|
Mary Shirley, Countess Ferrers
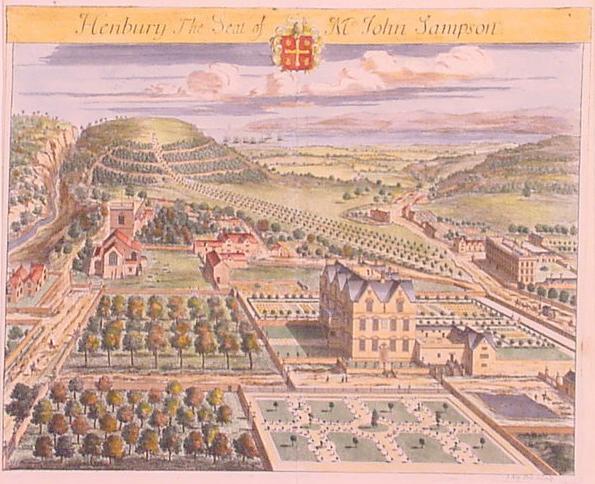
Mary Shirley, Countess Ferrers (c.1730 – 25 July 1807), formerly Mary Meredith, later Lady Frederick Campbell, was an English noblewoman. Mary was the youngest daughter of Amos Meredith of Henbury, Cheshire, and his wife, the former Joanna Cholmondeley. Her brother, William, was an MP and became 3rd Baronet Meredith in 1752, on the death of his grandfather. On 16 September 1752, she married Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers. In 1758, the couple were legally separated, with Mary citing the earl's cruelty as the cause. He was widely believed to come from a family where mental illness was congenital, and in 1760 he was found guilty of murdering one of his servants, and was hanged at Tyburn in May 1760. At his execution he wore his wedding suit, claiming that his "unhappy conduct" was the result of "a forced marriage". There were no children from the marriage, On 28 March 1769, Mary married Lord Frederick Campbell Lord Frederick Campbell (20 June 1729 – 8 June 1816) was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Frederick Campbell Gainsborough
The word ''lady'' is a term for a girl or woman, with various connotations. Once used to describe only women of a high social class or status, the equivalent of lord, now it may refer to any adult woman, as gentleman can be used for men. Informal use is sometimes euphemistic ("lady of the night" for prostitute) or, in American slang, condescending in direct address (equivalent to "mister" or "man"). "Lady" is also a formal title in the United Kingdom. "Lady" is used before the family name of a woman with a title of nobility or honorary title ''suo jure'' (in her own right), or the wife of a lord, a baronet, Scottish feudal baron, laird, or a knight, and also before the first name of the daughter of a duke, marquess, or earl. Etymology The word comes from Old English '; the first part of the word is a mutated form of ', "loaf, bread", also seen in the corresponding ', "lord". The second part is usually taken to be from the root ''dig-'', "to knead", seen also in dough; the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir William Meredith, 3rd Baronet
Sir William Meredith, 3rd Baronet (c. 1725 – 2 January 1790), was a British landowner who sat in the House of Commons from 1754 to 1780. A Rockingham Whig, he served as a Lord of the Admiralty from 1765 to 1766. Early life Meredith was the son of Amos Meredith (1688–1745) of Chester and Johanna Cholmondely, daughter of Thomas Cholmondely of Vale Royal, Chester. He matriculated at Christ Church, Oxford, on 24 March 1743, aged 18. His father died in 1744, and in 1752, he inherited his baronetcy and estates on the death of his grandfather, Sir William Meredith, 2nd Baronet. Political career At the 1754 general election, Meredith was returned unopposed as one of the two Members of Parliament for Wigan. By the time of the 1761 general election, the opposition at Wigan had consolidated against him and he stood instead for Liverpool, where he was returned after a contest. As one of the Rockingham Whigs, he served as a Lord of the Admiralty from 1765 to 1766. He was returned uno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
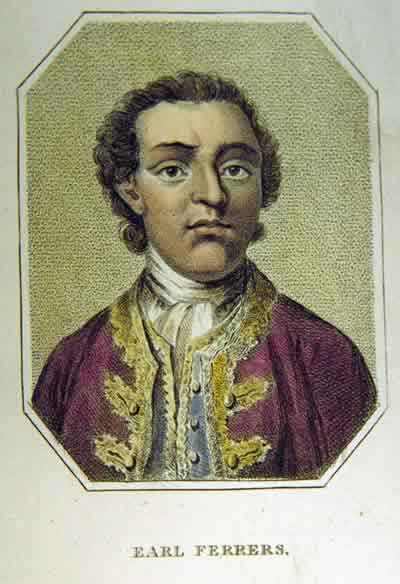
Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers
Laurence Shirley, 4th Earl Ferrers (18 August 1720 – 5 May 1760) was an English nobleman, notable for being the last peer to be hanged, following his conviction for murdering his steward. Biography Shirley was the eldest son of Laurence Ferrers, himself the third son of the first Earl Ferrers. At the age of twenty, he quit his estates and Oxford University education, and began living a debauched life in France in Paris. At the age of 25 he inherited his title from his insane uncle the 3rd Earl Ferrers, and with it estates in Leicestershire, Derbyshire and Northamptonshire. He lived at Staunton Harold Hall in northwest Leicestershire. In 1752, he married Mary, the youngest sister of Sir William Meredith, 3rd Baronet. Ferrers was also a cousin to Selina, Countess of Huntingdon, the prominent Methodist lady and supporter of George Whitefield, though he was not involved in the Methodist revival. Marriage troubles Ferrers had a family history of insanity, and from an ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroline Girle
Caroline Girle (27 December 1736 – 17 November 1817) was a diarist who kept a journal throughout her life. Although some volumes were destroyed, what remains is in the British Library. These journals earned her the sobriquet "The Oxfordshire Diarist". Girle was the daughter of John Girle (–1761) and Barbara Slaney (1717–1801), and had an elder brother, John (1735–1746). On 5 August 1762, in Whitchurch-on-Thames, Oxfordshire, Girle married Philip Lybbe Powys; they had four children: # Caroline (1763–1764) # Philip Lybbe (1765–1838) # Thomas (1768–1817) # Caroline Isabella (1775 – 28 August 1838), who married the Rev. Edward Cooper, a first cousin of Jane Austen Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots of .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Girle, Caroline 1736 birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Frederick Campbell
Lord Frederick Campbell (20 June 1729 – 8 June 1816) was a Scottish nobleman and politician. He was lord clerk register of Scotland, 1768–1816; Member of parliament, Member of Parliament (MP) for Glasgow Burghs (UK Parliament constituency), Glasgow Burghs (1761–1780) and for Argyllshire (UK Parliament constituency), Argyllshire (1780–1799). Biography Frederick Campbell was the third son of John Campbell, 4th Duke of Argyll, and his wife, Mary, daughter of John, 2nd Lord Bellenden. Lord Frederick was educated at Westminster School (1743-6) and Christ Church, Oxford (1747) before entering Middle Temple (1751) and being called to the Bar in 1754. Although his father had intended him for the parliamentary seat of Ayr Burghs, he instead succeeded his brother John Campbell, 5th Duke of Argyll, Lord Lorne to the seat of Glasgow Burghs in 1761. In 1765, being very intimate with Mr. Grenville, Lord Frederick was active in the arrangements for transferring the prerogatives and rig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combe Bank School
Radnor House Sevenoaks School (formerly Combe Bank School) is a coeducational private day school located in Sundridge (near Sevenoaks) in the English county of Kent. In 2016, The Radnor House Group officially took over Combe Bank School (a girls only independent school). The school was re-launched on 1 September 2016 as Radnor House Sevenoaks, a co-educational independent school for boys and girls aged 2–18. It is a member of the ISA and IAPS. History The five eras of the Combe Bank estate: 18th century: Campbell family – Baron Sundridge’s seat, 19th century: Cardinal Manning and William Spottiswoode, The Mond era, The Order, and school to date, World Wars: evacuation and recuperation. The Combe Bank estate has been through a number of ownerships, as with many an estate. The grade 1 listed Palladian House by Roger Morris, was built for Col John Campbell and modelled on the Argyll family seat of Inverary. It became in the early 19th century the boyhood home of Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1730s Births
Year 173 ( CLXXIII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Pompeianus (or, less frequently, year 926 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 173 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Gnaeus Claudius Severus and Tiberius Claudius Pompeianus become Roman Consuls. * Given control of the Eastern Empire, Avidius Cassius, the governor of Syria, crushes an insurrection of shepherds known as the Boukoloi. Births * Maximinus Thrax ("the Thracian"), Roman emperor (d. 238) * Mi Heng, Chinese writer and musician (d. 198) Deaths * Donatus of Muenstereifel, Roman soldier and martyr (b. AD 140 Year 140 ( CXL) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian cale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1807 Deaths
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * 18 (film), ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * Eighteen (film), ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (Dragon Ball), 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * 18 (Moby album), ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * 18 (Nana Kitade album), ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * ''18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * 18 (5 Seconds of Summer song), "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * 18 (One Direction song), "18" (One Direction song), from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaths From Fire
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain death is sometimes used as a legal definition of death. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Death is an inevitable process that eventually occurs in almost all organisms. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the similar process seen in individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said to die. As of the early 21st century, over 150,000 humans die each day, with ageing being by far the most common cause of death. Many cultures and religions have the idea of an afterlife, and also may hold the idea of judgement of good and bad deeds in one's life (heaven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Countesses
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daughters Of Baronets
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show relations between groups or elements. From biological perspective, a daughter is a first degree relative. The word daughter also has several other connotations attached to it, one of these being used in reference to a female descendant or consanguinity. It can also be used as a term of endearment coming from an elder. In patriarchal societies, daughters often have different or lesser familial rights than sons. A family may prefer to have sons rather than daughters and subject daughters to female infanticide. In some societies it is the custom for a daughter to be 'sold' to her husband, who must pay a bride price. The reverse of this custom, where the parents pay the husband a sum of money to compensate for the financial burden of the woman and is known as a do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_by_Henry_Raeburn.jpg)
