|
McIntosh Cliffs
The McIntosh Cliffs are a line of steep, uneven, volcanic bluffs or cliffs, long, forming the southwest side of the Minna Bluff peninsula, at the northeast end of Hillary Coast, Ross Dependency, Antarctica. The height of the cliffs increases from west to east, ranging from above the Ross Ice Shelf. They were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1999 after William C. McIntosh of the Department of Geoscience, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology (NMIMT), Socorro, a member of the 1982 NMIMT field party that carried out the first geological mapping of Minna Bluff. McIntosh did additional field work at Mount Erebus, 1977–78, 1984–85; Mount Discovery and Mason Spur, 1983–84; Mount Murphy, 1985; the Executive Committee Range, 1989–90; and the Crary Mountains Crary Mountains () are a group of ice-covered volcanoes in Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. They consist of two or three shield volcanoes, named Mount Rees, Mount Steere and Mount Frakes, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minna Bluff
Minna Bluff is a rocky promontory at the eastern end of a volcanic Antarctic peninsula projecting deep into the Ross Ice Shelf at . It forms a long, narrow arm which culminates in a south-pointing hook feature (Minna Hook), and is the subject of research into Antarctic cryosphere history, funded by the National Science Foundation, Office of Polar Programs. The bluff is mentioned repeatedly in the history of Antarctic exploration. It was first sighted in June 1902, during Captain Robert Falcon Scott's ''Discovery'' Expedition, 1901–04. It was thereafter recognised as a key landmark and location for vital supply depots for southern journeys towards the South Pole. Originally identified simply as "the Bluff", it was later named by Scott after the wife of Royal Geographical Society former president Sir Clements Markham. Every expedition that followed Scott on this route after his pioneering journey (including Ernest Shackleton in 1908, Scott himself in 1911 and Shackleton's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillary Coast
The Hillary Coast is a portion of the coast of Antarctica along the western margin of the Ross Ice Shelf between Minna Bluff and Cape Selborne. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Sir Edmund Hillary, the leader of the New Zealand Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1956–58. Various New Zealand parties carried out detailed surveys of portions of this coast and pioneered routes up Skelton Glacier Skelton Glacier is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Discovery and naming Named after the Skelton Inlet by the New Zealand party ... and Darwin Glacier to the polar plateau. References Coasts of the Ross Dependency Edmund Hillary {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted only by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea, and includes part of Victoria Land, and most of the Ross Ice Shelf. Ross, Balleny, Scott and Roosevelt Islands also form part of the Dependency. History of claim Following his discovery of Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
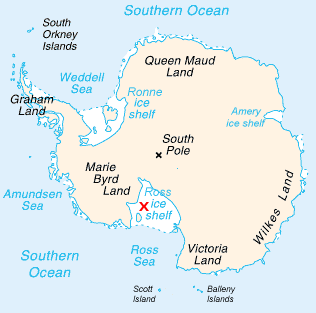
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William C
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico Institute Of Mining And Technology
The New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology (New Mexico Tech and formerly New Mexico School of Mines) is a public university in Socorro, New Mexico. It offers over 30 bachelor of science degrees in technology, the sciences, engineering, management, and technical communication, as well as graduate degrees at the masters and doctoral levels.Carey, John A. (February 2003) "New Mexico Tech One of State's Best Assets" ''New Mexico Business Journal'' 27:2 pp48-49 History With 1,244 undergraduate students as of 2021, New Mexico Tech is a relatively small university focused on science and engineering. The institution was founded by the New Mexico Territorial Legislature in the year 1889 as the New Mexico School of Mines to both boost the territorial economy and teach mining specialties on the college level. During the 1930s, petroleum engineering and technology also became an important field of study at the institute. In 1946, New Mexico Tech began offering graduate degrees. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socorro, New Mexico
Socorro (, '' sə-KOR-oh'') is a city in Socorro County in the U.S. state of New Mexico. It is in the Rio Grande Valley at an elevation of . In 2010 the population was 9,051. It is the county seat of Socorro County. Socorro is located south of Albuquerque and north of Las Cruces. History Founding In June 1598, Juan de Oñate led a group of Spanish settlers through the Jornada del Muerto, an inhospitable patch of desert that ends just south of the present-day city of Socorro. As the Spaniards emerged from the desert, Piro Indians of the pueblo of Teypana gave them food and water. Therefore, the Spaniards renamed this pueblo Socorro, which means "help" or "aid". Later, the name "Socorro" would be applied to the nearby Piro pueblo of Pilabó. Nuestra Señora de Perpetuo Socorro, the first Catholic mission in the area, was probably established c. 1626. Fray Agustín de Vetancurt would later write that around 600 people lived in the area during this period. Mines in the Socorr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Erebus
Mount Erebus () is the second-highest volcano in Antarctica (after Mount Sidley), the highest active volcano in Antarctica, and the southernmost active volcano on Earth. It is the sixth-highest ultra mountain on the continent. With a summit elevation of , it is located in the Ross Dependency on Ross Island, which is also home to three inactive volcanoes: Mount Terror, Mount Bird, and Mount Terra Nova. The volcano has been active since about 1.3 million years ago and has a long-lived lava lake in its inner summit crater that has been present since at least the early 1970s. The volcano was the site of the Air New Zealand Flight 901 accident, which occurred in November 1979. Geology and volcanology Mount Erebus is the world's southernmost active volcano. It is the current eruptive centre of the Erebus hotspot. The summit contains a persistent convecting phonolitic lava lake, one of five long-lasting lava lakes on Earth. Characteristic eruptive activity consists of Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Discovery
Mount Discovery is a conspicuous, isolated stratovolcano, lying at the head of McMurdo Sound and east of Koettlitz Glacier, overlooking the NW portion of the Ross Ice Shelf. It forms the center of a three-armed mass of which Brown Peninsula is one extension to the north; Minna Bluff is a second to the east; the third is Mount Morning to the west. Mount Discovery was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) and named for their expedition ship ''Discovery''. __NOTOC__ See also * Eady Ice Piedmont *List of volcanoes in Antarctica *List of Ultras of Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... References Sources * * * External links "Mount Discovery, Antarctica" on Peakbagger Stratovolcanoes of New Zealand Mountains of Victoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason Spur
Mason Spur () is an elevated spur, partially ice-covered and over high, which projects eastward from Mount Morning in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1963 for Robert Mason, a United States Antarctic Research Program representative at McMurdo Station McMurdo Station is a United States Antarctic research station on the south tip of Ross Island, which is in the New Zealand-claimed Ross Dependency on the shore of McMurdo Sound in Antarctica. It is operated by the United States through the Unit ... in 1962–63. Snow Petrel Peak marks the easternmost summit of Mason Spur. References Ridges of the Ross Dependency Hillary Coast {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Murphy
Mount Murphy is a massive, snow-covered and highly eroded shield volcano in Marie Byrd Land of West Antarctica with steep, rocky slopes. It is directly south of Bear Peninsula and is bounded by the Smith, Pope and Haynes Glaciers. Volcanic activity began in the Miocene with the eruption of basaltic and trachytic lava. Volcanism on the slopes of the volcano resumed much later during the Pleistocene, with a parasitic cone having been K–Ar dated to 0.9 million years old. Delineated from aerial photographs taken by US Navy Operation Highjump in January 1947. Named by US-ACAN for Robert Cushman Murphy of the American Museum of Natural History, noted authority on Antarctic and sub-Antarctic bird life. While serving on the whaler, he charted the Bay of Isles region of South Georgia. Features Bucher Peak () at , is one of the highest peaks in the west-central summit area of the Mount Murphy massif. Buettner Peak is a sharp peak rising midway along the north wall of Roos Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |