|
Maximal Information Coefficient
In statistics, the maximal information coefficient (MIC) is a measure of the strength of the linear or non-linear association between two variables ''X'' and ''Y''. The MIC belongs to the maximal information-based nonparametric exploration (MINE) class of statistics. In a simulation study, MIC outperformed some selected low power tests, however concerns have been raised regarding reduced statistical power in detecting some associations in settings with low sample size when compared to powerful methods such as distance correlation and Heller–Heller–Gorfine (HHG). Comparisons with these methods, in which MIC was outperformed, were made in Simon and Tibshirani and in Gorfine, Heller, and Heller. It is claimed that MIC approximately satisfies a property called ''equitability'' which is illustrated by selected simulation studies. It was later proved that no non-trivial coefficient can exactly satisfy the ''equitability'' property as defined by Reshef et al., although this resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
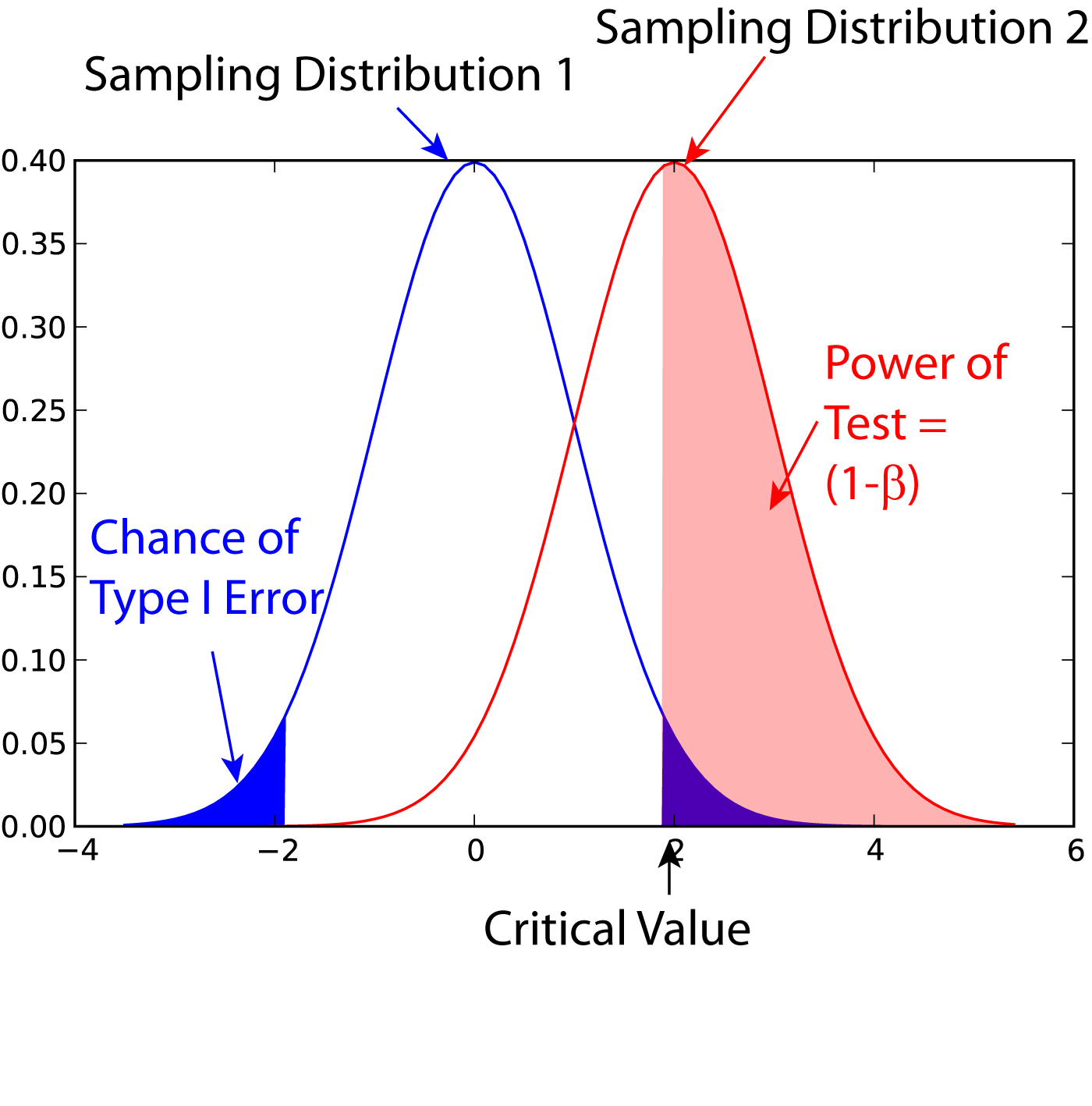
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance Correlation
In statistics and in probability theory, distance correlation or distance covariance is a measure of dependence between two paired random vectors of arbitrary, not necessarily equal, dimension. The population distance correlation coefficient is zero if and only if the random vectors are independent. Thus, distance correlation measures both linear and nonlinear association between two random variables or random vectors. This is in contrast to Pearson's correlation, which can only detect linear association between two random variables. Distance correlation can be used to perform a statistical test of dependence with a permutation test. One first computes the distance correlation (involving the re-centering of Euclidean distance matrices) between two random vectors, and then compares this value to the distance correlations of many shuffles of the data. Background The classical measure of dependence, the Pearson correlation coefficient, is mainly sensitive to a linear relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Binning
Data binning, also called data discrete binning or data bucketing, is a data pre-processing technique used to reduce the effects of minor observation errors. The original data values which fall into a given small interval, a '' bin'', are replaced by a value representative of that interval, often a central value (mean or median). It is related to quantization: data binning operates on the abscissa axis while quantization operates on the ordinate axis. Binning is a generalization of rounding. Statistical data binning is a way to group numbers of more-or-less continuous values into a smaller number of "bins". For example, if you have data about a group of people, you might want to arrange their ages into a smaller number of age intervals (for example, grouping every five years together). It can also be used in multivariate statistics, binning in several dimensions at once. In digital image processing, "binning" has a very different meaning. Pixel binning is the process of combining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the " amount of information" (in units such as shannons (bits), nats or hartleys) obtained about one random variable by observing the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intimately linked to that of entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory that quantifies the expected "amount of information" held in a random variable. Not limited to real-valued random variables and linear dependence like the correlation coefficient, MI is more general and determines how different the joint distribution of the pair (X,Y) is from the product of the marginal distributions of X and Y. MI is the expected value of the pointwise mutual information (PMI). The quantity was defined and analyzed by Claude Shannon in his landmark paper " A Mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measurement, measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, time, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limit (mathematics), limits, continuous function, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is mathematical notation, denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers subset, include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Sample
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset (a statistical sample) of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population in question. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection than measuring the entire population and can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population. Each observation measures one or more properties (such as weight, location, colour or mass) of independent objects or individuals. In survey sampling, weights can be applied to the data to adjust for the sample design, particularly in stratified sampling. Results from probability theory and statistical theory are employed to guide the practice. In business and medical research, sampling is widely used for gathering information about a population. Acceptance sampling is used to determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification, storage, and communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley, in the 1920s, and Claude Shannon in the 1940s. The field is at the intersection of probability theory, statistics, computer science, statistical mechanics, information engineering, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (with two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a die (with six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measures in information theory are mutual information, channel capacity, error exponents, and relative entropy. Important sub-fields of information theory include s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |