|
Mathildidae
Mathildidae is a family of minute sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Mathildoidea of the informal group of the Lower Heterobranchia.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2012). Mathildidae. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=23070 on 2012-06-29 Genera Genera within the family Mathildidae include: * '' Brookesena'' Finlay, 1926 * '' Mathilda'' Semper, 1865 * ''Tuba'' Lea, 1833 * '' Turritellopsis'' G. O. Sars, 1878 ;Genera brought into synonymy: * ''Eucharilda'' Iredale, 1929: synonym of ''Mathilda'' Semper, 1865 * ''Fimbriatella'' Sacco, 1895: synonym of ''Mathilda'' Semper, 1865 * ''Gegania'' Jeffreys, 1884: synonym of ''Tuba The tuba (; ) is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the ne ...'' Lea, 1833 * ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brookesena
''Brookesena'' is a genus of sea snails, marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusks in the family (biology), family Mathildidae,Rosenberg, G.; Gofas, S. (2012). Brookesena. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138169 on 2012-06-29 Species * ''Brookesena neozelanica'' (Suter, 1908) * ''Brookesena succincta'' (Suter, 1908) * ''Brookesena turrita'' (Warén, 1996) References * Gofas, S.; Le Renard, J.; Bouchet, P. (2001). Mollusca, in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). ''European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification.'' Collection Patrimoines Naturels, 50: pp. 180–213 (l * Spencer, H.; Marshall. B. (2009). ''All Mollusca except Opisthobranchia''. In: Gordon, D. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand Inventory of Biodiversity. Volume One: Kingdom Animalia. 584 pp External links Spencer H.G., Willan R.C., Marshall B.A. & Murray T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
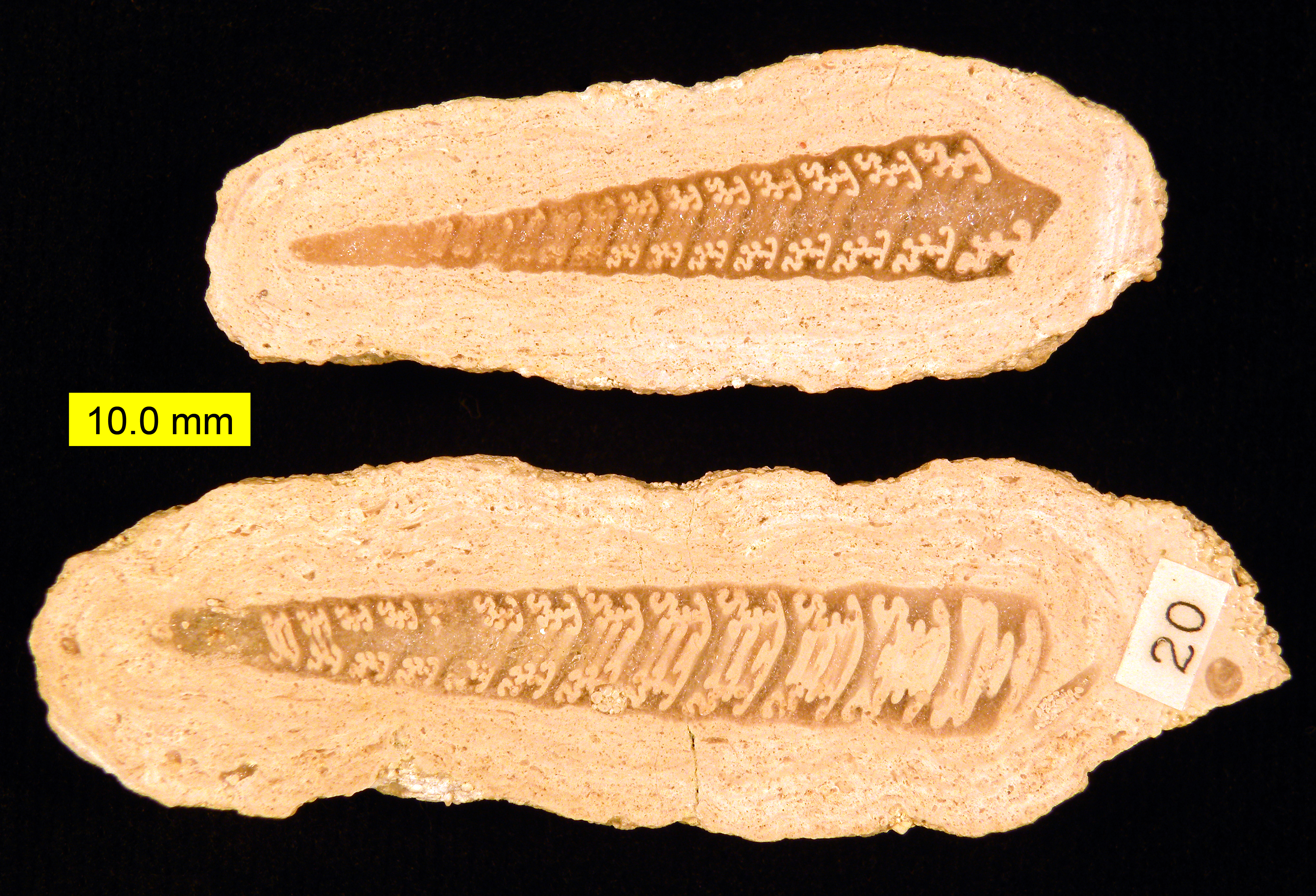
Mathilda (gastropod)
''Mathilda '' is a genus of sea snails, marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusks in the family (biology), family Mathildidae.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2012). Mathilda. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138170 on 2012-06-29 Species * ''Mathilda amaea'' Dall, 1927 * ''Mathilda amanda'' Thiele, 1925 * ''Mathilda argentina'' Castellanos, 1990 * ''Mathilda barbadensis'' Dall, 1889 * ''Mathilda bieleri'' Smriglio & Mariottini, 2007 * ''Mathilda boucheti'' Bieler, 1995 * ''Mathilda brevicula'' Bavay, 1922 * ''Mathilda brownae'' Smriglio, Mariottini & Swinnen, 2017 * ''Mathilda cancellata'' Kuroda, 1958 * ''Mathilda carystia'' Melvill & Standen, 1903 * ''Mathilda cerea'' Kuroda, 1958 * ''Mathilda cochlaeformis'' Brugnone, 1873 * ''Mathilda coronata'' Monterosato, 1875 * ''Mathilda cryptostoma'' de Folin, 1874 * ''Mathilda decorata'' Hedley, 1903 * ''Mathilda epicharis'' de Folin, 1870 * ''Mathilda fusca'' (Okutani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathildoidea
Mathildoidea is a superfamily of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the informal group Lower Heterobranchia.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Mathildoidea Dall, 1889. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=411861 on 2021-06-25 Families Families within the superfamily Mathildoidea include: *Family Mathildidae Mathildidae is a family of minute sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Mathildoidea of the informal group of the Lower Heterobranchia.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2012). Mathildidae. Accessed through: World Register of Marin ... * † Family Ampezzanildidae * † Family Anoptychiidae * † Family Gordenellidae * Family Tofanellidae * † Family Trachoecidae References * Jensen, R. H. (1997). A Checklist and Bibliography of the Marine Molluscs of Bermuda. Unp. , 547 pp * Bouchet P., Rocroi J.P., Hausdorf B., Kaim A., Kano Y., Nützel A., Parkhaev P., Schrödl M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example species in the genus '' Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails. Anatomy Sea snails are a very large group of animals and a very diverse one. Most snails that live in salt water respire using a gill or gills; a few species, though, have a lung, are intertidal, and are active only at low tide when they can move around in the air. These air-breathing species includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided."Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Heterobranchia
Lower Heterobranchia, also known as the Allogastropoda, is a group of rather specialized, highly evolved sea slugs and sea snails, ( marine gastropod mollusks) within the subclass Heterobranchia. WoRMS (2020). "Lower Heterobranchia". Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1054700 on 2020-05-16 Although the great majority of Lower Heterobranchs are indeed marine, a few have succeeded in making the transition to freshwater. Description The shell shapes in this group are typically those that are seen in the sundial, pyramid, rissoella and orbitestellid families of snails. Taxonomy 2005 taxonomy In the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005, the Lower Heterobranchia is an Informal Group. Superfamilies within the Lower Heterobranchia include: *Unassigned to a superfamily (orbitestellid-shells) ** Family Cimidae ** † Family Dolomitellidae ** † Family Heterosubulitidae ** † Family Kuskokwimiidae ** † Family Misurinellid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuba (gastropod)
The tuba (; ) is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the newer instruments in the modern orchestra and concert band. The tuba largely replaced the ophicleide. ''Tuba'' is Latin for " trumpet". A person who plays the tuba is called a tubaist, a tubist, or simply a tuba player. In a British brass band or military band, they are known as bass players. History Prussian Patent No. 19 was granted to Wilhelm Friedrich Wieprecht and Johann Gottfried Moritz (1777–1840) on September 12, 1835 for a "bass tuba" in F1. The original Wieprecht and Moritz instrument used five valves of the Berlinerpumpen type that were the forerunners of the modern piston valve. The first tenor tuba was invented in 1838 by Carl Wilhelm Moritz (1810–1855), son of Johann Gottfried Moritz. The addition of valves made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)