qualities were soon abundantly evident to Mr. Stark, as well as to United States Pomologist Colonel Brackett, in Washington, and the nursery bought the tree and ground on which it stands from Mr. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternaria Mali
''Alternaria mali'', also called alternaria blotch of apple, is a pathogenic fungus affecting plants. It is prevalent in the southern United States and elsewhere, and damages the leaves of infected apple trees. Pathogenesis ''Aleternaria mali'' can overwinter as mycelium on dead leaves on the ground, in mechanical injuries in twigs, or in dormant buds. Primary infection occurs about one month after petal fall the following year. The disease is favoured by temperatures between 77 and 86 °F (25–30 °C), and by wet conditions. Infection occurs at optimum temperatures with 5.5 hours of wetting, and an outbreak can become serious within two days of infection. The fungus attacks susceptible cultivars using a chemical toxin. Affected plants exhibit circular spots on the leaves that enlarge as the disease advances. Normally, hyphae cannot adhere to the surface of the host, but under moist conditions light-grey mycelium might be present on the surface. Normally the fungus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neofabraea Malicorticis
''Neofabraea malicorticis'' is a plant pathogen that causes bull's-eye rot on apple and pear Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the p .... References Fungal tree pathogens and diseases Apple tree diseases Pear tree diseases Dermateaceae {{fungus-tree-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rot
Black rot is a name used for various diseases of cultivated plants caused by fungi or bacteria, producing dark brown discoloration and decay in the leaves of fruit and vegetables: * A disease of the apple, pear and quince caused by a fungus (''Botryosphaeria obtusa'' or ''Physalospora cydoniae'') * A disease of grape vines caused by a fungus (''Guignardia bidwellii''), affecting the aboveground part of the vine, and favored by warm, humid weather; also called grape rot * A disease of cabbage and related plants caused by a bacterium (''Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris''). Occurring around the world, it affects primarily the aboveground parts of plants. Vegetables in the crucifer family are susceptible, including broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, kale, mustard, radish, rutabaga, and turnip. Many weeds may host this pathogen including Shepherd's Purse, wild mustard, and yellow rocket. * A disease of the potato caused by a bacterium (''Erwinia atrose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
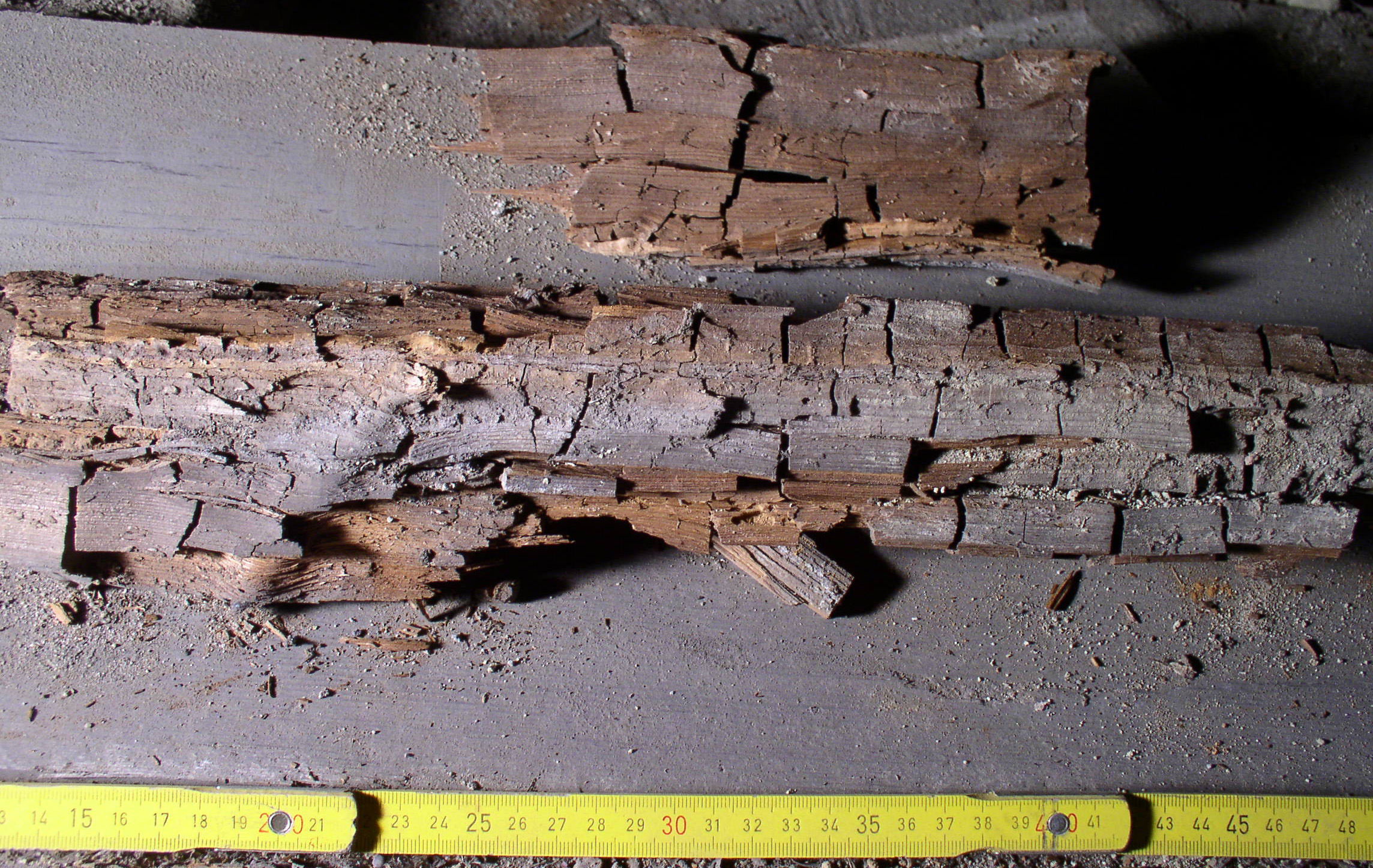
Wood-decay Fungus
A wood-decay or xylophagous fungus is any species of fungus that digests moist wood, causing it to rot. Some species of wood-decay fungi attack dead wood, such as brown rot, and some, such as ''Armillaria'' (honey fungus), are parasitic and colonize living trees. Excessive moisture above the fibre saturation point in wood is required for fungal colonization and proliferation. In nature, this process causes the breakdown of complex molecules and leads to the return of nutrients to the soil. Wood-decay fungi consume wood in various ways; for example, some attack the carbohydrates in wood and some others decay lignin. The rate of decay of wooden materials in various climates can be estimated by empirical models.Viitanen, T. et al. (2010). Towards modelling of decay risk of wooden materials. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 68:303-313. Wood-decay fungi can be classified according to the type of decay that they cause. The best-known types are brown rot, soft rot, and whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectria
''Nectria'' is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. They are most often encountered as saprophytes on decaying wood but some species can also occur as parasites of trees, especially fruit trees (for example apple) and a number of other hardwood trees. Some species are significant pests causing diseases such as apple canker, Nectria twig blight, and coral spot in orchards. It is ubiquitous in cool temperate Europe and North America and appears to be an introduced species in New Zealand and Australia. The occurrence in New Zealand was first identified in 1996 in Otago and Southland although it is believed to have been present since the 1980s. In North America, ''Nectria'' infections have had economically important impacts on forestry and forest products including aspen, red oak, maple, beech, poplar, and birch. Species of ''Nectria'' also occur in warmer climates including island groups such as Hawaii. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the genus contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosporangium Globosum
''Gymnosporangium globosum'' is a fungal plant pathogen that causes cedar-hawthorn rust. Hosts and symptoms ''Gymnosporangium globosum'' is a heteroecious rust fungus that requires two hosts to complete its life cycle. Its telial stage occurs on eastern red cedar, Rocky Mountain juniper, southern red cedar, and other common junipers while its aecial stage will be found on apple, crabapple, hawthorne, and occasionally on pear, quince, and serviceberry. The symptoms on the evergreens (telial stage) start with small galls that form on its twigs and small branches. After the galls grow to be ⅛ to ½ inch in diameter, circular indents (similar to those of a golf ball) will begin to appear on the twig side of the gall. Once spring arrives, a reddish-brown structure will begin to grow out of the indent eventually producing orange, jelly-like telial horns. These telial horns can reach up to 4 inches long and can be easily seen. The symptoms of the deciduous trees (aecial stage) begin wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosporangium Clavipes
''Gymnosporangium clavipes'' is a plant pathogen, a fungus that causes cedar-quince rust. Similar to ''Gymnosporangium juniperi-virginianae'' and ''Gymnosporangium globosum'', the fungus infects a wide range of Rosaceae, such as apple, hawthorn and quince trees, and also requires an evergreen host such as eastern red cedar ''Juniperus virginiana'', also known as red cedar, eastern red cedar, Virginian juniper, eastern juniper, red juniper, and other local names, is a species of juniper native to eastern North America from southeastern Canada to the Gulf of Mexico a ... or a number of other juniper species to complete its life cycle.James SchusterCedar-Quince Rust Accessed July 16, 2008. References External links Pucciniales Apple tree diseases Fruit tree diseases Fungal tree pathogens and diseases Galls Fungi described in 1873 {{fungus-tree-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosporangium Juniperi-virginianae
''Gymnosporangium juniperi-virginianae'' is a plant pathogen that causes cedar-apple rust. In virtually any location where apples or crabapples (''Malus'') and Eastern red cedar (''Juniperus virginiana'') coexist, cedar apple rust can be a destructive or disfiguring disease on both the apples and cedars. Apples, crabapples, and eastern red cedar are the most common hosts for this disease. Similar diseases can be found on Quince and hawthorn and many species of juniper can substitute for the eastern red cedars. Symptoms On the apple tree, the infections occur on leaves, fruit and young twigs. The brightly colored spots produced on the leaves make it easy to identify. Small, yellow-orange spots appear on the upper surfaces of the leaves, through April and June. These spots gradually enlarge and turn orange or red and may show concentric rings of color. Drops of orange liquid may be visible on the spots. Later in the season, black dots appear on the orange spots on the upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant. Powdery mildew grows well in environments with high humidity and moderate temperatures. Greenhouses provide an ideal moist, temperate environment for the spread of the disease. This causes harm to agricultural and horticultural practices where powdery mildew may thrive in a greenhouse setting. In an agricultural or horticultural setting, the pathogen can be controlle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |