|
Maya Maize God
Like other Mesoamerican peoples, the traditional Maya civilization, Maya recognize in their staple crop, maize, a vital force with which they strongly identify. This is clearly shown by their mythological traditions. According to the 16th-century Popol Vuh, the Hero Twins have maize plants for alter egos and man himself is created from maize. The discovery and opening of the Maize Mountain – the place where the corn seeds are hidden – is still one of the most popular of Maya tales. In the Classic period (200-900 AD), the maize deity shows aspects of a culture hero. Female and male deities In Maya oral tradition, maize is usually personified as a woman — like rice in Southeast Asia, or wheat in ancient Greece and Rome. The acquisition of this woman through bridal capture constitutes one of the basic Maya myths. In contrast to this, the pre-Spanish Maya aristocracy appears to have primarily conceived of maize as male. The classic period distinguished two male forms: a foliated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Taube
Karl Andreas Taube (born September 14, 1957) is an American Mesoamericanist, Mayanist, iconographer and ethnohistory, ethnohistorian, known for his publications and research into the pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica and the American Southwest. He is Distinguished Professor of Anthropology at the College of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences, University of California, Riverside.Board of Regents, UC (2006) In 2008 he was named the College of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences distinguished lecturer. Family background Karl Taube's father, Canadian-born Henry Taube (d. 2005), whose parents were ethnic Germans, was the recipient of the 1983 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Education Taube commenced his undergraduate education at Stanford University, Stanford, relocating to University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley where he completed a Bachelor of Arts, B.A. in Anthropology in 1980. He enrolled in graduate studies in Anthropology at Yale University, Yale, where he comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicomecōātl
In Aztec mythology, Chicōmecōātl "Seven Serpent", was the Aztec goddess of agriculture during the Middle Culture period. She is sometimes called "goddess of nourishment", a goddess of plenty and the female aspect of maize. More generally, Chicōmecōātl can be described as a deity of food, drink, and human livelihood. She is regarded as the female counterpart of the maize god ''Centeōtl'', their symbol being an ear of corn. She is occasionally called ''Xīlōnen'', (meaning doll made of corn), who was married also to ''Tezcatlipoca''. Significance of Name Chicomecōātl's name, "Seven Serpent", is thought to be a reference to the duality of the deity. While she symbolizes the gathering of maize and agricultural prosperity, she also is thought to be harmful to the Aztecs, as she was thought to be of blame during years of poor harvest. Appearance & Depiction Her appearance is mostly represented with red ochre on the face, paper headdress on top, water-flowers patterned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centeōtl
In Aztec mythology, Centeōtl (also known as Centeocihuatl or Cinteotl) is the maize deity. ''Cintli'' means "dried maize still on the cob" and ''teōtl'' means "deity".''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1997). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved September 1, 2012, frolink According to the Florentine Codex,Miller, ''The Gods and Symbols of Ancient Mexico and the Maya'' (London: Thames and Hudson, 1993) p62 Centeotl is the son of the earth goddess, Tlazolteotl and solar deity Piltzintecuhtli, the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury. He was born on the day-sign 1 Xochitl. Another myth claims him as the son of the goddess Xochiquetzal. The majority of evidence gathered on Centeotl suggests that he is usually portrayed as a young man (although a debate is still ongoing), with yellow body colouration. Some specialists believe that Centeotl used to be the maize goddess Chicomecoatl, Chicomecōātl. Centeotl was considered one of the most important deities of the Aztec era. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Moon Goddess
The traditional Mayas generally assume the Moon to be female, and the Moon's perceived phases are accordingly conceived as the stages of a woman's life. The Maya moon goddess wields great influence in many areas. Being in the image of a woman, she is associated with sexuality and procreation, fertility and growth, not only of human beings, but also of the vegetation and the crops. Since growth can also cause all sorts of ailments, the moon goddess is also a goddess of disease. Everywhere in Mesoamerica, including the Mayan area, she is specifically associated with water, be it wells, rainfall, or the rainy season. In the codices, she has a terrestrial counterpart in goddess I. Lunar mythology The sources for Maya lunar mythology are almost entirely contemporaneous, with the exception of the Popol Vuh. A division can be made according to the moon's kinship roles. *''Moon as a male sibling: celestial power''. In the Popol Vuh (16th century), the Maya Hero Twins are finally transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popoluca
Popoluca is a Nahuatl term for various Indigenous peoples of southeastern Veracruz and Oaxaca. Many of them (about 30,000"The Popoluca." ''University of Minnesota, Mankota E-museum.'' (retrieved 1 Feb 2011)) speak languages of the Mixe–Zoque family. Others speak the unrelated , in which case the name in English and Spanish is generally spelled Popoloca. Various peoples called Popoluca The Mixe–Zoque languages called Popoluca are, * Mixean ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoque People
The Zoque are an Indigenous people of Mexico, who are related to the Mixe. They speak various languages, also called Zoque, which has several branches and dialects. The Zoque consists of 41,609 people, according to the 2000 census. They live mainly in the northerly sector of Chiapas state, principally in the '' municipios'' and towns of Amatán, Copainalá, Chapultenango, Francisco León, Ixhuatán, Ixtacomitán, Jitotol, Ocotepec, Ostuacán, Pantepec, Rayón, Totolapa, Tapilula, Tecpatán, Acala, Blanca rosa, and Ocozocoautla. They also live in the northern part of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, in the state of Oaxaca, including the Selva Zoque. In the pre-Hispanic era, the Zoque lived throughout Chiapas, and Isthmus of Tehuantepec and parts of the state of Tabasco. They may have been descendants of the Olmec. They had a good social and commercial relationship with the later Mexica, which contributed to the economic prosperity of their culture in Chiapas. In 1494 during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuas
The Nahuas ( ) are a Uto-Nahuan ethnicity and one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest Indigenous group in Mexico, as well as the largest population out of any North American Indigenous people group who are native speakers of their respective Indigenous language. Amongst the Nahua, this is Nahuatl. When ranked amongst all Indigenous languages across the Americas, Nahuas list third after speakers of Guaraní and Quechua. The Mexica (Aztecs) are of Nahua ethnicity, as are their historical enemies and allies of the Spaniards: the Tlaxcallans (Tlaxcaltecs). The Toltecs which predated both groups are often thought to have been Nahua as well. However, in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity. Their Nahuan languages, or Nahuatl, consist of many variants, several of which are mutually uninte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totonacs
The Totonac are an Indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a city which they claim to have built). Until the mid-19th century they were the world's main producers of vanilla. The Totonac people cultivated vanilla in Papantla, but faced with competition when the French island of Réunion entered the market. This group of people also encountered conflicts over land ownership during the course of the 19th and early 20th centuries, as the privatization of communal land in Papantla became more of a concern to local elites. Etymology The term "totonac" refers to the people living in Totonacapan. There is no agreement as to the origin of the term. Some authors have translated the term "totonac" as a Nahuatl word meaning "People of Hot Land". The translation for this word in the Totonac Language, according to so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huastec People
The Huastec or Téenek (contraction of ''Te' Inik'', "people from here"; also known as Huaxtec, Wastek or Huastecos) are an Indigenous people of Mexico, living in the La Huasteca region including the Mexican state, states of Hidalgo (Mexico), Hidalgo, Veracruz, San Luis Potosí and Tamaulipas concentrated along the route of the Pánuco River and along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. There are approximately 66,000 Huastec speakers today, of which two-thirds are in San Luis Potosí and one-third in Veracruz, although their population was probably much higher, as much as half a million, when the Spanish arrived in 1529. The ancient Huastec civilization is one of the pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures. Judging from archaeological remains, they are thought to date back to approximately the 10th century BCE, although their most productive period of civilization is usually considered to be the Mesoamerican chronology, Postclassic era between the fall of Teotihuacan and the rise of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
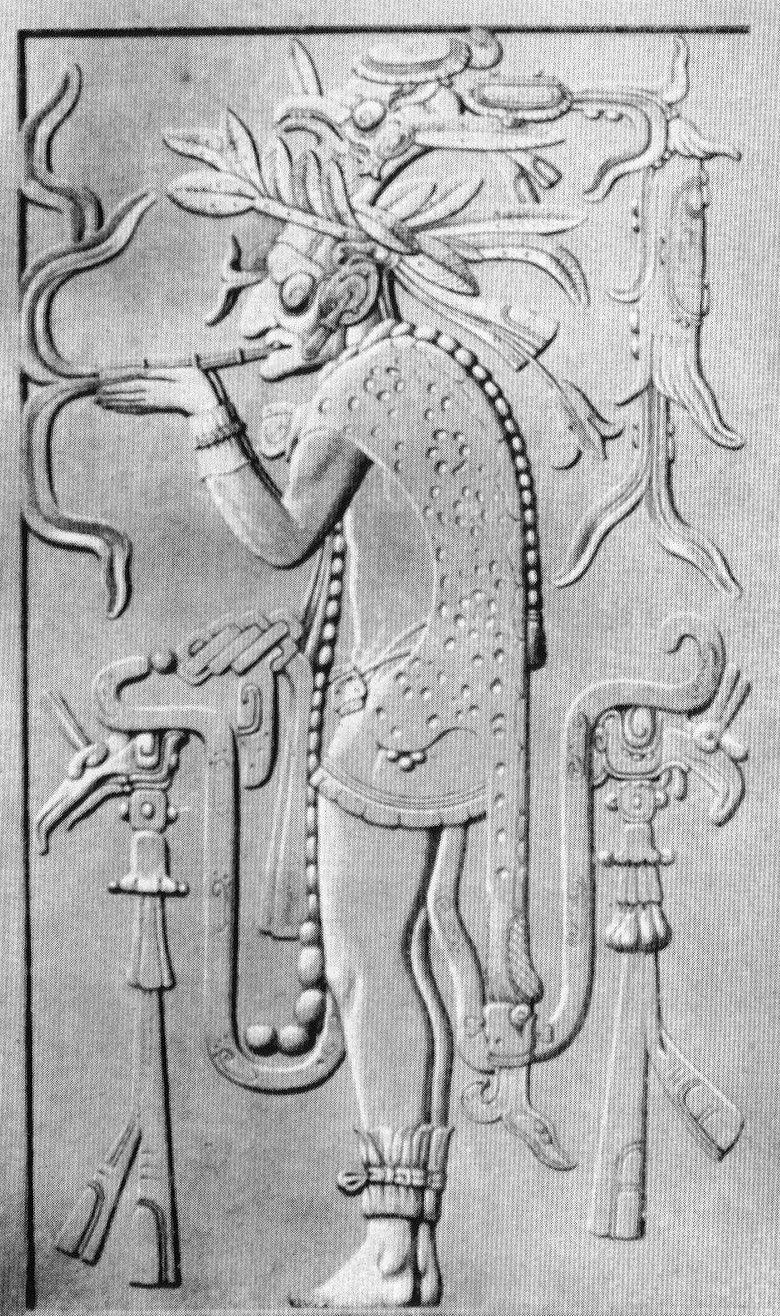
God L
God L of the Schellhas-Zimmermann-Taube classification of codical gods is one of the major pre-Spanish Maya deities, specifically associated with trade. Characterized by high age, he is one of the Mam ('Grandfather') deities. More specifically, he evinces jaguar traits (particularly the ear), a broad feathery hat topped by an owl, and a jaguar mantle or a cape with a pattern somewhat resembling that of an armadillo shell. The best-known monumental representation is on a doorjamb of the inner sanctuary of Palenque's Temple of the Cross. Name The main sign of god L's name glyph in the Dresden Codex consists of the head of an aged man painted black. The reading is unknown, but may conceivably have been Ekʼ Chuah (see below). Functions Attributes and scenes of god L are indicative of at least three main functions. Wealth Recurrent attributes are a bundle of merchandise and a walking-stick. The floating ends of god L's cloth can show footsteps, again pointing to travelling merchants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Martin (Mayanist)
Simon Martin is a British epigrapher, historian, writer and Mayanist scholar. He is best known for his contributions to the study and decipherment of the Maya script, the writing system used by the pre-Columbian Maya civilisation of Mesoamerica. As one of the leading epigraphers active in contemporary Mayanist research, Martin has specialised in the study of the political interactions and dynastic histories of Classic-era Maya polities. Since 2003 Martin has held positions at the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology where he is currently an Associate Curator and Keeper in the American Section, while teaching select courses as an Adjunct Associate Professor in the Department of Anthropology at the University of Pennsylvania. Early life and career Simon Martin entered the field of Mayanist research with a professional background in graphic design. He attended the Royal College of Art in London during the 1980s, completing his Master's in Communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |