|
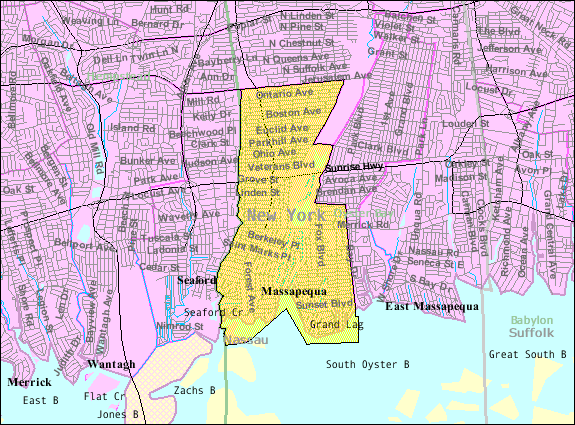
Massapequa Union Free School District
Massapequa (, ) is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Oyster Bay (town), New York, Town of Oyster Bay in Nassau County, New York, Nassau County, on the South Shore (Long Island), South Shore of Long Island, in New York (state), New York, United States. It is considered the anchor community of the Greater Massapequa area. The population of the CDP was 21,685 at the time of the 2010 census. The Greater Massapequa area, which includes the nearby CDPs of North Massapequa, New York, North Massapequa and East Massapequa, New York, East Massapequa, as well as the Massapequa Park, New York, Incorporated Village of Massapequa Park, has a combined population of over 75,000. History A 19th-century writer identified Massapequa as one of the "Metoac, 13 tribes of Long Island," but additional research has shown that they were a band of Lenape, the Algonquian-speaking people who occupied the western part of the island at the time of European encounter. The ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (New York)
The administrative divisions of New York are the various units of government that provide local services in the State of New York. The state is divided into boroughs, counties, cities, townships called "towns", and villages. (The only boroughs, the five boroughs of New York City, have the same boundaries as their respective counties.) They are municipal corporations, chartered (created) by the New York State Legislature, as under the New York Constitution the only body that can create governmental units is the state. All of them have their own governments, sometimes with no paid employees, that provide local services. Centers of population that are not incorporated and have no government or local services are designated hamlets. Whether a municipality is defined as a borough, city, town, or village is determined not by population or land area, but rather on the form of government selected by the residents and approved by the New York Legislature. Each type of local government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Massapequa, New York
East Massapequa (formerly known as West Amityville) is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) located within the Town of Oyster Bay in Nassau County, on the South Shore of Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 19,069 at the 2010 census. History The easternmost third of East Massapequa (within the Amityville School District) was previously the hamlet of West Amityville and started utilizing a Massapequa mailing address in 1975. The name "East Massapequa" reflects the fact that the hamlet is located east of Massapequa and Massapequa Park. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.51%, is water. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 19,565 people, 6,432 households, and 5,107 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 5,592.8 per square mile (2,158.3/km2). There were 6,535 housing units at an average density of 1,868.1/sq mi (720.9/km2). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southern United States to its south, and the Midwestern United States to its west. The Northeast is one of the four regions defined by the U.S. Census Bureau for the collection and analysis of statistics. The region is usually defined as including nine U.S. states: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont. The U.S. Census Bureau–defined region of the Northeastern United States has a total area of with of that being land mass, making it the smallest region of the United States by both land mass and total area. The Northeastern region is the nation's most economically developed, densely populated, and culturally diverse region. Of the nation's four census regions, the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce and its director is appointed by the President of the United States. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the U.S. House of Representatives to the states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses make informed decisions. The information provided by the census informs decisions on where to build and maintain schools, hospitals, transportation infrastructure, and police and fire departments. In addition to the decennial census, the Census Bureau continually conducts over 130 surveys and programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Fork (Long Island)
The South Fork of Suffolk County, New York is a peninsula in the southeastern section of the county on the South Shore of Long Island. The South Fork includes most of the Hamptons. The shorter, more northerly peninsula is known as the North Fork. Geography The South Fork is composed of all of the Town of East Hampton and a substantial part of the Town of Southampton. The body of water to the south is the Atlantic Ocean. The South Fork and North Fork split at Riverhead, New York where the Peconic River empties into Peconic Bay. It has long been noted that Long Island resembles a fish with the forks forming a tail. The native name for this is "Paumanok". This name is also used to name a trail that navigates the entirety of the South Fork (as well as parts of Long Island), the Paumanok Path. The South Fork and North Fork are separated by Great Peconic Bay, Little Peconic Bay, and Gardiners Bay. Between the two forks lie several islands, including Gardiners Island and She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinnecock Reservation
Shinnecock Reservation is a Native American reservation for members of the Shinnecock Indian Nation in the town of Southampton in Suffolk County, New York, United States. It is the furthermost east of the two Native American reservations in Suffolk County; the other being Poospatuck Reservation in the town of Brookhaven. It lies on the east side of Shinnecock Bay on southeastern Long Island, near Tuckahoe, Shinnecock Hills, and the village of Southampton. The population was 819 as of the 2020 census. Roughly that many tribal members additionally live off the reservation. In 2010, the Nation received federal recognition as a tribe, a status which it pursued for 32 years. This will enable the tribe to move forward with its plans for a casino; it has already been discussing this with the state and local governments. Opposition to additional casinos in the New York market is based in part on dilution of demand: both the Foxwoods Casino in Connecticut and those in Atlantic City, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Recognized Tribe
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.Federal Acknowledgment of the Pamunkey Indian Tribe Of these, 231 are located in Alaska. Description  In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants
In the United States, the Indian tribe is a fundamental unit, and the constitution grants
|
Shinnecock Indian Nation
The Shinnecock Indian Nation is a federally recognized tribe of historically Algonquian-speaking Native Americans based at the eastern end of Long Island, New York. This tribe is headquartered in Suffolk County, on the southeastern shore. Since the mid-19th century, the tribe's landbase is the Shinnecock Reservation within the geographic boundaries of the Town of Southampton. Their name roughly translates into English as "people of the stony shore". History The Shinnecock were among the thirteen Indian bands loosely based on kinship on Long Island, which were named by their geographic locations, but the people were highly decentralized. The most common pattern of indigenous life on Long Island prior to their economic and cultural destruction - and, on occasion, actual enslavement - by the Europeans was the autonomous village linked by kinship to its neighbors. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montaukett
= Montauketts = An indigenous Native American People. Name and Identifications The Montaukett ("Metoac" or Matouwac), currently more commonly known as Montauk. The meaning of the name ''Montauk'' is unknown. Native Americans living on Long Island are often known in colonial writings by the place name of their geographic territories, such as the Montauk and the Shinnecock, which may or may not be the same as their name for themselves. European colonists tended to mistakenly assume that the different bands they encountered were different tribes, even in cases where the bands clearly shared the same culture and language. Language The Montauks are an Algonquian-speaking Native American people from the eastern and central sections of Long Island, New York. The Montauk spoke an Eastern Algonquian language. Prior to the 17th century, Montauk people spoke the Mohegan-Pequot language, also known as the Algonquian "N" dialect of the Algonquin language until about 1600, they th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquian Languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic languages, Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin language, Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term ''Algonquin'' has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (), "they are our relatives/allies". A number of Algonquian languages are considered extinct languages by the modern linguistic definition. Algonquian peoples, Speakers of Algonquian languages stretch from the east coast of North America to the Rocky Mountains. The proto-language from which all of the languages of the family descend, Proto-Algonquian language, Proto-Algonquian, was spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago. There is no scholarly consensus about wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pequot People
The Pequot () are a Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut including the Eastern Pequot Tribal Nation, or the Brothertown Indians of Wisconsin.Pritzker, Barry (2000) ''A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples'', pp. 656–657. Oxford University Press. . They historically spoke Pequot, a dialect of the Mohegan-Pequot language, which became extinct by the early 20th century. Some tribal members are undertaking revival efforts. The Pequot and the Mohegan were formerly a single group, but the Mohegan split off in the 17th century as the Pequot came to control much of Connecticut. Simmering tensions with the New England Colonies led to the Pequot War of 1634–1638, which dramatically reduced the population and influence of the Pequot; many members were killed, enslaved, or dispersed. Small numbers of Pequots remained in Connecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |