|
Mazatlán Literature Prize
Mazatlán () is a city in the Mexican state of Sinaloa. The city serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding '' municipio'', known as the Mazatlán Municipality. It is located at on the Pacific coast, across from the southernmost tip of the Baja California Peninsula. ''Mazatlán'' is a Nahuatl word meaning "place of deer". The city was founded in 1531 by an army of Spaniards and indigenous people. By the mid-19th century, a large group of immigrants arrived from Germany. Over time, Mazatlán developed into a commercial seaport, importing equipment for the nearby gold and silver mines. It served as the capital of Sinaloa from 1859 to 1873. The German settlers also influenced the local music, banda, with some genres being an alteration of Bavarian folk music. The settlers also established the Pacifico Brewery on March 14, 1900. Mazatlán has a rich culture and art community. In addition to the Angela Peralta Theater, Mazatlán has many galleries and artist's studios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
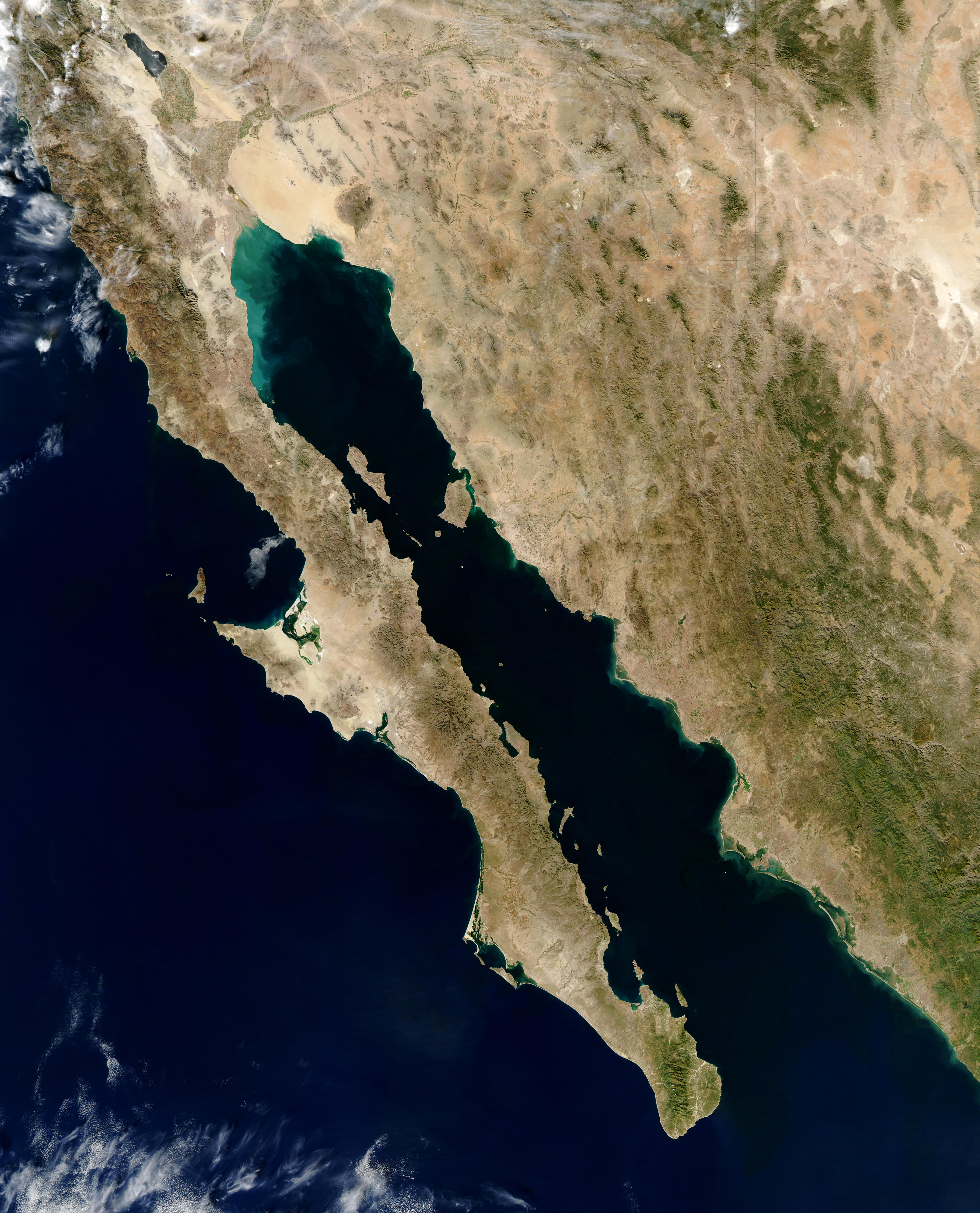
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizpe Municipality
Arizpe (municipality) is a municipality in Sonora in north-western Mexico. The Municipality of Arizpe is one of the 72 municipalities of the Mexican state of Sonora, located in the north-central region of the state in the Sierra Madre Occidental area. It has 72 localities within the municipality, its municipal seat and the most populated locality is the homonymous town of Arizpe, while other important ones are: Sinoquipe, Bacanuchi and Chinapa. It was named for the first time as a municipality in 1813 and according to the 14th Population and Housing Census carried out in 2020 by the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) the municipality has a total population of 2,788 inhabitants. This municipality has an area of 1,186.56 square miles (3,073.17 km²). Its Gross Domestic Product per capita is USD 11,012, and its Human Development Index (HDI) is 0.8292. Like most of the municipalities of Sonora, the name was given by that of its municipal seat. The region of the mun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayo River (Mexico)
The Mayo River is located in the Mexican state of Sonora. The Adolfo Ruiz Cortines Dam generates electricity and irrigates agriculture in the Mayo Valley. It is 30 km east of the city of Navojoa, in the municipality of Álamos. Adolfo Ruiz Cortines was a president of Mexico. See also *List of longest rivers of Mexico Among the longest rivers of Mexico are 26 streams of at least . In the case of rivers such as the Colorado River, Colorado, the length listed in the table below is solely that of the main stem. In the case of the Grijalva River, Grijalva and Usum ... References Rivers of the Gulf of California Rivers of Sonora Rivers of the Sierra Madre Occidental {{Mexico-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copala, Sinaloa
Copala, formerly known as San José de Copala, is a four-century-old silver-mining town in the Mexican state of Sinaloa. The town is in the municipality of Concordia. History The area was occupied and ruled by the indigenous peoples until 1564, when Francisco de Ibarra crossed the Sierra Madre Occidental from Durango and conquered the area for Spain. In 1565 prospectors discovered silver veins and the town of Copala was founded to serve the mines. The town was named after a mythical city of gold for which de Ibarra had unsuccessfully searched in northern Mexico. The town of Copala was destroyed in 1616 by an uprising of Tepehuan Indians, but was rebuilt after the rebellion was quelled the following year.Luis Navarro Garcia (1967) ''Sonora y Sinaloa en el Siglo XVII'', Seville: Escuela de Estudios Hispano-Americanos, p.14-17. Economy The economy of Copala is based on tourism, mining, and agriculture. Geography Copala is located at , at an altitude of 610 m. The town is alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuño De Guzmán
Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán (c. 14901558) was a Spanish conquistador and colonial administrator in New Spain. He was the governor of the province of Pánuco from 1525 to 1533 and of Nueva Galicia from 1529 to 1534, and president of the first Royal Audiencia of Mexico – the high court that governed New Spain – from 1528 to 1530. He founded several cities in Northwestern Mexico, including Guadalajara. Originally a bodyguard of Charles I of Spain, he was sent to Mexico to counterbalance the influence of the leader of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, Hernán Cortés, since the King worried he was becoming too powerful. As Governor of Pánuco, Guzmán cracked down hard on the supporters of Cortés, stripping him and his supporters of property and rights. He conducted numerous expeditions of conquest into the northwestern areas of Mexico, enslaving thousands of Indians and shipping them to the Caribbean colonies. In the resulting power struggles where he also made himself a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
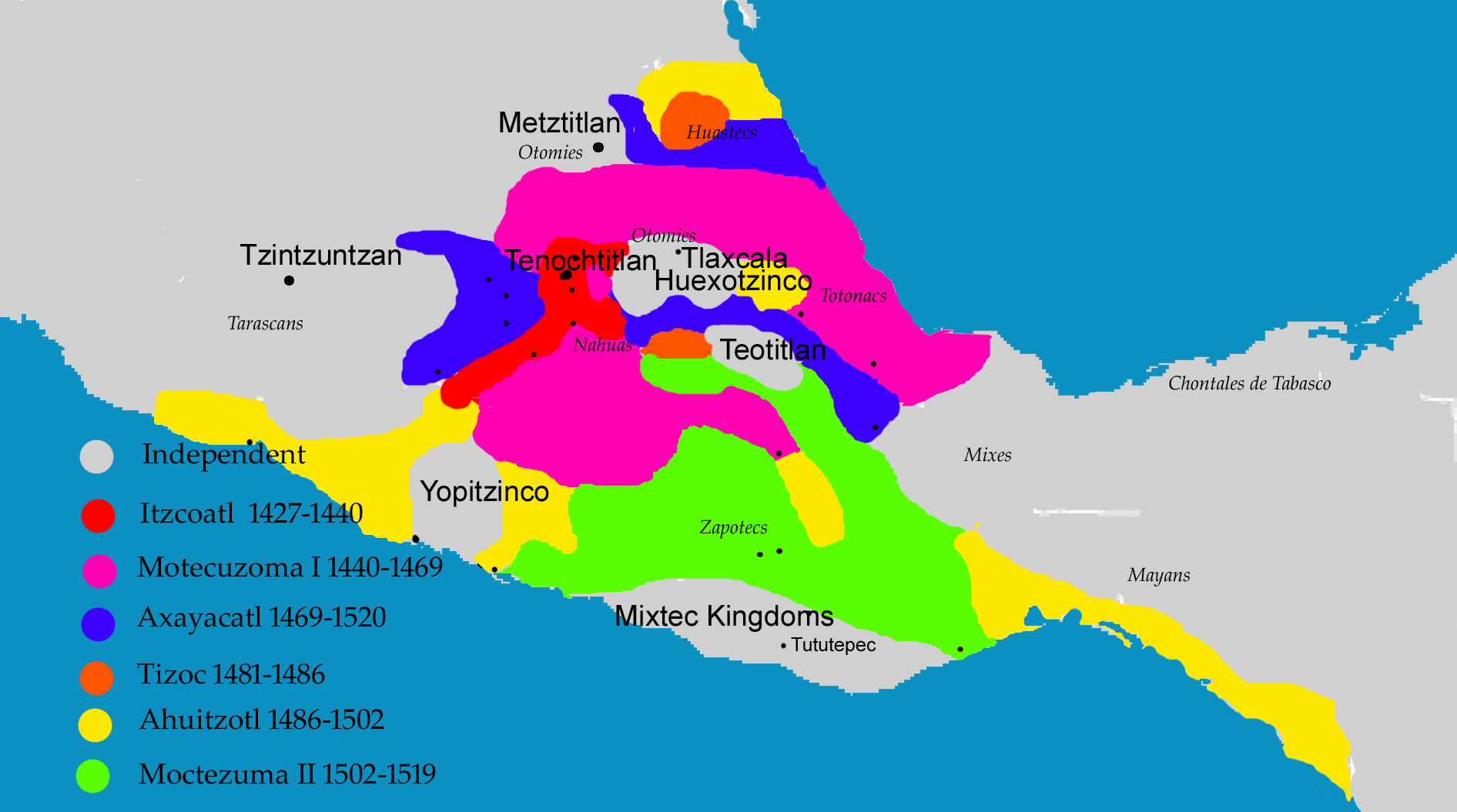
Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) was an alliance of three Nahua peoples, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under defeated them in 1521. The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles. The alliance waged wars of conquest and expanded after its formation. The alliance controlled most of central Mexico at its height, as well as some more di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tizoc
Tizocic or Tizocicatzin usually known in English as Tizoc, was the seventh ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan. His name means, "He who makes sacrifices" or "He who does penance." Either Tizoc or his successor Ahuitzotl was the first ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan to assume the title ''Huey Tlatoani'' ("supreme ''tlatoani''") to make their superiority over the other cities in the Triple Alliance (Aztec Empire) clear. Biography Family Tizoc was a son of the princess Atotoztli II and her cousin, prince Tezozomoc. He was a grandson of Emperors Moctezuma I and Itzcoatl. He was a descendant of the King Cuauhtototzin. He was successor of his brother Axayacatl and was succeeded by his other brother, Ahuitzotl; his sister was the Queen Chalchiuhnenetzin, married to Moquihuix, tlatoani of Tlatelōlco. He was an uncle of Emperors Cuauhtémoc, Moctezuma II and Cuitláhuac and grandfather of Diego de San Francisco Tehuetzquititzin. Reign Most sources agree that Tizoc took power in 1481 (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Mendoza
The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec codex, believed to have been created around the year 1541. It contains a history of both the Aztec rulers and their conquests as well as a description of the daily life of pre-conquest Aztec society. The codex is written in the Nahuatl language using traditional Aztec pictograms with a translation and explanation of the text provided in Spanish. It is named after Don Antonio de Mendoza (1495-1552), the viceroy of New Spain, who supervised its creation and who was a leading patron of native artists. Mendoza knew that the ravages of the conquest had destroyed multiple native artifacts, and that the craft traditions that generated them had been effaced. When the Spanish crown ordered Mendoza to provide evidence of the Aztec political and tribute system, he invited skilled artists and scribes who were being schooled at the Franciscan college in Tlatelolco to gather in a workshop under the supervision of Spanish priests where they could recreate the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiximes
The Xixime were an indigenous people who inhabited a portion of the Sierra Madre Occidental mountains in the present day states of Durango and Sinaloa, Mexico. The Xixime are noted for their reported practice of cannibalism and resistance to Spanish colonization in the form of the Xixime Rebellion of 1610. Language The Xixime spoke Xixime, a poorly documented, now-extinct Uto-Aztecan language. Dialects of Xixime included Hine and Hume (to the north and south of the Xixime territory, respectively). The exact classification of the language is unknown although it may belong to the Taracahitic branch. Cannibalism A considerable amount of the scholarship and media attention devoted to the Xixime has focused on the group's reported practice of cannibalism. While a variety of colonial Spanish accounts of the Xixime report the culture engaged in frequent, ritual consumption of enemy peoples, the historical accuracy of the allegations is disputed. A number of historians including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of Mexico
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now Mexico before the arrival of the Spanish. The number of indigenous Mexicans is defined through the second article of the Mexican Constitution. The Mexican census does not classify individuals by race, using the cultural- ethnicity of indigenous communities that preserve their indigenous languages, traditions, beliefs, and cultures. According to the National Indigenous Institute (INI) and the National Institute of Indigenous Peoples (CDI), in 2012 the indigenous population was approximately 15 million people, divided into 68 ethnic groups. The 2020 Censo General de Población y Vivienda reported 11.8 million people living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estado De Occidente
Estado de Occidente ( en, Western State; also known as Sonora y Sinaloa) was a Mexican state established in 1824. The constitution was drafted in that year and the government was initially established with its capital at El Fuerte, Sinaloa. The first governor was Juan Miguel Riesgo. The state consisted of modern Sonora and Sinaloa, and also modern Arizona more or less south of the Gila River (although in much of this area the Yaqui, Pima, Apaches, and other native inhabitants in certain time did not recognize the rule of the state). The constitution was established in 1825 with one of its principles being the making of all inhabitants of the state citizens. This was resented by the Yaqui since they now had to pay taxes, which they had been exempt from before. The Yaqui also considered themselves possessed of sovereignty and territorial rights which were threatened by the state's new constitution. This led to a new outbreak of war between the Mexicans and the Yaquis (see Yaqui War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_MAZATLAN%2C_MEXICO.jpg)

.jpg)