|
Maxwell–Jüttner Distribution
In physics, the Maxwell–Jüttner distribution is the distribution of speeds of particles in a hypothetical gas of relativistic particles. Similar to Maxwell's distribution, the Maxwell–Jüttner distribution considers a classical ideal gas where the particles are dilute and do not significantly interact with each other. The distinction from Maxwell's case is that effects of special relativity are taken into account. In the limit of low temperatures T much less than mc^2/k (where m is the mass of the kind of particle making up the gas, c is the speed of light and k is Boltzmann's constant), this distribution becomes identical to the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution. The distribution can be attributed to Ferencz Jüttner, who derived it in 1911. It has become known as the Maxwell–Jüttner distribution by analogy to the name Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution that is commonly used to refer to Maxwell's distribution. Definition As the gas becomes hotter and kT approaches or excee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
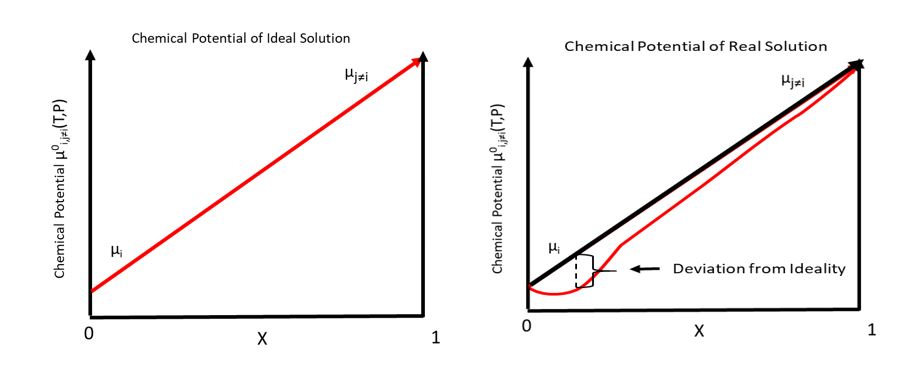
Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum. In a system in diffusion equilibrium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gases
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma). A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms (e.g. carbon dioxide). A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. What distinguishes a gas from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation usually makes a colourless gas invisible to the human observer. The gaseous state of matter occurs between the liquid and plasma states, the latter of which provides the upper temperature boundary for gases. Bounding the lower end of the temperature scale lie degenerative quantum gases which are gaining increasing attention. High-density atomic gases super-cooled to very low temperatures are classified by their statistical behavior as either Bose gases or Fermi gases. For a compreh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Statistics
In quantum statistics, Bose–Einstein statistics (B–E statistics) describes one of two possible ways in which a collection of non-interacting, indistinguishable particles may occupy a set of available discrete energy states at thermodynamic equilibrium. The aggregation of particles in the same state, which is a characteristic of particles obeying Bose–Einstein statistics, accounts for the cohesive streaming of laser light and the frictionless creeping of superfluid helium. The theory of this behaviour was developed (1924–25) by Satyendra Nath Bose, who recognized that a collection of identical and indistinguishable particles can be distributed in this way. The idea was later adopted and extended by Albert Einstein in collaboration with Bose. The Bose–Einstein statistics applies only to the particles not limited to single occupancy of the same state – that is, particles that do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle restrictions. Such particles have integer values of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0,1,2 ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have odd half-integer spin (,, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Bosons are named after physicist Satyendra Nath Bose. Some bosons are elementary particles and occupy a special role in particle physics unlike that of fermions, which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter". Some elementary bosons (for example, gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) gives rise to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, superfluidity arises because composite bosons (bose particles), such as low temperature helium-4 atoms, follow Bose� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle which is the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or atomic lattice. Since in a normal atom or crystal lattice the negative charge of the electrons is balanced by the positive charge of the atomic nuclei, the absence of an electron leaves a net positive charge at the hole's location. Holes in a metal or semiconductor crystal lattice can move through the lattice as electrons can, and act similarly to positively-charged particles. They play an important role in the operation of semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits. If an electron is excited into a higher state it leaves a hole in its old state. This meaning is used in Auger electron spectroscopy (and other x-ray techniques), in computational chemistry, and to explain the low electron-electron scattering-rate in crystals (metals, semiconductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac Statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac distribution of particles over energy states. It is named after Enrico Fermi and Paul Dirac, each of whom derived the distribution independently in 1926 (although Fermi derived it before Dirac). Fermi–Dirac statistics is a part of the field of statistical mechanics and uses the principles of quantum mechanics. F–D statistics applies to identical and indistinguishable particles with half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, etc.), called fermions, in thermodynamic equilibrium. For the case of negligible interaction between particles, the system can be described in terms of single-particle energy states. A result is the F–D distribution of particles over these states where no two particles can occupy the same state, which has a considerable effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Generally, it has a half-odd-integer spin: spin , spin , etc. In addition, these particles obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Fermions include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referred to as the spin-statistics relation is, in fact, a spin statistics-quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifest Covariance
In general relativity, a manifestly covariant equation is one in which all expressions are tensors. The operations of addition, tensor multiplication, tensor contraction, raising and lowering indices, and covariant differentiation may appear in the equation. Forbidden terms include but are not restricted to partial derivatives. Tensor densities, especially integrands and variables of integration, may be allowed in manifestly covariant equations if they are clearly weighted by the appropriate power of the determinant of the metric. Writing an equation in manifestly covariant form is useful because it guarantees general covariance upon quick inspection. If an equation is manifestly covariant, and if it reduces to a correct, corresponding equation in special relativity when evaluated instantaneously in a local inertial frame, then it is usually the correct generalization of the special relativistic equation in general relativity. Example An equation may be Lorentz cova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Distribution
Maxwell's, last known as Maxwell's Tavern, was a bar/restaurant and music club in Hoboken, New Jersey. Over several decades the venue attracted a wide variety of acts looking for a change from the New York City concert spaces across the river. Maxwell's initially closed its doors on July 31, 2013, and reopened as Maxwell's Tavern in 2014, under new ownership. It closed again in February 2018. History The club was opened in August 1978 by Steve Fallon. When the Fallon family bought the corner building in uptown Hoboken with its street-level tavern, Steve Fallon's sisters Kathryn Jackson Fallon and Anne Fallon Mazzolla along with brother-in-law Mario Mazzola were interested in turning the factory workers' tavern (General Foods' Maxwell House Coffee factory was a block away on the Hudson River) into more of a restaurant. The Hoboken band "a" (featuring Glenn Morrow, Richard Barone, Frank Giannini and Rob Norris; the latter three later forming the Bongos) asked if they could rehearse i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessel Function
Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and then generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions of Bessel's differential equation x^2 \frac + x \frac + \left(x^2 - \alpha^2 \right)y = 0 for an arbitrary complex number \alpha, the ''order'' of the Bessel function. Although \alpha and -\alpha produce the same differential equation, it is conventional to define different Bessel functions for these two values in such a way that the Bessel functions are mostly smooth functions of \alpha. The most important cases are when \alpha is an integer or half-integer. Bessel functions for integer \alpha are also known as cylinder functions or the cylindrical harmonics because they appear in the solution to Laplace's equation in cylindrical coordinates. #Spherical Bessel functions, Spherical Bessel functions with half-integer \alpha are obtained when the Helmholtz equation is solved in spherical coordinates. Applications of Bessel functions The Bessel f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |