|
Mashak
The mashak (also known as , , , ', ', ', ', '', )'' is a type of bagpipe found in Northern India, Uttarakhand, Sudurpaschim Province (especially Baitadi and Darchula district) of Nepal and parts of Pakistan and Afghanistan. The pipe was associated with weddings and festive occasions. In India it is historically found in Garhwal (kumaon) in Uttarakhand, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. This bagpipe uses single reeds, and can be played either as a drone or as a melody instrument. Etymology The etymology of the term ''mashak'' stems from its common use in India, referring to a skin bag used for carrying water. This skin bag shares a similar function to the air bag of the bag pipes. Relation with the Scottish Highland pipes Some academics dispute any indigenous origins of the mashak; researcher Ander Burton Alter wrote in 2000 that the pipes today played in Kumaon are Scottish Highland bagpipes with one bass and two tenor drones, with no local manufacturer or evidence of existence p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titti (bagpipe)
The titti ( te, titti, masaka titti, or tutti) is a type of bagpipe played in Andhra Pradesh, India, made from an entire goat-skin.Subhash Kak (Louisiana State University). The Indian Epic Song Tradition'. Presented at The 7th International Conference and Festival of Asian Music, Busan, Korea, Sept 26-Sept 30, 2002. The instrument is described as a goatskin with a double-reed inserted into one leg, and a bamboo blowpipe into the other. The term ''tittii'' is used in Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam. History Several paintings possibly depicting bagpipes are shown in Kerala, from the early eighteenth century. Colonel James Tod (1782–1835 CE) notes that the Yanadis, a forest tribe in Madras, also play the bagpipes,as do later sources in 1900 describing the Yanadi. Usage The instrument is often used to provide solely a constant drone. References note the instrument being used as a drone accompaniment by storytellers and singers, as well as for village dance-dramas. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai regions. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north; the Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal to the east; the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh to the south and Himachal Pradesh to the west and north-west. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun, the largest city of the state, which is a rail head. Bhararisain, a town in Chamoli district, is the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital. Archaeological evidence supports the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai regions. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north; the Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal to the east; the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh to the south and Himachal Pradesh to the west and north-west. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun, the largest city of the state, which is a rail head. Bhararisain, a town in Chamoli district, is the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital. Archaeological evidence supports the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Musical Instruments
Indian musical instruments can be broadly classified according to the Hornbostel–Sachs system into four categories: chordophones (string instruments), aerophones (wind instruments), membranophones (drums) and idiophones (non-drum percussion instruments). Chordophones Plucked strings Bowed strings * Chikara * Dhantara * Dilruba * Ektara violin * Esraj * Kamaicha * Kingri (string instrument) * Mayuri Vina or Taus * Onavillu * Behala (violin type) * Pena (musical instrument) * Pinaka vina * Pulluvan Veena - one stringed violin * Ravanahatha * Sarangi * Classical Sarangi * Sarinda * Tar Shehnai * Villu Paatu - arched bow instrument + Behala - Bengal Murshidabad Violin Persian "Behaaleh" (Restless) Other string instruments * Gethu or Jhallari – struck tanpura * Gubguba or Jamuku (khamak) * Pulluvan kutam * Santoor – Hammered dulcimer Aerophones Single reed *Pepa *Pungi or Been Double reed * Kuzhal * Mukhavina * Nadaswaram * Shehnai * Sundari * Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sruti Upanga
The sruti upanga ("drone bagpipe", or bhazana-śruti,Payer, Alois (1944 - ). '. (Materialien zur karnatischen Musik). Fassung vom 2009-05-20. druthi, or nosbug) is a type of bagpipe played in Tamil Nadu, southern India. The instrument was often used to supply a drone to accompany '' mukha vina'' (Tamil oboe) music. The instrument was described by Charles Russel Day (1860-1900): Playing method Beatrice Edgerly notes in 1942, similar to Day, that the pitch of the instrument was controlled by inserting wire or bits of silk. See also * Mashak, a Northern Indian bagpipe * Titti (bagpipe), a bagpipe in Andhra Pradesh and Kerala References {{reflist External linksOnline Shruti BoxFree Online Shruti box. Bagpipes Indian musical instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagpipe
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia. The term ''bagpipe'' is equally correct in the singular or the plural, though pipers usually refer to the bagpipes as "the pipes", "a set of pipes" or "a stand of pipes". Construction A set of bagpipes minimally consists of an air supply, a bag, a chanter, and usually at least one drone. Many bagpipes have more than one drone (and, sometimes, more than one chanter) in various combinations, held in place in stocks—sockets that fasten the various pipes to the bag. Air supply The most common method of supplying air to the bag is through blowing into a blowpipe or blowstick. In some pipes the player must cover the tip of the blowpipe with their ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagpipes
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia. The term ''bagpipe'' is equally correct in the singular or the plural, though pipers usually refer to the bagpipes as "the pipes", "a set of pipes" or "a stand of pipes". Construction A set of bagpipes minimally consists of an air supply, a bag, a chanter, and usually at least one drone. Many bagpipes have more than one drone (and, sometimes, more than one chanter) in various combinations, held in place in stocks—sockets that fasten the various pipes to the bag. Air supply The most common method of supplying air to the bag is through blowing into a blowpipe or blowstick. In some pipes the player must cover the tip of the blowpipe with their t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
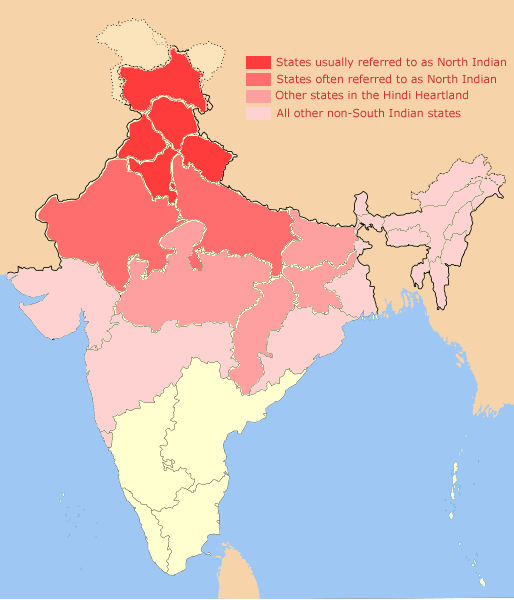
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwal Division
Garhwal (IPA: /ɡəɽʋːɔɭ/) is one of the two administrative divisions of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Lying in the Himalayas The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ..., it is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Kumaon division, Kumaon, on the south by Uttar Pradesh state, and on the northwest by Himachal Pradesh state. It includes the districts of Chamoli District, Chamoli, Dehradun District, Dehradun, Haridwar District, Haridwar, Pauri Garhwal, Rudraprayag District, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal District, Tehri Garhwal, and Uttarkashi District, Uttarkashi. The people of Garhwal are known as Garhwali people, Garhwali and speak the Garhwali language. The administrative center for Garhwal division is the town of Pauri. The Divisional Commissioner is the admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwali People
The Garhwali people are an Indian ethnolinguistic group native to the Garhwal, in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, who speak Garhwali, an Indo-Aryan language. Etymology In modern usage, "Garhwali" is used to refer to anyone whose linguistic, cultural, and ancestral or genetic origins is from the Garhwal Himalayas. Their ethnonym is derived from the word ‘''Garhwal''’ or '''Gadwal. The exact origin of the word Garhwal is unknown. However, it is believed to be derived from the title ‘''Garh-wala''’ (owner of forts) given to the ruler Mayal, who is said to have consolidated 52 principalities to form the kingdom in the 14th century. After this conquest, the domain under Mayal is said to have been called ‘''Garhwal''’, possibly due to the numerous forts in the region. Prior to Mayal, the name of the area and its people was unknown. However, some historians like "Atkinson" have alluded to ‘''Khas-des''’ (Land of the Khasas), and "Sircar" has stated that ‘''Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Baines
Anthony Cuthbert Baines (1912–1997) was an English organologist who produced a wide variety of works on the history of musical instruments, and was a founding member of the Galpin Society. He attended Westminster School and then read for a degree in chemistry at Christ Church, Oxford. He subsequently won a scholarship to the Royal College of Music as a bassoon player, and went on to perform with the London Philharmonic Orchestra.A. C. Baines (ed.): ''Musical Instruments Through the Ages'' (Harmondsworth: Pelican Books, 1961), cover text. Selected publications * ''Woodwind Instruments and their History'' (London: Faber & Faber, 1957; reprinted 1962, 1967, 1991) * ''Bagpipes'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1960; reprinted 1979, 1995), * ''Musical Instruments Through the Ages'' (Harmondsworth: Pelican, 1961; revised edition, London: Faber, 1966), * ''European and American Musical Instruments'' (London: B. T. Batsford, 1966; London: Chancellor, 1983) * ''Brass Instruments: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ander Burton Alter
The masculine name Ander is a variant of the Greek name "Andreas". Other variants of the Greek name "Andreas" are Andrés and Andrew, as well as Anders. The masculine name Ander is a variant Basque form of Andrew. Notable people with the name Ander include: Given name * Ander Crenshaw (born 1944), American banker, attorney and politician * Ander Monson, American novelist, poet, and nonfiction writer * Ander Monro (born 1981), Canadian rugby player * Ander Herrera (born 1989), Spanish footballer * Ander Lafuente Aguado (born 1983), Spanish footballer * Ander Elosegi (born 1987), Spanish slalom canoeist * Ander Gago (born 1984), Spanish footballer * Ander García, Spanish basketball player * Ander Garitano (born 1969), Spanish football player and coach * Ander Iturraspe (born 1989), Spanish footballer * Ander Mirambell (born 1983), Spanish skeleton racer * Ander Murillo (born 1983), Spanish/Basque footballer * Ander Olaizola (born 1989), Spanish footballer * Ander Vilariño (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |