|
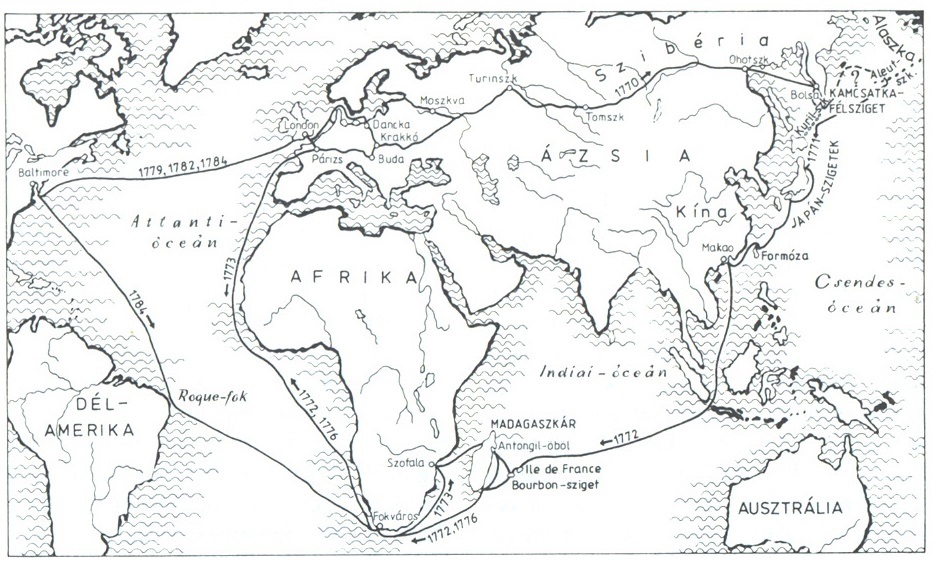
Maurycy Beniowski
Count Maurice Benyovszky de Benyó et Urbanó ( hu, Benyovszky Máté Móric Mihály Ferenc Szerafin Ágost; pl, Maurycy Beniowski; sk, Móric Beňovský; 20 September 1746 – 24 May 1786) was a renowned military officer, adventurer, and writer from the Kingdom of Hungary, who described himself as both a Hungarian and a Pole. He is considered a national hero in Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. Benyovszky was born and raised in Verbó, Kingdom of Hungary (present-day Vrbové, Slovakia). In 1769, while fighting for the Polish armies under the Bar Confederation, he was captured by the Russians and exiled to Kamchatka. He subsequently escaped and returned to Europe via Macau and Mauritius, arriving in France. In 1773, Benyovszky reached agreement with the French government to establish a trading post on Madagascar. Facing significant problems with the climate, the terrain, and the native Sakalava people, he abandoned the trading post in 1776. Benyovszky then returned to Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary (1526–1867)
The Kingdom of Hungary between 1526 and 1867 existed as a state outside the Holy Roman Empire, but part of the lands of the Habsburg monarchy that became the Austrian Empire in 1804. After the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the country was ruled by two crowned kings (John I and Ferdinand I). Initially, the exact territory under Habsburg rule was disputed because both rulers claimed the whole kingdom. This unsettled period lasted until 1570 when John Sigismund Zápolya (John II) abdicated as King of Hungary in Emperor Maximilian II's favor. In the early stages, the lands that were ruled by the Habsburg Hungarian kings were regarded as both the "Kingdom of Hungary" and "Royal Hungary". Royal Hungary was the symbol of the continuity of formal law after the Ottoman occupation, because it could preserve its legal traditions, but in general, it was ''de facto'' a Habsburg province.Raphael PataThe Jews of Hungary: History, Culture, Psychology Wayne State University Press, 1996, p. 153 Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Pasfield Oliver
Samuel Pasfield Oliver (1838–1907) was an English artillery officer, geographer and antiquary. Life Born at Bovinger, Essex, on 30 October 1838, he was the eldest and only surviving son of William Macjanley Oliver, rector of Bovinger, by his wife Jane Weldon. He entered Eton College in 1853; and after passing through the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, he received a commission in the Royal Artillery on 1 April 1859. In the following year he went out with his battery to China, where hostilities had been renewed. The First Convention of Beijing was however signed soon after Oliver's arrival (24 October 1860), and his service was confined to garrison duty at Canton. On the establishment of a British embassy at Beijing in 1861 he accompanied General Sir John Michel on a visit to the capital, and subsequently made a tour through Japan. In the following year he was transferred to Mauritius; and from there with Major-general Johnstone on a mission to Madagascar to congratulate Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, seventh largest EU country, covering a combined area of . It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and Temperate climate, temperate transitional climate. The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Humans have been present on Polish soil since the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Glacial Period over 12,000 years ago. Culturally diverse throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
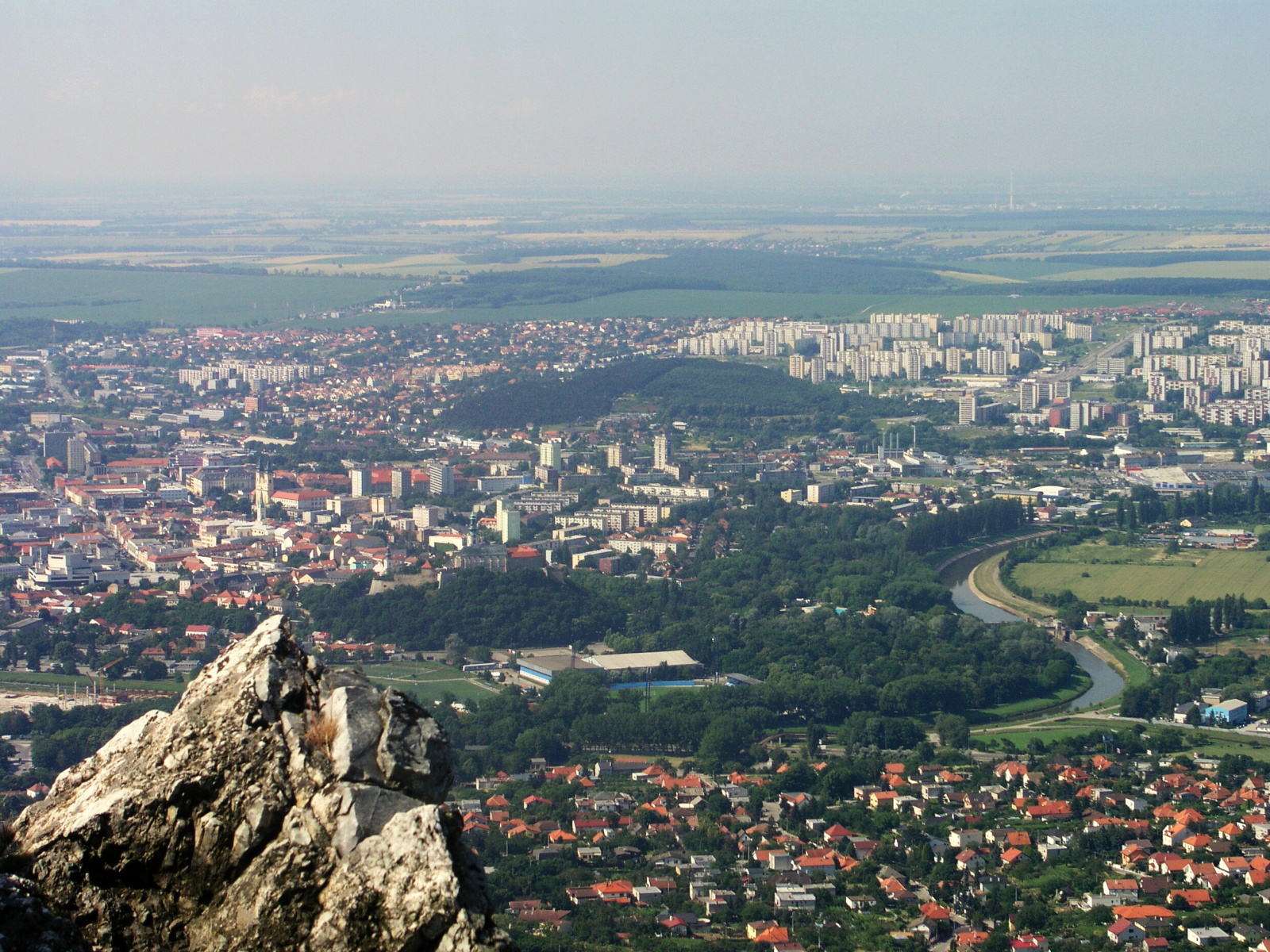
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of about 78,353, it is the fifth largest city in Slovakia. Nitra is also one of the oldest cities in Slovakia; it was the political center of the Principality of Nitra. Today, it is a seat of a ''Regions of Slovakia, kraj'' (Nitra Region), and an ''Districts of Slovakia, okres'' (Nitra District). Etymology The first mention of Nitra dates back to the 9th century. The name of the city is derived from the Nitra river. The name is Indo-European languages, Indo-European, but the question of its History of Proto-Slavic#Pre-Slavic, pre-Slavic or Slavic people, Slavic origin has not been satisfactorily answered. Nitra might be derived from the old Indo-European root ''neit-'', ''nit-'' meaning "to cut" or "to burn" using a derivation element ''-r-'' (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (, also ; ; german: Preßburg/Pressburg ; hu, Pozsony) is the capital and largest city of Slovakia. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, it is estimated to be more than 660,000 — approximately 140% of the official figures. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the River Danube and the left bank of the River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital that borders two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarians, Jews, Romani, Serbs and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; eleven Hungarian kings and eight queens were crowned in St Martin's Cathedral. Most Hungarian parliament assemblies were held here from the 17th century until the Hunga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svätý Jur
Svätý Jur (; german: Sankt Georgen; he, Yergen; hu, Szentgyörgy; formerly ''Jur pri Bratislave'') is a small historical town northeast of Bratislava, located in the Bratislava Region. The city is situated on the slopes of Little Carpathians mountains and surrounded by typical terraced vineyards with more than 700 years of winemaking tradition. In 1990, the intact city center was declared a protected city reservation. Cadastrially, Svätý Jur includes also the natural reserve Šúr, established in 1952 to protect one of the last and largest remnants of a tall-stem swamp alder forest in Central Europe. Today, Svätý Jur has a population of over 5 thousand citizens. The town is well connected with a major road between Pezinok and Bratislava passing through and the Svätý Jur railway station situated on the main Košice - Bratislava railway line. The city is bordered by the Little Carpathian mountains to the west, Bratislava to the south, natural reserve Šúr to the east an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piarist
The Piarists (), officially named the Order of Poor Clerics Regular of the Mother of God of the Pious Schools ( la, Ordo Clericorum Regularium pauperum Matris Dei Scholarum Piarum), abbreviated SchP, is a religious order of clerics regular of the Catholic Church founded in 1617 by Spanish priest Joseph Calasanz. It is the oldest religious order dedicated to education, and the main occupation of the Piarist fathers is teaching children and youth, the primary goal being to provide free education for poor children. The Piarist practice was to become a model for numerous later Catholic societies devoted to teaching, while some state-supported public school systems in Europe also followed their example. The Piarists have had a considerable success in the education of physically or mentally disabled persons. Some notable individuals taught at Piarist schools include Pope Pius IX, Goya, Schubert, Gregor Mendel, Tadeusz Kościuszko and Victor Hugo. History Joseph Calasanz Joseph Calasan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Péter Révay
Baron Péter Révay de Szklabina et Blathnicza (used aliases of his name include Révai, Rewa, Réva; 2 February 1568 – 4 June 1622) was a Hungarian nobleman, Royal Crown Guard for the Holy Crown of Hungary, poet, state official, soldier, and historian. He was the grandson of Ferenc Révay. Life Péter Révay was born in Szklabina, a member of an old family from the Turóc region. He was the third child of Mihály Révay and his mother Anna Bakics. He received his education in Bártfa, Jihlava, probably also in Vienna, and between 1589 and 1591 in Strasbourg, where he was awarded the title of a Master of Philosophy. In 1598 he became the hereditary county head (called a főispán) of the Turóc Comitatus. From 1601 he discharged the duties of a Royal Commissary. He became Royal Crown Guard in 1608. In 1610 he became the Royal Courtmaster, from 1615 the Chief Doormaster, and from 1619 a Tablemaster. He had a relatively wide-reaching knowledge of philosophy and history, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Révay Family
The Révay family was a Hungarian noble family, who owned estates in Turóc county, the Kingdom of Hungary (Turiec region in today's Slovakia) until the early 20th century. Their property included i.a. the Rococo-classical manor house in Mošovce, the so-called ''Old Manor house'' demolished in the middle of the 20th century, the ''Noblemen's Mansion'' and the park in Mošovce, a castle in Blatnica, lands and a castle in Sklabiňa, as well as a manor-house with a park in Turčianska Štiavnička. Family history The Révay family has been known since the 13th century. The first known ancestor of the family was called ''Comes Jakab'' (Count Jakab) in the early 13th century. The main estates of the family were situated in the region of Syrmia until the Ottoman occupation of southern Hungary. In 1556 and 1635 the family was promoted to Barons and on 17 June 1723 to Counts. The coat of arms of the ''Masters de Reva'', which can be seen at the façade of their manor house, is comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussars
A hussar ( , ; hu, huszár, pl, husarz, sh, husar / ) was a member of a class of light cavalry, originating in Central Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. The title and distinctive dress of these horsemen were subsequently widely adopted by light cavalry regiments in European armies in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. By the 19th century, hussars wore jackets decorated with braid and shako or busby hats and they developed a romanticized image of being dashing and adventurous. A small number of modern armies retain the designation of hussars for some armored (tank) units. As well, some modern armies have ceremonial mounted units which wear historical hussar uniforms on parades or to provide a VIP escort to national leaders. Historically, the term derives from the cavalry of late medieval Hungary, under Matthias Corvinus, with mainly Serb warriors. Etymology Etymologists are divided over the derivation of the word ''hussar''. Several alternative theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
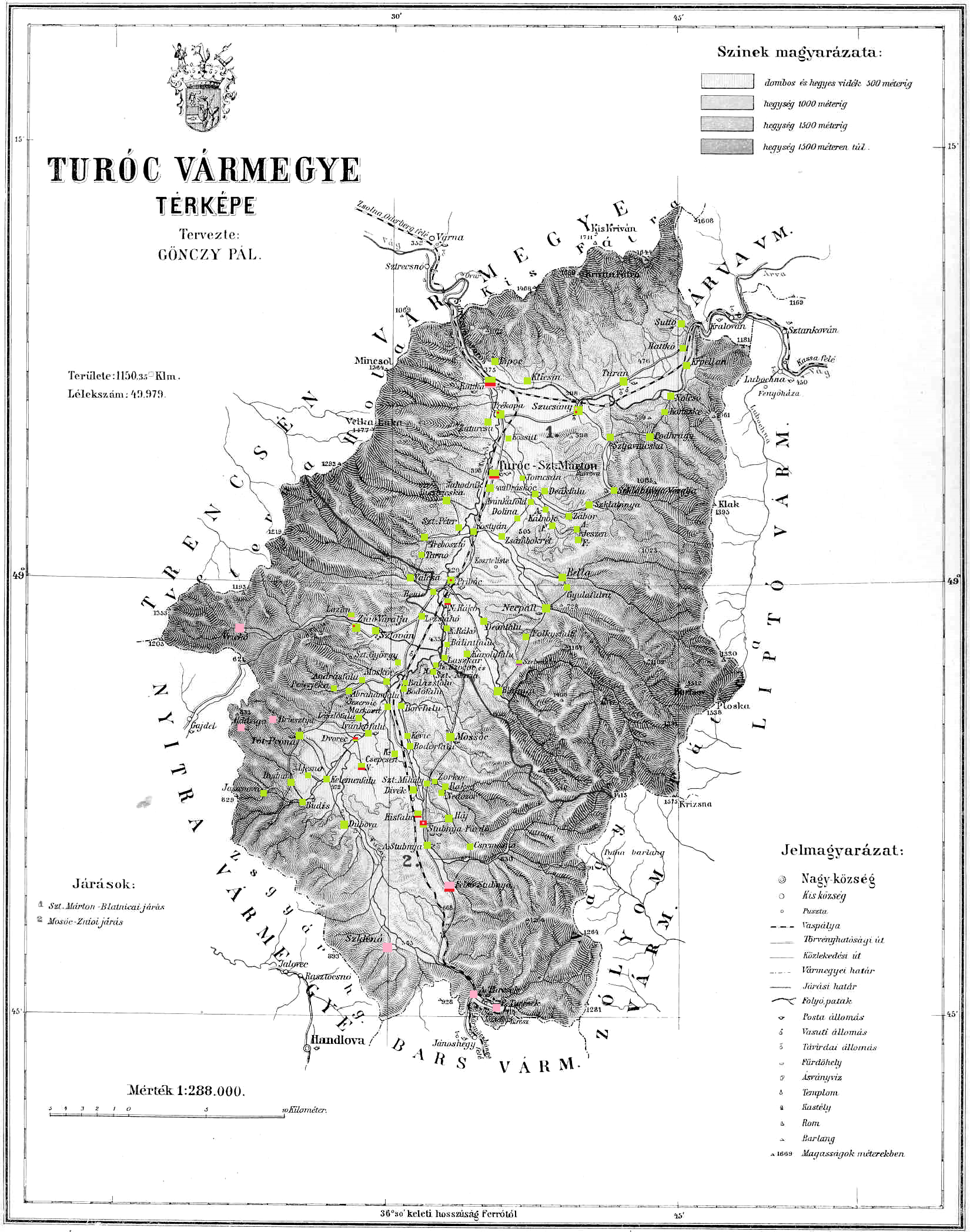
Turiec
Turiec is a region in central Slovakia, one of the 21 official tourism regions. The region is not an administrative division today, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was the Turóc County in the Kingdom of Hungary. Etymology The region was named after the Turiec river. History Turóc county () as a Hungarian comitatus arose before the 15th century. In 1920, by the Treaty of Trianon, the territory became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia. Between 1939-1945, after Czechoslovakia was abolished, Turiec was part of the First Slovak Republic. After World War II, it became part of Czechoslovakia again. In 1993, Czechoslovakia was split and Turiec became part of Slovakia. Geography The region covers the area of the Turiec basin and is determined by the mountain ranges of Veľká Fatra to the east, Malá Fatra to the west and north, Žiar to the south and west and Kremnica Mountains to the south. The Turiec river flows through the entire region and inflows into Váh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turóc County
Turóc ( Hungarian, historically also spelled ''Túrócz''), , /''comitatus Thurociensis'', ) was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in north-western Slovakia, where the corresponding Slovak name Turiec is only an informal designation of the corresponding territory. Geography Turóc county shared borders with the counties of Nyitra, Trencsén, Árva, Liptó, Zólyom and Bars, situated between the Lesser Fatra (Kis-Fátra) and Greater Fatra (Nagy-Fátra) Mountains. The river Turóc flowed through the county. Its area was 1123 km² around 1910. Capitals The capitals of the Turóc county were the Szklabinya Castle and Turócszentmárton (present-day Martin; Slovak name until 1950: ''Turčiansky Svätý Martin''); from 1772 only Turócszentmárton was the capital. History Turóc county as a Hungarian ''comitatus'' arose in the 14th century. In the aftermath of World War I, the area of the now defunct Turóc county bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |