|
Matthew Barton (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Matthew Barton (–1795) was an officer of the Royal Navy. He rose to the rank of admiral during a long and distinguished career, in which he served in the War of Jenkins' Ear, the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War. He fought at several major battles, and commanded a number of amphibious assaults off the French coast and in the West Indies. Though he lived until 1795 his health was broken after service in the tropics, and he never served at sea again after 1763. Early career Barton entered the navy in 1730, on board the ''Fox'', under the command of Captain Arnold, and served with him on the coast of South Carolina. Afterwards he served in the Mediterranean under Captains John Byng, Philip VanBrugh, and Lord Augustus Fitzroy, as a midshipman. From lieutenant to admiral In March 1739, being then a midshipman of , he was made lieutenant in the prize ship ''St. Joseph'' by Admiral Nicholas Haddock. He was then appointed to the 70-gun , and was eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral (Royal Navy)
Admiral is a senior rank of the Royal Navy, which equates to the NATO rank code OF-9, outranked only by the rank of admiral of the fleet. Royal Navy officers holding the ranks of rear admiral, vice admiral and admiral of the fleet are sometimes considered generically to be admirals. The rank of admiral is currently the highest rank to which a serving officer in the Royal Navy can be promoted, admiral of the fleet being in abeyance except for honorary promotions of retired officers and members of the Royal Family. The equivalent rank in the British Army and Royal Marines is general; and in the Royal Air Force, it is air chief marshal. History The first admirals (1224 to 1523) King Henry III of England appointed the first known English Admiral Sir Richard de Lucy on 29 August 1224. De Lucy was followed by Sir Thomas Moulton in 1264, who also held the title of ''Keeper of the Sea and Sea Ports''. Moulton was succeeded by Sir William de Leybourne, (the son of Sir Roger de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant (navy)
LieutenantThe pronunciation of ''lieutenant'' is generally split between , , generally in the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Commonwealth countries, and , , generally associated with the United States. See lieutenant. (abbreviated Lt, LT (U.S.), LT(USN), Lieut and LEUT, depending on nation) is a commissioned officer rank in many English-speaking nations' navies and coast guards. It is typically the most senior of junior officer ranks. In most navies, the rank's insignia may consist of two medium gold braid stripes, the uppermost stripe featuring an executive curl in many Commonwealth of Nations; or three stripes of equal or unequal width. The now immediately senior rank of lieutenant commander was formerly a senior naval lieutenant rank. Many navies also use a subordinate rank of sub-lieutenant. The appointment of "first lieutenant" in many navies is held by a senior lieutenant. This naval lieutenant ranks higher than an army lieutenants; within NATO countries the naval rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Mahon
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xebec
A xebec ( or ), also spelled zebec, was a Mediterranean sailing ship that was used mostly for trading. Xebecs had a long overhanging bowsprit and aft-set mizzen mast. The term can also refer to a small, fast vessel of the sixteenth to nineteenth centuries, used almost exclusively in the Mediterranean Sea. Description Xebecs were ships similar to galleys primarily used by Barbary pirates, which have both lateen sails and oars for propulsion. Early xebecs had two masts while later ships had three. Xebecs featured a distinctive hull with pronounced overhanging bow and stern, and rarely displaced more than 200 tons, making them slightly smaller and with slightly fewer guns than frigates of the period. Use by Barbary corsairs These ships were easy to produce and were cheap, and thus nearly every corsair captain (''Raïs'') had at least one xebec in his fleet. They could be of varying sizes. Some ships had only three guns while others had up to forty. Most xebecs had around 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Medley
Henry Medley (1687 – 5 August 1747) was an officer of the Royal Navy, rising to the rank of vice-admiral. Life Medley entered the Royal Navy in 1703, and in 1706 was midshipman of the 80-gun with Captain Price at the relief of Barcelona. He passed his examination as lieutenant on 8 February 1710, and on 5 September 1710 was promoted by Sir John Norris to be lieutenant of ; a few months later he was moved into the 70-gun . In 1717 he was a lieutenant of the 90-gun , flagship of Sir George Byng in the Baltic Sea. Early in 1720 Medley was promoted to the command of , a fire-ship, and on 17 February 1721 was posted into the 60-gun . In 1722, while commanding the 50-gun in the Mediterranean, he seized a ship named the ''Revolution'', lying within the mole of Genoa, on information of her being in the service of the Old Pretender. He later commanded the ''Leopard'' on the coast of Portugal and in the English Channel until the end of 1728. From 1731 to 1735 Medley was employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fireship
A fire ship or fireship, used in the days of wooden rowed or sailing ships, was a ship filled with combustibles, or gunpowder deliberately set on fire and steered (or, when possible, allowed to drift) into an enemy fleet, in order to destroy ships, or to create panic and make the enemy break formation. Ships used as fire ships were either warships whose munitions were fully spent in battle, surplus ones which were old and worn out, or inexpensive purpose-built vessels rigged to be set afire, steered toward targets, and abandoned quickly by the crew. Explosion ships or "hellburners" were a variation on the fire ship, intended to cause damage by blowing up in proximity to enemy ships. Fireships were used to great effect by the outgunned English fleet against the Spanish Armada during the Battle of Gravelines, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
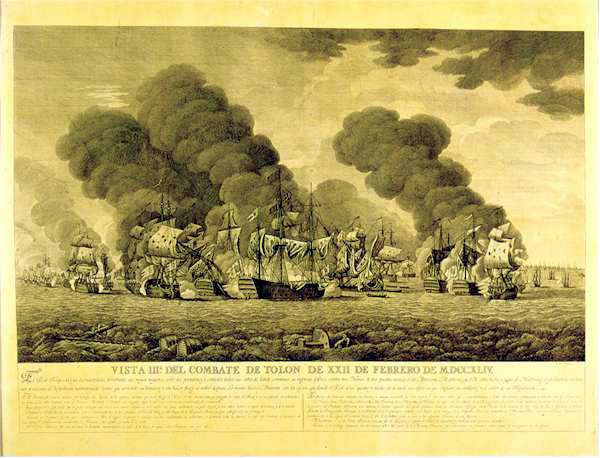
William Rowley (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral of the Fleet Sir William Rowley KB (c. 1690 – 1 January 1768) was a Royal Navy officer. He distinguished himself by his determination as commander of the vanguard at the Battle of Toulon in February 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession. He went on to be Commander-in-Chief of the Mediterranean Fleet in August 1744 and successfully kept the Spanish and French fleets out of the Mediterranean area but was relieved of his command following criticism of his decision as presiding officer at a court-martial. Rowley later became a Lord Commissioner of the Admiralty on the Board of Admiralty. He was a Member of Parliament for Taunton and then for Portsmouth. Early career Born the second son of William Rowley and his wife, Elizabeth Rowley (née Baldwin), Rowley joined the Royal Navy as a volunteer in 1704. He was assigned to the third-rate HMS ''Orford'', commanded by Captain John Norris, and saw action in the Mediterranean during the War of the Spanish Succession.H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS St Michael (1669)
HMS ''St Michael'' was a 90-gun second rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by John Tippetts of Portsmouth Dockyard and launched in 1669. ''St Michael'' was rebuilt at Blackwall Yard in 1706, at which time she was also renamed HMS ''Marlborough''. On 5 April 1725 ''Marlborough'' was ordered to be taken to pieces and rebuilt at Chatham. She was relaunched on 25 September 1732. On 11 February 1744 during the Battle of Toulon. ''Marlborough'' and ''Namur'' bore the brunt of the Spanish fire, her captain James Cornewall, and 42 crew were killed and 120 wounded out of her crew of 750 men. Command passed to his distant cousin, Frederick Cornewall, the First Lieutenant, who was severely wounded and lost his right arm. Cornewall was buried at sea. ''Marlborough'' was reduced to a 68-gun ship in 1752. She formed part of Sir George Pocock's fleet at the taking of Havana from the Spanish in 1762. Whilst making her way back to Britain Britain most often refers to: * The Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Vernon
Admiral Edward Vernon (12 November 1684 – 30 October 1757) was an English naval officer. He had a long and distinguished career, rising to the rank of admiral after 46 years service. As a vice admiral during the War of Jenkins' Ear, in 1739 he was responsible for the capture of Porto Bello, seen as expunging the failure of Admiral Hosier there in a previous conflict. However, his amphibious operation against the Spanish port of Cartagena de Indias was a disastrous defeat. Vernon also served as a Member of Parliament (MP) on three occasions and was outspoken on naval matters in Parliament, making him a controversial figure. The origin of the name "grog" for rum diluted with water is attributed to Vernon. He was known for wearing coats made of grogram cloth, earning him the nickname of "Old Grog", which in turn came to mean the diluted rum that he first introduced into his naval squadron. He is also the eponym of George Washington's estate Mount Vernon, and thereby th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola (the island containing the countries of Haiti and the Dominican Republic); the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands lies some to the north-west. Originally inhabited by the indigenous Taíno peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, when England (later Great Britain) conquered it, renaming it ''Jamaica''. Under British colonial rule Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with a plantation economy dependent on the African slaves and later their des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaloner Ogle
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Chaloner Ogle KB (1681 – 11 April 1750) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. After serving as a junior officer during the Nine Years' War, a ship he was commanding was captured by three French ships off Ostend in July 1706 in an action during the War of the Spanish Succession. Ogle was given command of the fourth-rate HMS ''Swallow'' and saw action against the pirate fleet of Bartholomew Roberts in the Battle of Cape Lopez in February 1722. The action was to prove a turning point in the war against the pirates and many consider the death of Roberts to mark the end of the Golden Age of Piracy. In December 1741 Ogle was despatched with a fleet of some 30 ships to support Admiral Edward Vernon in his engagement with Spanish naval forces under Admiral Blas de Lezo off the coast of Colombia during the War of Jenkins' Ear. The attack on Fort San Lazaro was a disaster for the British forces and the Battle of Cartagena de Indias ultimately proved a deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Ranelagh (1697)
HMS ''Ranelagh'' was a three-decker 80-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Deptford Dockyard on 25 June 1697. She took part in a number of actions during the War of the Spanish Succession, including the Battle of Vigo Bay, Battle of Vigo in 1702 and the Battle of Vélez-Málaga in 1704. On 20 August 1723 she was ordered to be taken to pieces and rebuilt according to the 1719 Establishment at Woolwich. She was renamed HMS ''Princess Caroline'' in 1728 (while rebuilding). She was relaunched on 15 March 1731. ''Princess Caroline'' was Admiral Edward Vernon's flagship at the Battle of Cartagena de Indias during his second Spanish Caribbean campaign, in the War of Jenkins' Ear. George Washington's half-brother, Lawrence Washington (1718–1752), Lawrence Washington, served on ''Princess Caroline'' as a Captain (land), Captain of the marine (military), Marines in 1741, and named his estate Mount Vernon in honour of his commander.Ranft, Brian, editor. ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |