|
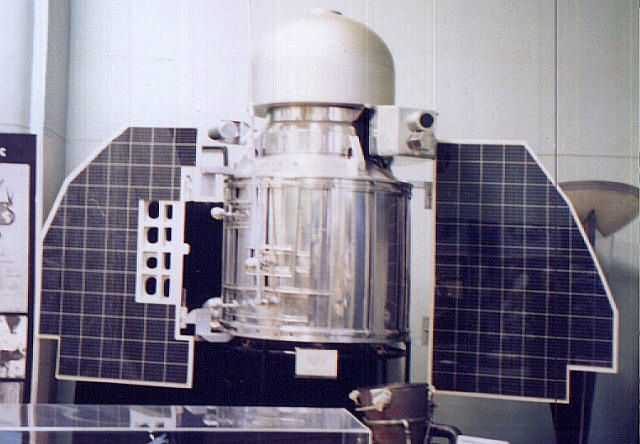
Mars 1M
Mars 1M was a series of two uncrewed spacecraft which were used in the first Soviet missions to explore Mars. They were the earliest missions of the Mars program. The Western media dubbed the spacecraft "''Marsnik''", a portmanteau of ''Mars'' and ''Sputnik''. Spacecraft Mars 1M No.1, known in the West as Marsnik 1, Mars 1960A and Korabl 4, was destroyed in a launch failure on October 10, 1960. In 1962, NASA Administrator James E. Webb informed the United States Congress that NASA believed the mission was an attempt at a Mars flyby probe. Some Soviet scientists involved with the program at that time claim no knowledge of this mission, stating that only the second launch was an intended Mars mission. However, V. G. Perminov, the leading designer of planetary spacecraft at the Lavochkin design bureau, states that this mission was indeed intended for Mars and was identical to the later mission. Mars 1M No.2, known in the West as Marsnik 2, Korabl 5 and Mars 1960B, was launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaic Module
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors. A photovoltaic system employs solar modules, each comprising a number of solar cells, which generate electrical power. PV installations may be ground-mounted, rooftop-mounted, wall-mounted or floating. The mount may be fixed or use a solar tracker to follow the sun across the sky. Photovoltaic technology helps to mitigate climate change because it emits much less carbon dioxide than fossil fuels. Solar PV has specific advantages as an energy source: once installed, its operation generates no pollution and no greenhouse gas emissions, it shows scalability in respect of power needs and silicon has large availability in the Earth's crust, although other materials required in PV sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Gain Antenna
A directional antenna or beam antenna is an antenna which radiates or receives greater power in specific directions allowing increased performance and reduced interference from unwanted sources. Directional antennas provide increased performance over dipole antennas—or omnidirectional antennas in general—when greater concentration of radiation in a certain direction is desired. A high-gain antenna (HGA) is a directional antenna with a focused, narrow radiowave beam width, permitting more precise targeting of the radio signals. Most commonly referred to during space missions, these antennas are also in use all over Earth, most successfully in flat, open areas where there are no mountains to disrupt radiowaves. By contrast, a low-gain antenna (LGA) is an omnidirectional antenna with a broad radiowave beam width, that allows the signal to propagate reasonably well even in mountainous regions and is thus more reliable regardless of terrain. Low-gain antennas are often used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver-oxide Battery
A silver-oxide battery (IEC code: S) is a primary cell using silver oxide as the cathode material and zinc for the anode. These cells maintain a nearly constant nominal voltage during discharge until fully depleted. They are available in small sizes as button cells, where the amount of silver used is minimal and not a prohibitively expensive contributor to the overall product cost. Silver-oxide primary batteries account for 30% of all primary battery sales in Japan (64 out of 212 million in February 2020). Silver-oxide batteries were used on Apollo program lunar missions for the lunar module and lunar rover power supplies because of their high energy-to-weight ratio.Lyons, Pete; "10 Best Ahead-of-Their-Time Machines", ''Car and Driver'', Jan. 1988, p.78 Chemistry A silver-oxide battery uses silver(I) oxide as the positive electrode (cathode), zinc as the negative electrode (anode), plus an alkaline electrolyte, usually sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipropellant Rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket utilizes a rocket engine that uses liquid propellants. Liquids are desirable because they have a reasonably high density and high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. It is also possible to use lightweight centrifugal turbopumps to pump the rocket propellant from the tanks into the combustion chamber, which means that the propellants can be kept under low pressure. This permits the use of low-mass propellant tanks that do not need to resist the high pressures needed to store significant amounts of gasses, resulting in a low mass ratio for the rocket. An inert gas stored in a tank at a high pressure is sometimes used instead of pumps in simpler small engines to force the propellants into the combustion chamber. These engines may have a higher mass ratio, but are usually more reliable, and are therefore used widely in satellites for orbit maintenance. Liquid rockets can be mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as pigments in inks and dyes. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH; 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, НДМГ or codenamed Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is used as a rocket propellant. It is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical for organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. In concentration between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine, 1,2-dimethylhydrazine is also known but is not as useful. Production UDMH is produced industrially by two routes. Based on the Olin Raschig process, one method involves reaction of monochloramine with dimethylamine giving 1,1-dimethylhydrazinium chloride: :(CH3)2NH + NH2Cl → (CH3)2NNH2 ⋅ HCl In the presence of suitable catalysts, acetylhydrazine can be N-dimethylated using formaldehyde and hydrogen to give the N,N-dimethyl-N'-acetylhydrazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimulus (physiology), stimuli, metabolism, energy transformation, and reproduction. Various forms of life exist, such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. Biology is the science that studies life. The gene is the unit of heredity, whereas the Cell (biology), cell is the structural and functional unit of life. There are two kinds of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, both of which consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane and contain many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Cells reproduce through a process of cell division, in which the parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells and passes its genes onto a new generation, sometimes producing genetic variation. Organisms, or the individual en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. The IAU officially defines meteorites as 30 micrometers to 1 meter; micrometeorites are the small end of the range (~submillimeter). They are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter Earth's atmosphere at high velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through atmospheric friction and compression. Micrometeorites individually weigh between 10−9 and 10−4 g and collectively comprise most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present-day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to describe dust-sized objects that fall to the Earth. Sometimes meteoroids and micrometeoroids entering the Earth's atmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometer
A radiometer or roentgenometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of electromagnetic radiation. Generally, a radiometer is an infrared radiation detector or an ultraviolet detector. Microwave radiometers operate in the microwave wavelengths. While the term ''radiometer'' can refer to any device that measures electromagnetic radiation (e.g. light), the term is often used to refer specifically to a Crookes radiometer ("light-mill"), a device invented in 1873 in which a rotor (having vanes which are dark on one side, and light on the other) in a partial vacuum spins when exposed to light. A common belief (one originally held even by Crookes) is that the momentum of the absorbed light on the black faces makes the radiometer operate. If this were true, however, the radiometer would spin away from the non-black faces, since the photons bouncing off those faces impart more momentum than the photons absorbed on the black faces. Photons do exert radiation pressure on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

