|
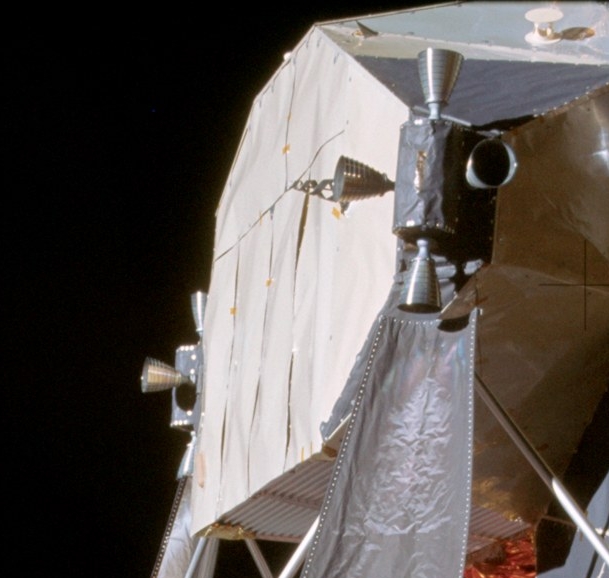
Martin X-23 PRIME
The Martin X-23A PRIME (Precision Reentry Including Maneuvering reEntry) (SV-5D) was a small lifting-body re-entry vehicle tested by the United States Air Force in the mid-1960s. Unlike ASSET, primarily used for structural and heating research, the X-23A PRIME was developed to study the effects of maneuvering during re-entry of Earth's atmosphere, including cross-range maneuvers up to from the ballistic track. Design Each X-23A was constructed from titanium, beryllium, stainless steel, and aluminium. The craft consisted of two sections—the aft main structure and a removable forward "glove section". The structure was completely covered with a Martin-developed ablative heat shield thick, and the nose cap was constructed of carbon phenolic material. Aerodynamic control was provided by a pair of lower flaps, and fixed upper flaps and rudders. A nitrogen-gas reaction control system was used outside the atmosphere. At Mach 2 a drogue ballute deployed and slowed the vehicle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolytic Carbon
Pyrolytic carbon is a material similar to graphite, but with some covalent bonding between its graphene sheets as a result of imperfections in its production. Pyrolytic carbon is man-made and is thought not to be found in nature.Ratner, Buddy D. (2004). Pyrolytic carbon. In Biomaterials science: an introduction to materials in medicine'. Academic Press. p. 171-180. . Google Book Search. Retrieved 7 July 2011. Generally it is produced by heating a hydrocarbon nearly to its decomposition temperature, and permitting the graphite to crystalize (pyrolysis). One method is to heat synthetic fibers in a vacuum. It is used in high temperature applications such as missile nose cones, rocket motors, heat shields, laboratory furnaces, in graphite-reinforced plastic, coating nuclear fuel particles, and in biomedical prostheses. Physical properties Pyrolytic graphite samples usually have a single cleavage (crystal), cleavage plane, similar to mica, because the graphene sheets crystallize in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandenberg AFB
Vandenberg Space Force Base , previously Vandenberg Air Force Base, is a United States Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County, California. Established in 1941, Vandenberg Space Force Base is a space launch base, launching spacecraft from the Western Range, and also performs missile testing. The United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 30 serves as the host delta for the base. In addition to its military space launch mission, Vandenberg Space Force Base also performs space launches for civil and commercial space entities, such as NASA and SpaceX. History United States Army Camp Cooke (1941–1953) In 1941, the United States Army embarked on an initiative to acquire lands in the United States to be used to train its infantry and armored forces. These areas needed to be of a varied nature to ensure relevant training. In March 1941, the Army acquired approximately of open ranch lands along the Central Coast of California between Lompoc and Santa Maria. Most of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed C-130 Hercules
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 was originally designed as a troop, medevac, and cargo transport aircraft. The versatile airframe has found uses in other roles, including as a gunship (AC-130), for airborne assault, search and rescue, scientific research support, weather reconnaissance, aerial refueling, maritime patrol, and aerial firefighting. It is now the main tactical airlifter for many military forces worldwide. More than 40 variants of the Hercules, including civilian versions marketed as the Lockheed L-100, operate in more than 60 nations. The C-130 entered service with the U.S. in 1956, followed by Australia and many other nations. During its years of service, the Hercules has participated in numerous military, civilian and humanitarian aid operations. In 2007, the C-130 became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-air Retrieval
Mid-air retrieval is a technique used in atmospheric reentry when the reentering vehicle is incapable of a satisfactory unassisted landing. The vehicle is slowed by means of parachutes, and then a specially-equipped aircraft matches the vehicle's trajectory and catches it in mid-air. This is a risky technique, and so is only used when other forms of landing are infeasible. Successful mid-air retrieval requires correct operation of the retrieving aircraft, favourable atmospheric conditions, and successful execution of a tricky manoeuvre, in addition to correct operation of the vehicle itself. These risks can be mitigated somewhat: for example, multiple recovery aircraft can be used. The need for human aviators to perform a manoeuvre which would normally be classed as a stunt may in the future be avoided by advances in unmanned aerial vehicles. Notable uses of the technique: * The first use of midair retrieval was in 1955, with Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar transports being used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or, in a ram-air parachute, aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, who can exit from an aircraft at height and descend safely to earth. A parachute is usually made of a light, strong fabric. Early parachutes were made of silk. The most common fabric today is nylon. A parachute's canopy is typically dome-shaped, but some are rectangles, inverted domes, and other shapes. A variety of loads are attached to parachutes, including people, food, equipment, space capsules, and bombs. History Middle Ages In 852, in Córdoba, Spain, the Moorish man Armen Firman attempted unsuccessfully to fly by jumping from a tower while wearing a large cloak. It was recorded that "there was enough air in the folds of his cloak to prevent great injury when he reached the ground." Early Renaissance The earliest evidence f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballute
The ballute (a portmanteau of ''balloon'' and ''parachute'') is a parachute-like braking device optimized for use at high altitudes and supersonic velocities. The original ballute configuration was invented in 1948 by the Goodyear company. The innovation soon caught the attention of other organisations, including NASA; the agency incorporated ballutes into the escape system of the Gemini spacecraft. It has subsequently seen extensive use within the aerospace sector as a means of retarding the descent of various payloads, such as sections of rockets and atmospheric probes. Various proposals involving ballutes, such as for deorbiting/recovering low-mass satellites and interplanetary research programmes, have been issued in recent decades. Design The ballute is an inflatable device used to generate drag. In terms of its basic configuration, it is a cone-shaped balloon, featuring a toroidal burble fence (an inflated structure intended to ensure flow separation) that is fitted aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drogue
A drogue (also known as a storm drogue) is a device trailed behind a boat on a long line attached to the stern. A drogue is used to slow the boat down in a storm and to prevent the hull (watercraft), hull from becoming side-on to the water waves, waves. A boat that has deployed a drogue should not overspeed down the slope of a wave and crash into the next one, nor will the vessel Broach (sailing), broach. By slowing the vessel, the drogue makes the vessel easier to control in heavy weather and will help to prevent wikt:pitchpole, pitchpoling. A drogue works by providing substantial Drag (physics), resistance when dragged through the water. An alternative device is the sea anchor, a much larger item than a drogue, which is streamed from the bows. The advantage of the sea anchor is that the bows of a yacht are invariably finer than the stern, thereby giving a safer and more comfortable experience in a storm. Both drogues and sea anchors will have "tripping lines" to aid recovery o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mach Number
Mach number (M or Ma) (; ) is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics representing the ratio of flow velocity past a boundary to the local speed of sound. It is named after the Moravian physicist and philosopher Ernst Mach. : \mathrm = \frac, where: : is the local Mach number, : is the local flow velocity with respect to the boundaries (either internal, such as an object immersed in the flow, or external, like a channel), and : is the speed of sound in the medium, which in air varies with the square root of the thermodynamic temperature. By definition, at Mach1, the local flow velocity is equal to the speed of sound. At Mach0.65, is 65% of the speed of sound (subsonic), and, at Mach1.35, is 35% faster than the speed of sound (supersonic). Pilots of high-altitude aerospace vehicles use flight Mach number to express a vehicle's true airspeed, but the flow field around a vehicle varies in three dimensions, with corresponding variations in local Mach number. The local spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses thrusters to provide attitude control and translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels are used for attitude control. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation (roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small ( vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecraft reaction control systems are used for: * attitude control during different stages of a mission; * station keeping in orbit; * close maneuvering during docking procedures; * control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)