|
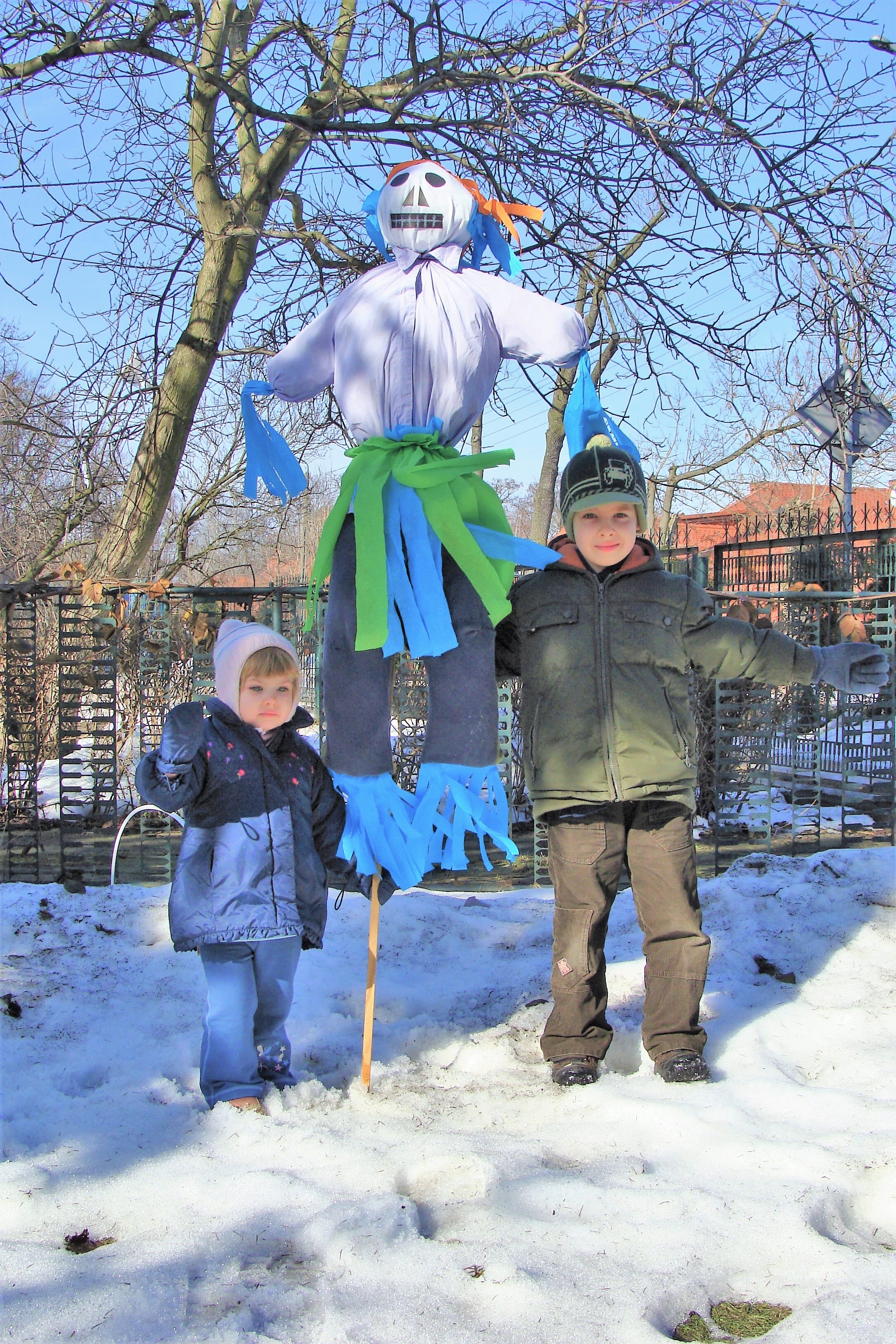
Marzana Fiedtkou
Marzanna (in Polish), Morė (in Lithuanian), Marena (in Russian), Mara (in Ukrainian), Morana (in Czech, Slovene and Serbo-Croatian), Morena (in Slovak and Macedonian) or Mora (in Bulgarian) is a pagan Slavic goddess associated with seasonal rites based on the idea of death and rebirth of nature. She is an ancient goddess associated with winter's death, rebirth and dreams. In ancient Slavic rites, the death of the Goddess Marzanna at the end of winter becomes the rebirth of Spring of the Goddess Kostroma (Russian), Lada or Vesna representing the coming of Spring. Some medieval Christian sources such as the Czech 13th century Mater Verborum compare her to the Greek goddess Hecate, associating her with sorcery. 15th century Polish chronicler Jan Długosz likened her in his ''Annales'' to Ceres, the Roman goddess of agriculture (together with another Slavic goddess Dziewanna). Lithuanian, Latvian and some Estonian sources, dated between the 13th and 14th century, note the wors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moryana
Moryana (russian: Моря́на, ) is a female sea spirit in Slavic folklore, possibly a goddess. Moryana was a sea vodyanitsa and daughter of the Morskoy Tsar, and also, according to some beliefs, she ruled the winds. Sometimes the ''moryany/moryanki'' (plural; russian: моряны, морянки; Polish: moriany) were said to be numerous spirits of the sea and a marine kind of rusalki, which posed a great threat to ships, but usually Moryana was represented as a single entity. Due to the consonance of her name with the name of the goddess Marena, Moryana was sometimes identified with her and was called the goddess of death. Etymology Moryana's name is derived from ''море'' meaning "sea", and with the feminine ending ''яна'' it is roughly translated as "she of the sea". Moryana's name is used in some regions of Russia to describe the cold and harsh winds she personifies; these winds blow from the sea to the land and are also called ''морянка'', ''морянн ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brynica (other)
The Brynica Brynica (German: ''Brinitz'') is a river in Silesia, Poland. It has a length of 55 km and is the main tributary of Czarna Przemsza. It has a source in Mysłów, and flows through Piekary Śląskie, Wojkowice, Czeladź, Siemianowice Śląsk ... is a river in southern Poland. Brynica may also refer to the following villages: * Brynica, Łódź Voivodeship (central Poland) * Brynica, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (south-central Poland) * Brynica, Kluczbork County in Opole Voivodeship (south-west Poland) * Brynica, Opole County in Opole Voivodeship (south-west Poland) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as " God"), whereas polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheistic religions accept one supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eternal creator deity, but may accept a pantheon of deities which live, die and may be reborn like any other being. Although most monotheistic religions traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Toporov
Vladimir Nikolayevich Toporov (russian: Влади́мир Никола́евич Топоро́в; 5 July 1928 in Moscow5 December 2005 in Moscow) was a leading Russian philologist associated with the Tartu-Moscow semiotic school. His wife was Tatyana Elizarenkova. Toporov authored more than 1500 works, including ''Akhmatova and Dante'' (1972), ''Towards the Reconstruction of the Indo-European Rite'' (1982), ''Aeneas: a Man of Destiny'' (1993), ''Myth. Rite. Symbol. Image'' (1995), ''Holiness and Saints in the Russian Spiritual Culture'' (1998), and ''Petersburg Text of Russian Literature'' (2003). He translated the Dhammapada into Russian and supervised the ongoing edition of the most complete vocabulary of the Prussian language to date (5 volumes). Among Toporov's many honours were the USSR State Prize (1990), which he turned down to voice his protest against the repressive January Events of the Soviet administration in Lithuania; the first ever Solzhenitsyn Prize (1998), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyacheslav Ivanov (philologist)
Vyacheslav Vsevolodovich Ivanov (russian: Вячесла́в Все́володович Ива́нов , 21 August 1929 – 7 October 2017) was a prominent Soviet/Russian philologist, semiotician and Indo-Europeanist probably best known for his glottalic theory of Indo-European consonantism and for placing the Indo-European urheimat in the area of the Armenian Highlands and Lake Urmia. Early life Vyacheslav Ivanov's father was Vsevolod Ivanov, one of the most prominent Soviet writers. His mother was an actress who worked in the theatre of Vsevolod Meyerhold. His childhood was clouded by disease and war, especially in Tashkent. Ivanov was educated at Moscow University and worked there until 1958, when he was fired on account of his sympathy with Boris Pasternak and Roman Jakobson. By that time, he had made some important contributions to Indo-European studies and became one of the leading authorities on Hittite language. Career * 1959–1961 — head of the Research Group for Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars (mythology)
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Mars ( la, Mārs, ) was the god of war and also an agricultural guardian, a combination characteristic of early Rome. He was the son of Jupiter and Juno, and was pre-eminent among the Roman army's military gods. Most of his festivals were held in March, the month named for him ( Latin ''Martius''), and in October, which began the season for military campaigning and ended the season for farming. Under the influence of Greek culture, Mars was identified with the Greek god Ares,''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. whose myths were reinterpreted in Roman literature and art under the name of Mars. The character and dignity of Mars differed in fundamental ways from that of his Greek counterpart, who is often treated with contempt and revulsion in Greek literature. Mars's altar in the Campus Martius, the area of Rome that took its name from him, was supposed to have been dedicated by Numa, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of War Deities
A war god in mythology associated with war, combat, or bloodshed. They occur commonly in both monotheistic and polytheistic religions. Unlike most gods and goddesses in polytheistic religions, monotheistic deities have traditionally been portrayed in their mythologies as commanding war in order to spread religion. (The intimate connection between " holy war" and the "one true god" belief of monotheism has been noted by many scholars, including Jonathan Kirsch in his book ''God Against The Gods: The History of the War Between Monotheism and Polytheism'' and Joseph Campbell in ''The Masks of God, Vol. 3: Occidental Mythology''.) The following is a list of war deities: North Africa Egyptian * Anhur, god of war, not a native god * Bast, cat-headed goddess associated with war, protection of Lower Egypt and the pharaoh, the sun, perfumes, ointments, and embalming *Horus, god of the king, the sky, war, and protection *Maahes, lion-headed god of war *Menhit, goddess of war, "she w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theonym
A theonym (from Greek ''theos'' (Θεός), " god"'','' attached to ''onoma'' (ὄνομα), "name") is the proper name of a deity. Theonymy, the study of divine proper names, is a branch of onomastics (the study of the etymology, history, and use of proper names.); it helps develop an understanding of the function and societal views of particular gods and may help understand the origins of a society's language. Analysis of theonyms has been useful in understanding the connections of Indo-European languages, and possibly their religion. In all languages, the analysis of the possible etymological origin of a theonym can serve as basis for theories of its historical origin. Metaphysical and mystical meanings are also discerned in theonyms, as in Kabbalah. Theonyms can also appear as all or part of a name for a human, animal, thing or place. See also * -onym * Theo * Theology * Thealogy, similar origin as above, but female instead * God (word) * Names of God * Nomenclature * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
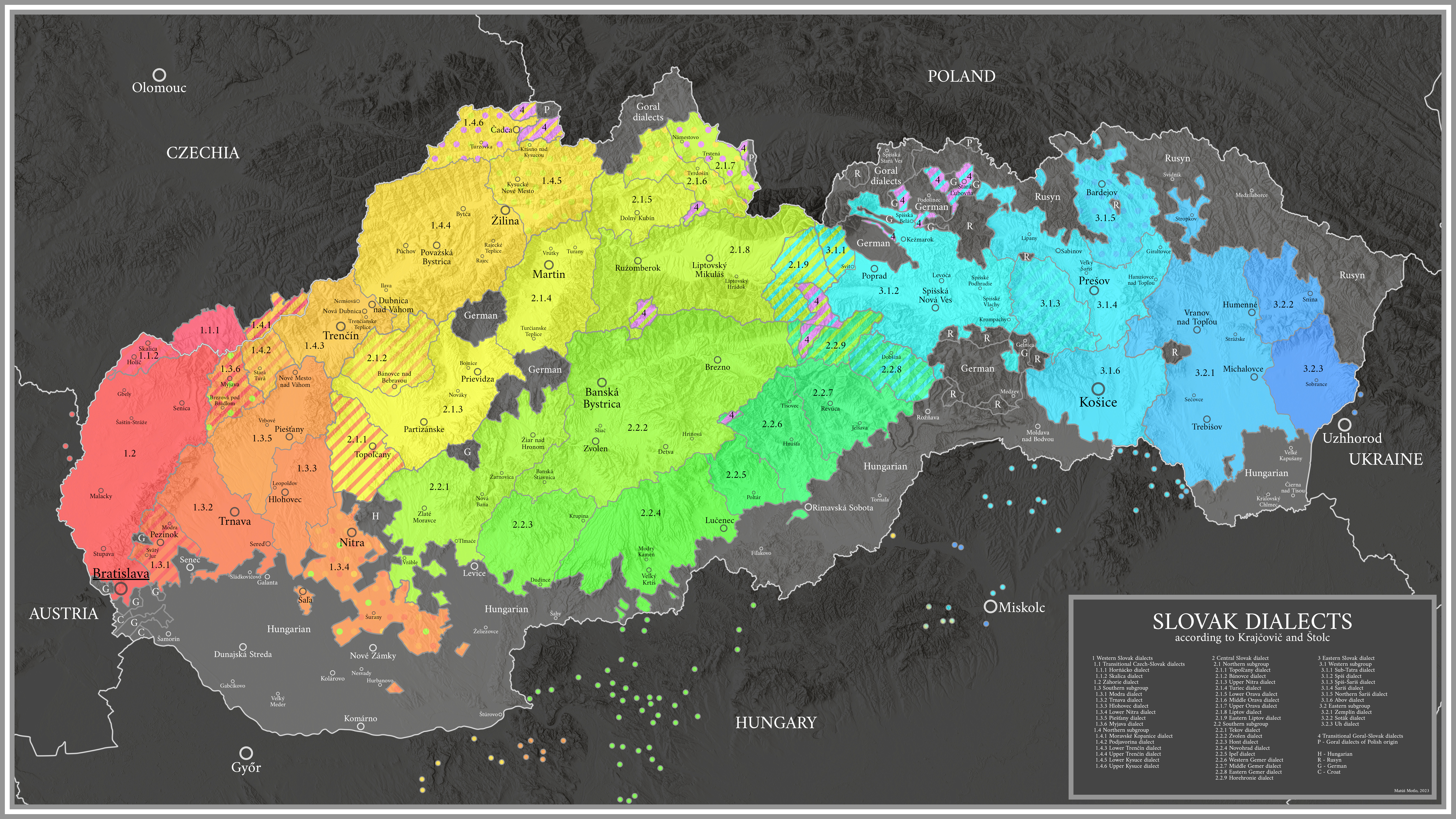
Slovak Language
Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech-Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech language, Czech, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree, as well as Polish language, Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German language, German and other Slavic languages. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)