|
Maximal Outerplanar Graph
In graph theory, an outerplanar graph is a graph that has a planar drawing for which all vertices belong to the outer face of the drawing. Outerplanar graphs may be characterized (analogously to Wagner's theorem for planar graphs) by the two forbidden minors and , or by their Colin de Verdière graph invariants. They have Hamiltonian cycles if and only if they are biconnected, in which case the outer face forms the unique Hamiltonian cycle. Every outerplanar graph is 3-colorable, and has degeneracy and treewidth at most 2. The outerplanar graphs are a subset of the planar graphs, the subgraphs of series–parallel graphs, and the circle graphs. The maximal outerplanar graphs, those to which no more edges can be added while preserving outerplanarity, are also chordal graphs and visibility graphs. History Outerplanar graphs were first studied and named by , in connection with the problem of determining the planarity of graphs formed by using a perfect matching to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangulation 3-coloring
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points. Applications In surveying Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle measurements at known points, rather than measuring distances to the point directly as in trilateration; the use of both angles and distance measurements is referred to as triangulateration. In computer vision Computer stereo vision and optical 3D measuring systems use this principle to determine the spatial dimensions and the geometry of an item. Basically, the configuration consists of two sensors observing the item. One of the sensors is typically a digital camera device, and the other one can also be a camera or a light projector. The projection centers of the sensors and the considered point on the object's surface define a (spatial) triangle. Within this triangle, the distance between the sensors is the base ''b'' and must be known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihedral Group
In mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, geometry, and chemistry. The notation for the dihedral group differs in geometry and abstract algebra. In geometry, or refers to the symmetries of the -gon, a group of order . In abstract algebra, refers to this same dihedral group. This article uses the geometric convention, . Definition Elements A regular polygon with n sides has 2n different symmetries: n rotational symmetries and n reflection symmetries. Usually, we take n \ge 3 here. The associated rotations and reflections make up the dihedral group \mathrm_n. If n is odd, each axis of symmetry connects the midpoint of one side to the opposite vertex. If n is even, there are n/2 axes of symmetry connecting the midpoints of opposite sides and n/2 axes of symmetry connecting oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycle (graph Theory)
In graph theory, a cycle in a graph is a non-empty trail in which only the first and last vertices are equal. A directed cycle in a directed graph is a non-empty directed trail in which only the first and last vertices are equal. A graph without cycles is called an ''acyclic graph''. A directed graph without directed cycles is called a ''directed acyclic graph''. A connected graph without cycles is called a ''tree''. Definitions Circuit and cycle * A circuit is a non-empty trail in which the first and last vertices are equal (''closed trail''). : Let be a graph. A circuit is a non-empty trail with a vertex sequence . * A cycle or simple circuit is a circuit in which only the first and last vertices are equal. Directed circuit and directed cycle * A directed circuit is a non-empty directed trail in which the first and last vertices are equal (''closed directed trail''). : Let be a directed graph. A directed circuit is a non-empty directed trail with a vertex sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
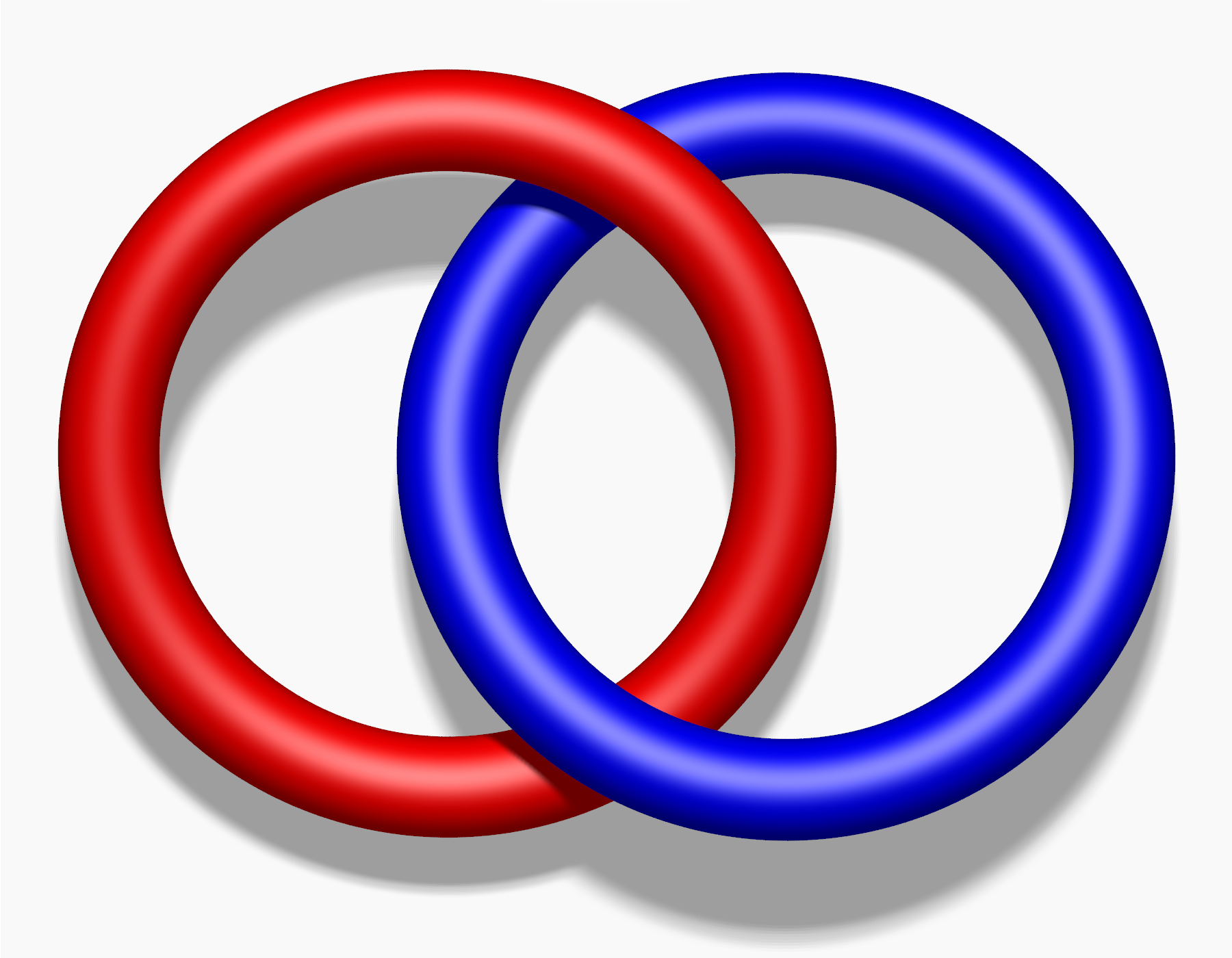
Linkless Embedding
In topological graph theory, a mathematical discipline, a linkless embedding of an undirected graph is an embedding of the graph into three-dimensional Euclidean space in such a way that no two cycles of the graph are linked. A flat embedding is an embedding with the property that every cycle is the boundary of a topological disk whose interior is disjoint from the graph. A linklessly embeddable graph is a graph that has a linkless or flat embedding; these graphs form a three-dimensional analogue of the planar graphs.. Complementarily, an intrinsically linked graph is a graph that does not have a linkless embedding. Flat embeddings are automatically linkless, but not vice versa. The complete graph , the Petersen graph, and the other five graphs in the Petersen family do not have linkless embeddings. Every graph minor of a linklessly embeddable graph is again linklessly embeddable, as is every graph that can be reached from a linklessly embeddable graph by a Y-Δ transform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle-free Graph
In the mathematical area of graph theory, a triangle-free graph is an undirected graph in which no three vertices form a triangle of edges. Triangle-free graphs may be equivalently defined as graphs with clique number ≤ 2, graphs with girth ≥ 4, graphs with no induced 3-cycle, or locally independent graphs. By Turán's theorem, the ''n''-vertex triangle-free graph with the maximum number of edges is a complete bipartite graph in which the numbers of vertices on each side of the bipartition are as equal as possible. Triangle finding problem The triangle finding problem is the problem of determining whether a graph is triangle-free or not. When the graph does contain a triangle, algorithms are often required to output three vertices which form a triangle in the graph. It is possible to test whether a graph with edges is triangle-free in time . Another approach is to find the trace of , where is the adjacency matrix of the graph. The trace is zero if and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor (graph Theory)
Minor may refer to: * Minor (law), a person under the age of certain legal activities. ** A person who has not reached the age of majority * Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education Music theory *Minor chord ** Barbershop seventh chord or minor seventh chord *Minor interval *Minor key *Minor scale Mathematics * Minor (graph theory), the relation of one graph to another given certain conditions * Minor (linear algebra), the determinant of a certain submatrix People * Charles Minor (1835–1903), American college administrator * Charles A. Minor (21st-century), Liberian diplomat * Dan Minor (1909–1982), American jazz trombonist * Dave Minor (1922–1998), American basketball player * James T. Minor, US academic administrator and sociologist * Jerry Minor (born 1969), American actor, comedian and writer * Kyle Minor (born 1976), American writer * Mike Minor (actor) (born 1940), American actor * Mike Minor (baseball) (born 1987), American baseball p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Bipartite Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete bipartite graph or biclique is a special kind of bipartite graph where every vertex of the first set is connected to every vertex of the second set..Electronic edition page 17. Graph theory itself is typically dated as beginning with Leonhard Euler's 1736 work on the Seven Bridges of Königsberg. However, drawings of complete bipartite graphs were already printed as early as 1669, in connection with an edition of the works of Ramon Llull edited by Athanasius Kircher. Llull himself had made similar drawings of complete graphs three centuries earlier.. Definition A complete bipartite graph is a graph whose vertices can be partitioned into two subsets and such that no edge has both endpoints in the same subset, and every possible edge that could connect vertices in different subsets is part of the graph. That is, it is a bipartite graph such that for every two vertices and, is an edge in . A complete bipartite graph w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a complete graph is a simple undirected graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a unique edge. A complete digraph is a directed graph in which every pair of distinct vertices is connected by a pair of unique edges (one in each direction). Graph theory itself is typically dated as beginning with Leonhard Euler's 1736 work on the Seven Bridges of Königsberg. However, drawings of complete graphs, with their vertices placed on the points of a regular polygon, had already appeared in the 13th century, in the work of Ramon Llull. Such a drawing is sometimes referred to as a mystic rose. Properties The complete graph on vertices is denoted by . Some sources claim that the letter in this notation stands for the German word , but the German name for a complete graph, , does not contain the letter , and other sources state that the notation honors the contributions of Kazimierz Kuratowski to graph theory. has edges (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbidden Graph Characterization
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, many important families of graphs can be described by a finite set of individual graphs that do not belong to the family and further exclude all graphs from the family which contain any of these forbidden graphs as (induced) subgraph or minor. A prototypical example of this phenomenon is Kuratowski's theorem, which states that a graph is planar (can be drawn without crossings in the plane) if and only if it does not contain either of two forbidden graphs, the complete graph and the complete bipartite graph . For Kuratowski's theorem, the notion of containment is that of graph homeomorphism, in which a subdivision of one graph appears as a subgraph of the other. Thus, every graph either has a planar drawing (in which case it belongs to the family of planar graphs) or it has a subdivision of at least one of these two graphs as a subgraph (in which case it does not belong to the planar graphs). Definition More generally, a forbidden grap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossing Number (graph Theory)
In graph theory, the crossing number of a graph is the lowest number of edge crossings of a plane drawing of the graph . For instance, a graph is planar if and only if its crossing number is zero. Determining the crossing number continues to be of great importance in graph drawing, as user studies have shown that drawing graphs with few crossings makes it easier for people to understand the drawing. The study of crossing numbers originated in Turán's brick factory problem, in which Pál Turán asked for a factory plan that minimized the number of crossings between tracks connecting brick kilns to storage sites. Mathematically, this problem can be formalized as asking for the crossing number of a complete bipartite graph. The same problem arose independently in sociology at approximately the same time, in connection with the construction of sociograms. Turán's conjectured formula for the crossing numbers of complete bipartite graphs remains unproven, as does an analogous formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Plane
In mathematics, the Euclidean plane is a Euclidean space of dimension two. That is, a geometric setting in which two real quantities are required to determine the position of each point ( element of the plane), which includes affine notions of parallel lines, and also metrical notions of distance, circles, and angle measurement. The set \mathbb^2 of pairs of real numbers (the real coordinate plane) augmented by appropriate structure often serves as the canonical example. History Books I through IV and VI of Euclid's Elements dealt with two-dimensional geometry, developing such notions as similarity of shapes, the Pythagorean theorem (Proposition 47), equality of angles and areas, parallelism, the sum of the angles in a triangle, and the three cases in which triangles are "equal" (have the same area), among many other topics. Later, the plane was described in a so-called '' Cartesian coordinate system'', a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Embedding
In topological graph theory, an embedding (also spelled imbedding) of a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph G on a surface (mathematics), surface \Sigma is a representation of G on \Sigma in which points of \Sigma are associated with graph theory, vertices and simple arcs (Homeomorphism, homeomorphic images of [0,1]) are associated with graph theory, edges in such a way that: * the endpoints of the arc associated with an edge e are the points associated with the end vertices of e, * no arcs include points associated with other vertices, * two arcs never intersect at a point which is interior to either of the arcs. Here a surface is a compact space, compact, connected space, connected 2-manifold. Informally, an embedding of a graph into a surface is a drawing of the graph on the surface in such a way that its edges may intersect only at their endpoints. It is well known that any finite graph can be embedded in 3-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^3.. A planar graph is one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |