|
Martin Bladen Hawke, 7th Baron Hawke
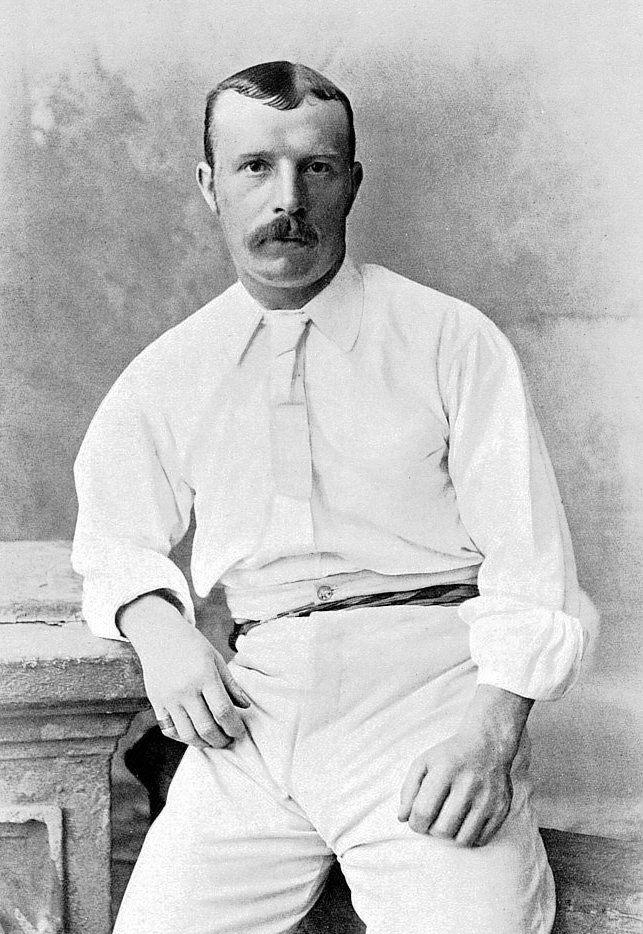
Martin Bladen Hawke, 7th Baron Hawke (16 August 1860 – 10 October 1938), generally known as Lord Hawke, was an English amateur cricketer active from 1881 to 1911 who played for Yorkshire and England. He was born in Willingham by Stow, near Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, and died in Edinburgh. He appeared in 633 first-class matches, including five Test matches, as a righthanded batsman, scoring 16,749 runs with a highest score of 166 and held 209 catches. He scored 13 centuries and 69 half-centuries. Since an 1870 inheritance of his father, Hawke was styled ; he inherited the barony on 5 December 1887 on the death of his father, Edward Henry Julius Hawke, Rector of Willingham 1854–1875, after which the family returned to its seat (main home held for a generation or more), Wighill House and Park, near Tadcaster, Yorkshire. Admiral Hawke, the first Baron, was among the few Admirals elevated for his roles during the Seven Years' War: at the Battle of Quiberon Bay, off N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is always pronounced. Countries with common or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century (cricket)
In cricket, a century is a score of 100 or more runs in a single innings by a batsman. The term is also included in "century partnership" which occurs when two batsmen add 100 runs to the team total when they are batting together. A century is regarded as a landmark score for batsmen and a player's number of centuries is generally recorded in their career statistics. Scoring a century is loosely equivalent in merit to a bowler taking a five-wicket haul, and is commonly referred to as a ton or hundred. Scores of more than 200 runs are still statistically counted as a century, although these scores are referred to as double (200–299 runs), triple (300–399 runs), and quadruple centuries (400–499 runs), and so on. Accordingly, reaching 50 runs in an innings is known as a half-century; if the batsman then goes on to score a century, the half-century is succeeded in statistics by the century. Scoring a century at Lord's earns the batsman a place on the Lord's honours boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1885 English Cricket Season
1885 was the 99th season of cricket in England since the foundation of Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC). It was the third in succession in which Nottinghamshire was proclaimed the champion county. Champion County * Nottinghamshire Playing record (by county) Leading batsmen (qualification 20 innings) Leading bowlers (qualification 1,000 balls) Notable events * 1 June – Kent captain Lord Harris writes a letter to Lancashire concerning the "unfair" bowling of Nash and Crossland and decides not to play Lancashire unless they refrain from employing those two bowlers – the refusal is maintained even when the pair drop out. * On 17 July, Johnny Briggs and Dick Pilling playing for Lancashire against Surrey set a record stand for the tenth wicket of 173, which stands until 1899.Webber, Roy; ''The Playfair Book of Cricket Records''; p. 127. Published 1951 by Playfair Books. Notes References Annual reviews * ''James Lillywhite’s Cricketers’ Annual'' (Red Lilly), Lillyw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (cricket)
The captain of a cricket team, often referred to as the skipper, is the appointed leader, having several additional roles and responsibilities over and above those of the other players. As in other sports, the captain is usually experienced and has good communication skills, and is likely to be one of the most regular members of the team, as the captain is responsible for the team selection. Before the game the captains toss for innings. During the match the captain decides the team's batting order, who will bowl each over, and where each fielder will be positioned. While the captain has the final say, decisions are often collaborative. A captain's knowledge of the complexities of cricket strategy and tactics, and shrewdness in the field, may contribute significantly to the team's success. Due to the smaller coaching/management role played out by support staff, as well as the need for greater on-field decision-making, the captain of a cricket team typically shoulders more re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue (university Sport)
A blue is an award of sporting colours earned by athletes at some universities and schools for competition at the highest level. The awarding of blues began at Oxford and Cambridge universities in England. They are now awarded at a number of other British universities and at some universities in Australia, Canada and New Zealand. History The first sporting contest between the universities of Oxford and Cambridge was held on 4 June 1827, when a two-day cricket match at Lord's, organized by Charles Wordsworth, nephew of the poet William, resulted in a draw. There is no record of any university "colours" being worn during the game. At the first Boat Race in 1829, the Oxford crew was dominated by students of Christ Church, whose college colours were dark blue. They wore white shirts with dark blue stripes, while Cambridge wore white with a pink or scarlet sash. At the second race, in 1836, a light blue ribbon was attached to the front of the Cambridge boat, as it was the colour of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalene College, Cambridge
Magdalene College ( ) is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college was founded in 1428 as a Benedictine hostel, in time coming to be known as Buckingham College, before being refounded in 1542 as the College of St Mary Magdalene. Magdalene counted some of the greatest men in the realm among its benefactors, including Britain's premier noble the Duke of Norfolk, the Duke of Buckingham and Lord Chief Justice Christopher Wray. Thomas Audley, Lord Chancellor under Henry VIII, was responsible for the refoundation of the college and also established its motto—''garde ta foy'' (Old French: "keep your faith"). Audley's successors in the Mastership and as benefactors of the College were, however, prone to dire ends; several benefactors were arraigned at various stages on charges of high treason and executed. The college remains one of the smaller in the University, numbering some 300 undergraduates. It has maintained strong academic performance over the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eton College
Eton College () is a public school in Eton, Berkshire, England. It was founded in 1440 by Henry VI under the name ''Kynge's College of Our Ladye of Eton besyde Windesore'',Nevill, p. 3 ff. intended as a sister institution to King's College, Cambridge, making it the 18th-oldest Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference (HMC) school. Eton is particularly well-known for its history, wealth, and notable alumni, called Old Etonians. Eton is one of only three public schools, along with Harrow (1572) and Radley (1847), to have retained the boys-only, boarding-only tradition, which means that its boys live at the school seven days a week. The remainder (such as Rugby in 1976, Charterhouse in 1971, Westminster in 1973, and Shrewsbury in 2015) have since become co-educational or, in the case of Winchester, as of 2021 are undergoing the transition to that status. Eton has educated prime ministers, world leaders, Nobel laureates, Academy Award and BAFTA award-winning actors, and ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Squadron
The Western Squadron was a squadron or formation (military), formation of the Royal Navy based at Plymouth Dockyard. It operated in waters of the English Channel, the Western Approaches, and the North Atlantic. It defended British trade sea lanes from 1650 to 1814 and 1831 to 1854. Following Admiralty orders to Lord Anson he was instructed to combine all existing commands in the English Channel - those at the Downs Station, Downs, Admiral of the Narrow Seas, Narrow Seas, Commander-in-Chief, Plymouth, Plymouth and the Commander-in-Chief, English Channel (Royal Navy), Spithead - under a centralized command under the Commander-in-Chief, Western Squadron in 1746. The squadron was commanded by the Flag Officer with the dual title of Commander-in-Chief, English Channel and Commander-in-Chief, Western Squadron History In 1650 Captain William Penn (Royal Navy officer), William Penn, was charged with guarding the Channel from Beachy Head to Land's End with six ships. This system continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabitants (2018). With Saint-Nazaire, a seaport on the Loire estuary, Nantes forms one of the main north-western French metropolitan agglomerations. It is the administrative seat of the Loire-Atlantique department and the Pays de la Loire region, one of 18 regions of France. Nantes belongs historically and culturally to Brittany, a former duchy and province, and its omission from the modern administrative region of Brittany is controversial. Nantes was identified during classical antiquity as a port on the Loire. It was the seat of a bishopric at the end of the Roman era before it was conquered by the Bretons in 851. Although Nantes was the primary residence of the 15th-century dukes of Brittany, Rennes became the provincial capital after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Quiberon Bay
The Battle of Quiberon Bay (known as ''Bataille des Cardinaux'' in French) was a decisive naval engagement during the Seven Years' War. It was fought on 20 November 1759 between the Royal Navy and the French Navy in Quiberon Bay, off the coast of France near St. Nazaire. The battle was the culmination of British efforts to eliminate French naval superiority, which could have given the French the ability to carry out their planned invasion of Great Britain. A British fleet of 24 ships of the line under Sir Edward Hawke tracked down and engaged a French fleet of 21 ships of the line under Marshal de Conflans. After hard fighting, the British fleet sank or ran aground six French ships, captured one and scattered the rest, giving the Royal Navy one of its greatest victories, and ending the threat of French invasion for good. The battle signalled the rise of the Royal Navy in becoming the world's foremost naval power, and, for the British, was part of the Annus Mirabilis of 1759 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Hawke, 1st Baron Hawke
Edward Hawke, 1st Baron Hawke, KB, PC (21 February 1705 – 17 October 1781), of Scarthingwell Hall in the parish of Towton, near Tadcaster, Yorkshire, was a Royal Navy officer. As captain of the third-rate , he took part in the Battle of Toulon in February 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession. He also captured six ships of a French squadron in the Bay of Biscay in the Second Battle of Cape Finisterre in October 1747. Hawke went on to achieve a victory over a French fleet at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November 1759 during the Seven Years' War, preventing a French invasion of Britain. He developed the concept of a Western Squadron, keeping an almost continuous blockade of the French coast throughout the war. Hawke also sat in the House of Commons from 1747 to 1776 and served as First Lord of the Admiralty for five years between 1766 and 1771. In this post, he was successful in bringing the navy's spending under control and also oversaw the mobilisation of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(cropped).jpg)




.jpg)