|
Maximal Expiratory Pressure
A respiratory pressure meter measures the maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressures that a patient can generate at either the mouth (MIP and MEP) or inspiratory pressure a patient can generate through their nose via a sniff manoeuvre (SNIP). These measurements require patient cooperation and are known as volitional tests of respiratory muscle strength. Handheld devices displaying the measurement achieved in cmH2O and the pressure trace created, allow quick patient testing away from the traditional pulmonary laboratory and are useful for ward based, out patient, and preoperative assessment as well as for use by pulmonologists and physiotherapists. The principal advantage of volitional tests is that they give an estimate of inspiratory or expiratory muscle strength, are simple to perform, and are well tolerated by patients.ATS/ERS Statement on Respiratory Muscle Testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol 166. pp 518–624, 2002 Causes of respiratory muscle impairment Impairment of ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Pressure Meter Device
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
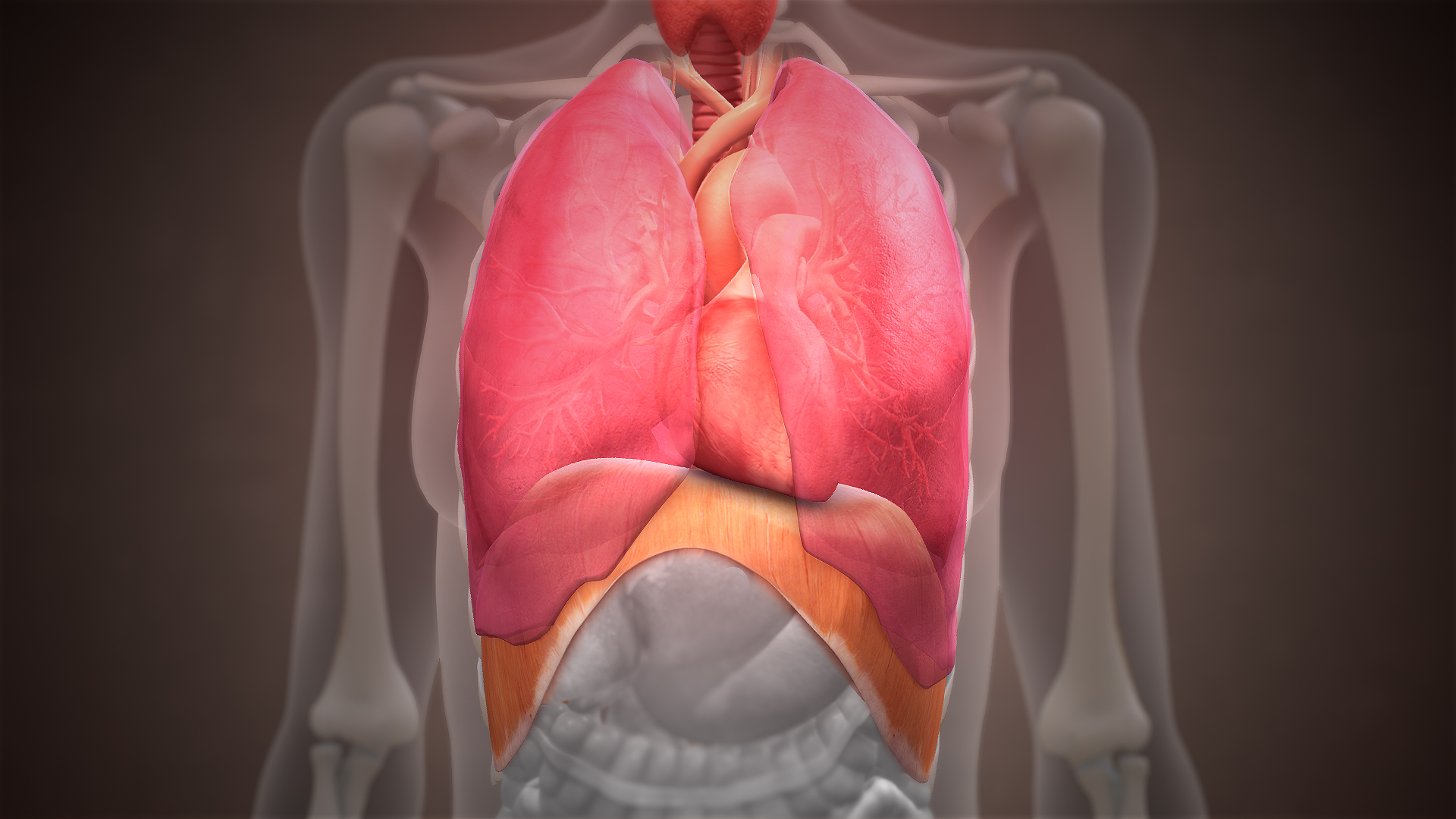
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity of pulmonary impairment. Pulmonary function testing has diagnostic and therapeutic roles and helps clinicians answer some general questions about patients with lung disease. PFTs are normally performed by a pulmonary function technician, respiratory therapist, respiratory physiologist, physiotherapist, pulmonologist, or general practitioner. Indications Pulmonary function testing is a diagnostic and management tool used for a variety of reasons, such as: * Diagnose lung disease. * Monitor the effect of chronic diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, or cystic fibrosis. * Detect early changes in lung function. * Identify narrowing in the airways. * Evaluate airway bronchodilator reactivity. * Show if environmental facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Physiology
In physiology, respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within Tissue (biology), tissues, and the transport, removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction that's to the environment. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the Cellular respiration, biochemical definition, which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products. Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thus life in animals, the processes are distinct: cellular respiration takes place in individual cells of the organism, while physiologic respiration concerns the Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow diffusion, diffusion and transport of metabolites between the organism and the external environment. Gas exchanges in the lung occurs by ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation refers to the in and out movement of air of the lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |