|
Max Mallowan
Sir Max Edgar Lucien Mallowan (6 May 1904 – 19 August 1978) was a prominent British archaeologist, specialising in ancient Middle Eastern history. He was the second husband of Dame Agatha Christie. Life and work Born Edgar Mallowan in Wandsworth on 6 May 1904, he was the son of Frederick Mallowan and his wife Marguerite (née Duvivier), whose mother was mezzo-soprano Marthe Duvivier. His father's family was from Austria. He was educated at Rokeby School and Lancing College (where he was a contemporary of Evelyn Waugh) and studied classics at New College, Oxford. He first worked as an apprentice to Leonard Woolley at the archaeological site of Ur (1925–1930), which was thought to be the capital of Mesopotamian civilization. It was at the Ur site, in 1930, that he first met Agatha Christie, the famous author, whom he married the same year. In 1932, after a short time working at Nineveh with Reginald Campbell Thompson, Mallowan became a field director for a series of expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agatha Christie
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English writer known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving around fictional detectives Hercule Poirot and Miss Marple. She also wrote the world's longest-running play, the murder mystery ''The Mousetrap'', which has been performed in the West End since 1952. A writer during the "Golden Age of Detective Fiction", Christie has been called the "Queen of Crime". She also wrote six novels under the pseudonym Mary Westmacott. In 1971, she was made a Dame (DBE) by Queen Elizabeth II for her contributions to literature. ''Guinness World Records'' lists Christie as the best-selling fiction writer of all time, her novels having sold more than two billion copies. Christie was born into a wealthy upper middle class family in Torquay, Devon, and was largely home-schooled. She was initially an unsuccessful writer with six co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Woolley
Sir Charles Leonard Woolley (17 April 1880 – 20 February 1960) was a British archaeologist best known for his Excavation (archaeology), excavations at Ur in Mesopotamia. He is recognized as one of the first "modern" archaeologists who excavated in a methodical way, keeping careful records, and using them to reconstruct ancient life and history. Woolley was knighted in 1935 for his contributions to the discipline of archaeology. He married the British archaeologist Katharine Woolley. Early life Woolley was the son of a clergyman, and was brother to Geoffrey Harold Woolley, Victoria Cross, VC, and George Cathcart Woolley. He was born at 13 Southwold Road, Upper Clapton, in the modern London Borough of Hackney and educated at St John's School, Leatherhead and New College, Oxford. He was interested in excavations from a young age. Career In 1905, Woolley became assistant of the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford. Volunteered by Arthur Evans to run the excavations on the Coria (Corbridge), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve
The Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve (RAFVR) was established in 1936 to support the preparedness of the U.K. Royal Air Force in the event of another war. The Air Ministry intended it to form a supplement to the Royal Auxiliary Air Force (RAuxAF), the active reserve for the RAF, by providing an additional non-active reserve. However during the Second World War the high demand for aircrew absorbed all available RAuxAF personnel and led the RAFVR to quickly become the main pathway of aircrew entry into the RAF. It was initially composed of civilians recruited from neighbourhood reserve flying schools, run by civilian contractors with largely RAF-trained flying instructors as well as other instructors in related air war functions, such as observers and wireless operators. After the war, and with the end of conscription in the early 1960s, the RAFVR considerably reduced in size and most functions were absorbed into the RAuxAF. The RAFVR now forms the working elements of the Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balikh River
The Balikh River ( ar, نهر البليخ) is a perennial river that originates in the spring of Ain al-Arous near Tell Abyad in the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests ecoregion. It flows due south and joins the Euphrates at the modern city of Raqqa. The Balikh is the second largest tributary to the Euphrates in Syria, after the Khabur River. It is an important source of water and large sections have recently been subjected to canalization. Geography The primary source of the Balikh River is the karstic spring of Ain al-Arous, just south of the Syria–Turkey border. Additionally, the Balikh receives water from a number of periodical streams and wadis that drain the Harran Plain to the north, as well as the plains to the west and east of the river valley. These streams are the Jullab, the Wadi Qaramogh, and the Wadi al-Kheder. A few kilometres south of Ain al-Arous, the Balikh is joined by the channel of the Jullab. This small river rises from sprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Khabur
The Khabur River is the largest perennial tributary to the Euphrates in Syria. Although the Khabur originates in Turkey, the karstic springs around Ras al-Ayn are the river's main source of water. Several important wadis join the Khabur north of Al-Hasakah, together creating what is known as the Khabur Triangle, or Upper Khabur area. From north to south, annual rainfall in the Khabur basin decreases from over 400 mm to less than 200 mm, making the river a vital water source for agriculture throughout history. The Khabur joins the Euphrates near the town of Busayrah. Geography The course of the Khabur can be divided in two distinct zones: the Upper Khabur area or Khabur Triangle north of Al-Hasakah, and the Middle and Lower Khabur between Al-Hasakah and Busayrah. Tributaries The tributaries to the Khabur are listed from east to west. Most of these wadis only carry water for part of the year. * Wadi Radd * Wadi Khnezir * Wadi Jarrah *Jaghjagh River * Wadi Khanzir * Wadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Brak
Tell Brak (Nagar, Nawar) was an ancient city in Syria; its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of Al-Hasaka city, Al-Hasakah Governorate. The city's original name is unknown. During the second half of the third millennium BC, the city was known as Nagar and later on, Nawar. Starting as a small settlement in the seventh millennium BC, Tell Brak evolved during the fourth millennium BC into one of the biggest cities in Upper Mesopotamia, and interacted with the cultures of southern Mesopotamia. The city shrank in size at the beginning of the third millennium BC with the end of Uruk period, before expanding again around c. 2600 BC, when it became known as Nagar, and was the capital of a regional kingdom that controlled the Khabur river valley. Nagar was destroyed around c. 2300 BC, and came under the rule of the Akkadian Empire, followed by a period of independence as a Hurrian city-state, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
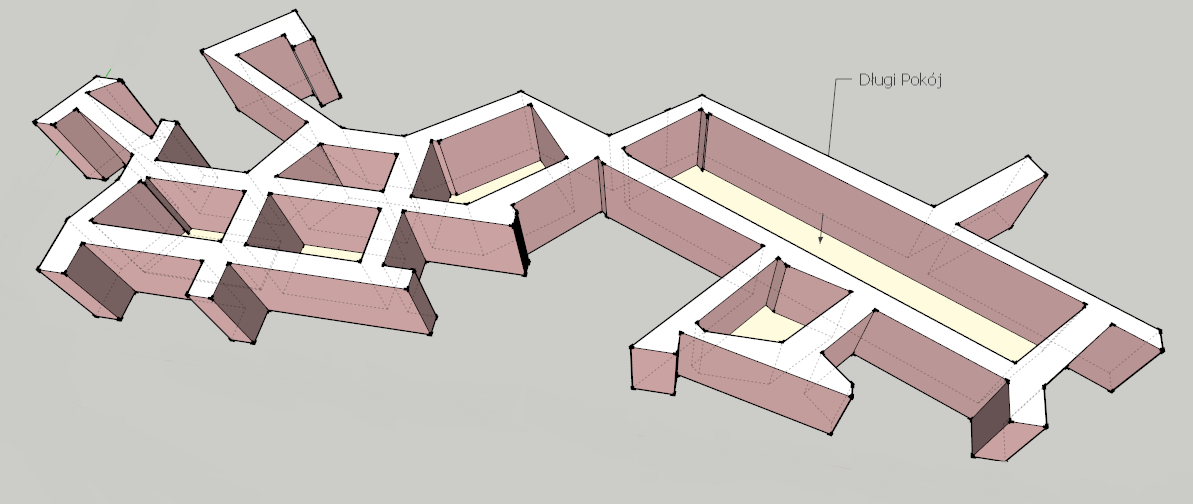
Chagar Bazar
Chagar Bazar (Šagir Bazar, Arabic: تل شاغربازار) is a tell, or settlement mound, in northern Al-Hasakah Governorate, Syria. It is a short distance from the major ancient city of Nagar (Tell Brak). The site was occupied from the Halaf period (c. 6100 to 5100 BC) until the middle of the 2nd millennium BC. Archaeology The site contains two mounds, a higher but smaller one to the south and a lower larger northern one. Occupation was Halaf at the northern end then at the southern end in the Late Chalcolithic period followed by full occupation in the 3rd millennium BC. The 2nd millennium BC occupation was restricted to the northern (5 hectare) mound. Chagar Bazar was excavated for three seasons by the British archaeologist Max Mallowan, with his wife Agatha Christie, from 1935 to 1937. Many of the artefacts discovered were brought to the British Museum. Besides pottery, a large number of Old Babylonian period clay tablets written in cuneiform script were discovered. Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Arpachiyah
Tell Arpachiyah (outside modern Mosul in Ninawa Governorate Iraq) is a prehistoric archaeological site in Nineveh Province (Iraq). It takes its name from a more recent village located about from Nineveh. The proper name of the mound on which the site is located is Tepe Reshwa. Tepe Gawra is also a contemporary Neolithic site located in the Mosul region. History of archaeological research After being scouted by Reginald Campbell Thompson in 1928, it was excavated by Max Mallowan and John Cruikshank Rose of the British School of Archaeology in Iraq, along with Agatha Christie, in 1933. Additional soundings were conducted in 1976 by a team led by Ismail Hijara.Ismail Hijara, Three New Graves at Arpachiyah, World Archaeology, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 125-128, 1978 Several Halaf structures were uncovered, including tholoi and the "Burnt House". An array of Halaf pottery and sealings were also found, along with some Ubaid burials. Tell Arpachiyah and its environment Tell Arpachiyah is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British School Of Archaeology In Iraq
The British Institute for the Study of Iraq (BISI) (formerly the British School of Archaeology in Iraq) is the only body in Britain devoted to research into the ancient civilizations and languages of Mesopotamia. It was founded in 1932 and its aims are to support and undertake research into the archaeology (and cognate subjects) of Iraq and the neighbouring countries from the earliest times to c. AD 1700, and to promote the cultural heritage of Iraq. Since 1934, the School has published a refereed journal, ''Iraq'', which is now published annually, in November/December of each year. It is a registered charity and has its headquarters in the office of the British Academy at Carlton House Terrace in London. History The School was founded in 1932 as a memorial to the life and works of Gertrude Bell. Bell was passionate about archaeology and bequeathed £6,000 for its founding when she died in 1926. Further fundraising in 1929 added £14,000, and although the Great Depression left th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present.Among the national museums in London, sculpture and decorative and applied art are in the Victoria and Albert Museum; the British Museum houses earlier art, non-Western art, prints and drawings. The National Gallery holds the national collection of Western European art to about 1900, while art of the 20th century on is at Tate Modern. Tate Britain holds British Art from 1500 onwards. Books, manuscripts and many works on paper are in the British Library. There are significant overlaps between the coverage of the various collections. The British Museum was the first public national museum to cover all fields of knowledge. The museum was established in 1753, largely b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Q73536.jpg)