|
Maryn Adriansen
Maryn Adriansen (1600 – c.1654) (also spelled Maryn Adriaensen, Marinus Adriaensz, Marijn Adriaensz, Marin Adriaensz, Marinus Ariaens) was an early settler to New Netherland. Originally emigrating under an Indenture agreement he later became a prominent member of society. His conflict with the governor at the time led to accusations and, eventually, acquittal. He owned property in New Amsterdam and a large plantation at Awiehaken. Background Maryn Adrieansen was born in Holland in 1600, and he came from Veere, in the Province of Zeeland. He was a boatswain from 1621 to 1627 under Captain Claes Gerritssen Compaen.. He married Lysbet Thyssen around 1628 and may have been in New Amsterdam as early as 1630 where an unnamed son was born. He died sometime before March 1654, and his widow, Lysbet Thysen, remarried Geerlief Michelsen. Rensselaerwyck Adriansen contracted with Kiliaen van Rensselaer to serve as a tobacco planter for the period of three years on January 12, 1631. He sail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to southwestern Cape Cod, while the more limited settled areas are now part of the U.S. states of New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Massachusetts and Connecticut, with small outposts in Pennsylvania and Rhode Island. The colony was conceived by the Dutch West India Company (WIC) in 1621 to capitalize on the North American fur trade. The colonization was slowed at first because of policy mismanagement by the WIC, and conflicts with Native Americans. The settlement of New Sweden by the Swedish South Company encroached on its southern flank, while its eastern border was redrawn to accommodate an expanding New England Confederation. The colony experienced dramatic growth during the 1650s, and became a major port for trade in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
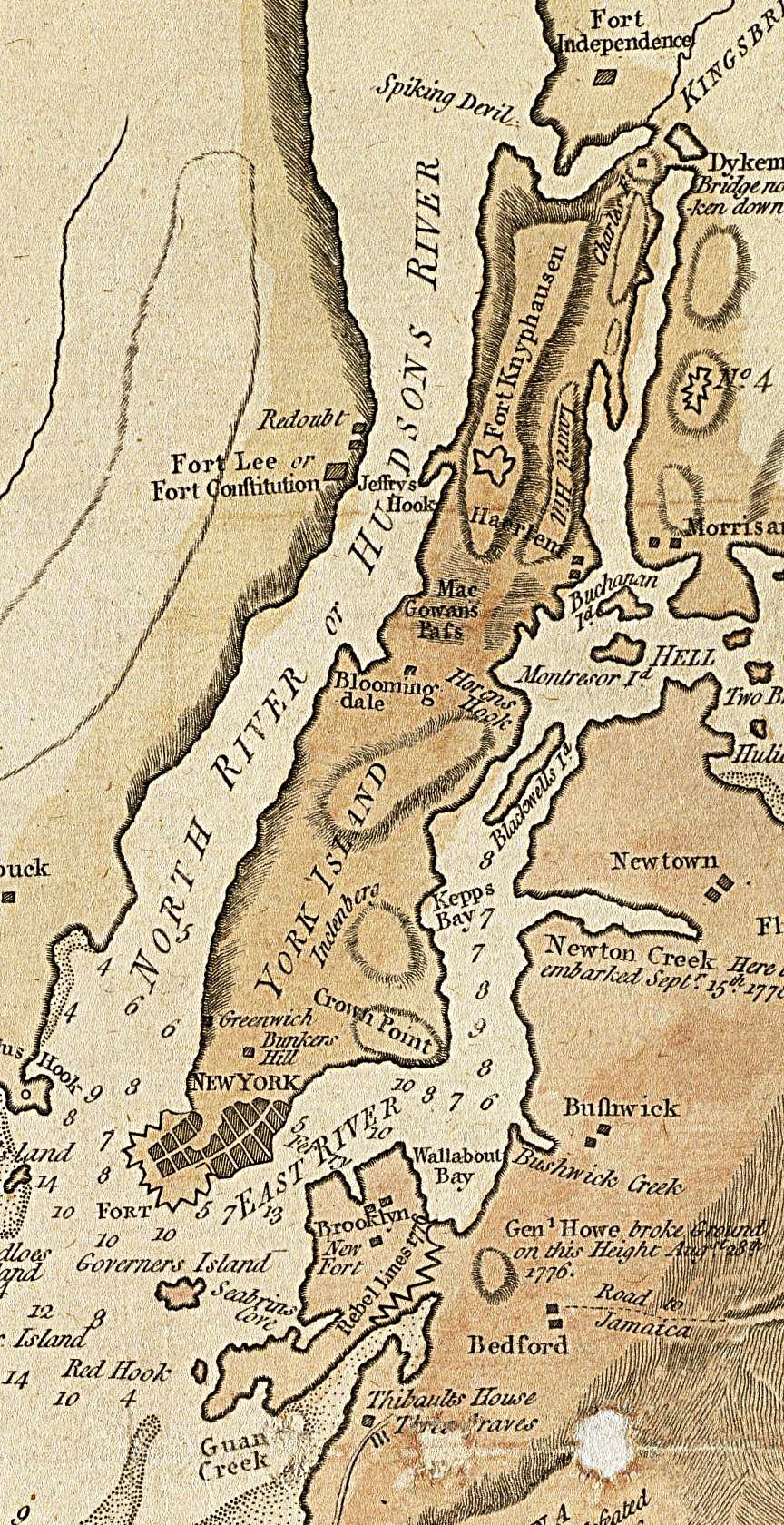
North River (Hudson River)
North River is an alternative name for the southernmost portion of the Hudson River in the vicinity of New York City and northeastern New Jersey in the United States. The entire watercourse was known as the North River by the Dutch in the early seventeenth century; the term fell out of general use for most of the river's 300+ mile course during the early 1900s. The name remains in limited use among local mariners and others and on some nautical charts and maps. The term is also used for infrastructure on and under the river, such as the North River piers, North River Tunnels, and the North River Wastewater Treatment Plant. At different times "North River" has referred to: * the entire Hudson * the approximate 160-mile portion of the Hudson below its confluence with the Mohawk River, which is under tidal influence * the portion of it running between Manhattan and New Jersey * the length flowing between Lower Manhattan and Hudson County, New Jersey. Its history is strongly conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kieft's War
Kieft's War (1643–1645), also known as the Wappinger War, was a conflict between the colonial province of New Netherland and the Wappinger and Lenape Indians in what is now New York and New Jersey. It is named for Director-General of New Netherland Willem Kieft, who had ordered an attack without approval of his advisory council and against the wishes of the colonists.Walter Giersbach, ''Governor Kieft's Personal War'' (published online, 26 Aug 2006) Dutch colonists attacked Lenape camps and massacred the inhabitants, which encouraged unification among the regional Algonquian tribes against the Dutch and precipitated waves of attacks on both sides. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massacre At Corlears Hook
The Massacre at Corlears Hook of February 25, 1643 was a colonial massacre of forty Wecquaesgeek of all ages and genders on the Lower East Side of Manhattan, perpetrated by a force led by Maryn Adriansen, acting under Willem Kieft, the Director of New Netherland. Kieft sought to take advantage of Wappinger who had been driven south by the Mohawks and Mahicans and taken refuge at their old settlement of ''Rechtauck'' on Corlears Hook, fleeing to lands controlled by their erstwhile Dutch allies. Launched on the same night as the larger Pavonia Massacre in modern Jersey City, the pair of unprovoked attacks instigated the two years' Kieft's War. An account comes from David Pietersz. de Vries David Pieterszoon de Vries ( – 13 September 1655) was a Dutch navigator from Hoorn.Joris van der MeeKoopman in de West; De indianen en de Nieuw Nederlanders in het journaal van David Pietersz. De Vries, 2001 (Dutch) Biography In 1617, De ..., the chairman of Kieft's council on Nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corlaers Hook
The Lower East Side, sometimes abbreviated as LES, is a historic neighborhood in the southeastern part of Manhattan in New York City. It is located roughly between the Bowery and the East River from Canal to Houston streets. Traditionally an immigrant, working-class neighborhood, it began rapid gentrification in the mid-2000s, prompting the National Trust for Historic Preservation to place the neighborhood on their list of America's Most Endangered Places in 2008. The Lower East Side is part of Manhattan Community District 3, and its primary ZIP Code is 10002. It is patrolled by the 7th Precinct of the New York City Police Department. Boundaries The Lower East Side is roughly bounded by East 14th Street on the north, by the East River to the east, by Fulton and Franklin Streets to the south, and by Pearl Street and Broadway to the west. This more extensive definition of the neighborhood includes Chinatown, the East Village, and Little Italy. A less extensive defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavonia Massacre
Pavonia was the first European settlement on the west bank of the North River (Hudson River) that was part of the seventeenth-century province of New Netherland in what would become the present Hudson County, New Jersey. Hudson and the Hackensack The first European to record exploration of the area was Robert Juet, first mate of Henry Hudson, an English sea captain commissioned by the Dutch East India Company. Their ship, the ''Halve Maen'' (''Half Moon''), ventured in the Kill van Kull and Newark Bay and anchored at Weehawken Cove during 1609, while exploring the Upper New York Bay and the Hudson Valley. By 1617 a ''factorij'', or trading post, was established at Communipaw. Others may have been established at Arresick or Hobokan Hackingh. Initially, these posts were set up for fur trade with the indigenous population. At that time the area was inhabited by bands of Algonquian language speaking peoples, known collectively as Lenni Lenape and later called the Delawares. Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Isaacsen Verplanck
Abraham Isaacsen Verplanck (1606–1690), also known as Abraham Isaacse Ver Planck, was an early and prominent settler in New Netherlands. A land developer and speculator, he was the progenitor of an extensive Verplanck family in the United States. Immigrating circa 1633, he received a land grant at Paulus Hook (in today's Jersey City) in 1638. He was one of the driving forces behind the bloody Kieft's War against the Native American population, set off by their retaliation to the Dutch's 1643 Pavonia massacre. His losses were so great at Pavonia he was forced to mortgage his Paulus Hook plantations. A property owner on a smaller scale on Manhattan for the remainder of his life, he died with outstanding debt, settled by his family in 1699 by sale of one of his holdings. Family Verplanck was the son of Isaac Ver Planck, born in Edam in Dutch Republic (Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden) in 1606. He married Maria de la Vigne in 1632. His children were Abigael Van L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelis Van Tienhoven
Cornelis van Tienhoven (ca. 1601 Utrecht- November 1656 ?, Manhattan ?) was secretary of the New Netherlands from 1638 to 1656 and as such one of the most influential people in New Amsterdam. Van Tienhoven was born the son of Luyt (Lucas) Cornelisz van Tienhoven and Jannetje Adriaens de Haes. He arrived in New Amsterdam as a Dutch West Indies Company accountant in 1633 on the same ship as the new director of the colony Wouter van Twiller. He was promoted to ''schout-fiscaal'' (usually translated as secretary) with the arrival of Director Willem Kieft in 1638 and retained that title under Peter Stuyvesant in 1647. In 1648 he married the 16-year-old Rachel Vigne. During the 1649 mission of Adriaen van der Donck to the Netherlands to plead to the States-General of the Netherlands for local governance for the residents of New Amsterdam, Cornelis van Tienhoven also went as the representative of Peter Stuyvesant and argued against it. When New Amsterdam was granted the right to establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrove Tuesday
Shrove Tuesday is the day before Ash Wednesday (the first day of Lent), observed in many Christian countries through participating in confession and absolution, the ritual burning of the previous year's Holy Week palms, finalizing one's Lenten sacrifice, as well as eating pancakes and other sweets. Shrove Tuesday is observed by many Christians, including Anglicans, Lutherans, Methodists and Roman Catholics, who "make a special point of self-examination, of considering what wrongs they need to repent, and what amendments of life or areas of spiritual growth they especially need to ask God's help in dealing with." This moveable feast is determined by Easter. The expression "Shrove Tuesday" comes from the word ''shrive'', meaning " absolve". As this is the last day of the Christian liturgical season historically known as Shrovetide, before the penitential season of Lent, related popular practices, such as indulging in food that one might give up as their Lenten sacrifice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Men
The Council of Twelve Men was a group of 12 men, chosen on 29 August 1641 by the residents of New Netherland to advise the Director of New Netherland, Willem Kieft, on relations with the Native Americans due to the murder of Claes Swits. Although the council was not permanent, it was the first representational form of democracy in the Dutch colony. The next two councils created were known as the Eight Men and the Nine Men. Background The Dutch West India Company had incurred significant expenses building and manning fortifications. Kieft sought to offset some of the cost by demanding contribution from the Indians, whom he saw as deriving protection from rival tribes. They declined, pointing out that the Dutch had not been invited in the first place, and with the Indian settlements so scattered, by the time word reached the fort any help dispatched would be too late. In the spring of 1640, some Raritan Indians attacked a Company trading boat near Staten Island and stole a canoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Kieft
Willem Kieft (September 1597 – September 27, 1647) was a Dutch merchant and the Director of New Netherland (of which New Amsterdam was the capital) from 1638 to 1647. Life and career Willem Kieft was appointed to the rank of director by the Dutch West India Company in 1638. He formed the council of twelve men, the first representative body in New Netherland, but ignored its advice. He tried to tax, and then, drive out, local Native Americans. He ordered attacks on Pavonia and Corlears Hook on February 25, 1643 in a massacre (129 Dutch soldiers killed 120 Indians, including women and children). The Dutch local citizen advisory group had been specifically against such a raid, and were aghast when they heard the details. "Infants were torn from their mother's breasts, and hacked to pieces in the presence of their parents, and pieces thrown into the fire and in the water, and other sucklings, being bound to small boards, were cut, stuck, and pierced, and miserably massacre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Director Of New Netherland
This is a list of Directors, appointed by the Dutch West India Company, of the 17th century Dutch province of New Netherland (''Nieuw-Nederland'' in Dutch) in North America. Only the last, Peter Stuyvesant, held the title of Director General. As the colony grew, citizens advisory boards – known as the Twelve Men, Eight Men, and Nine Men – exerted more influence on the director and thus affairs of province. There were New Netherland settlements in what later became the US states of New York, New Jersey, and Delaware, with short-lived outposts in areas of today's Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Pennsylvania. The capital, New Amsterdam, became the city of New York when the New Netherlanders provisionally ceded control of the colony to the English, who renamed the city and the rest of the province in June 1665. During the restitution to Dutch rule from August 1673 to November 1674, when New Netherland was under the jurisdiction of the City of Amsterdam, the first Dutch gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


