|
Marnaviridae Genome Edit
''Marnaviridae'' is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. The first species of this family that was isolated is ''Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus'' (HaRNAV) in the genus ''Marnavirus'', that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, ''Heterosigma akashiwo''. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family. HaRNAV was isolated from water collected in the Strait of Georgia in British Columbia, Canada, from a concentrated virus assemblage using the host ''Heterosigma akashiwo'' (NEPCC 522). It must not be confused with two other unrelated viruses that infect this host, ''Heterosigma akashiwo virus 01'' (HaV-1, isolate: HaV53) in the genus ''Raphidovirus'', and '' Heterosigma akashiwo Nuclear Inclusion Virus'' (HaNIV). Taxonomy The family contains the following seven genera: *'' Bacillarnavirus'' *'' Kusarnavirus'' *'' Labyrnavirus'' *'' Locarnavirus'' *''Marnavirus'' *'' Salish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillarnavirus
''Bacillarnavirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Marine diatoms serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Taxonomy The genus contains the following three species: *'' Chaetoceros socialis forma radians RNA virus 1'' *''Chaetoceros tenuissimus RNA virus 01 ''Chaetoceros'' is probably the largest genus of marine planktonic diatoms with approximately 400 species described, although many of these descriptions are no longer valid. It is often very difficult to distinguish between different ''Chaeto ...'' *'' Rhizosolenia setigera RNA virus 01'' Structure Viruses in ''Bacillarnavirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral, spherical, and round geometries, and T=pseudo3 symmetry. The diameter is around 30-32 nm. Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 8.8-9.5kb in length. The genome has 2 open reading frames. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the virus to host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosigma Akashiwo
''Heterosigma akashiwo'' is a species of microscopic algae of the class Raphidophyceae. It is a swimming marine alga that episodically forms toxic surface aggregations known as harmful algal bloom. The species name ''akashiwo'' is from the Japanese for "red tide". Synonyms include ''Olisthodiscus luteus'' (Hulburt 1965), and ''Entomosigma akashiwo'' (Hada 1967). ''H. akashiwo'' and ''H. inlandica'' have been recognized as two species of ''Heterosigma''. However, Hara and Chihara (1987) described both specimens as one species, validly describing them as ''H. akashiwo''. Description ''H. akashiwo'' cells are relatively small, ranging in size from 18 to 34 μm in diameter. They appear golden brown, and appear in clusters. Morphology is highly variable, but does not appear to vary significantly between locations. One culture may contain flat or round individual cells. Molecular techniques for identification (including quantitative PCR) are preferred over traditional mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
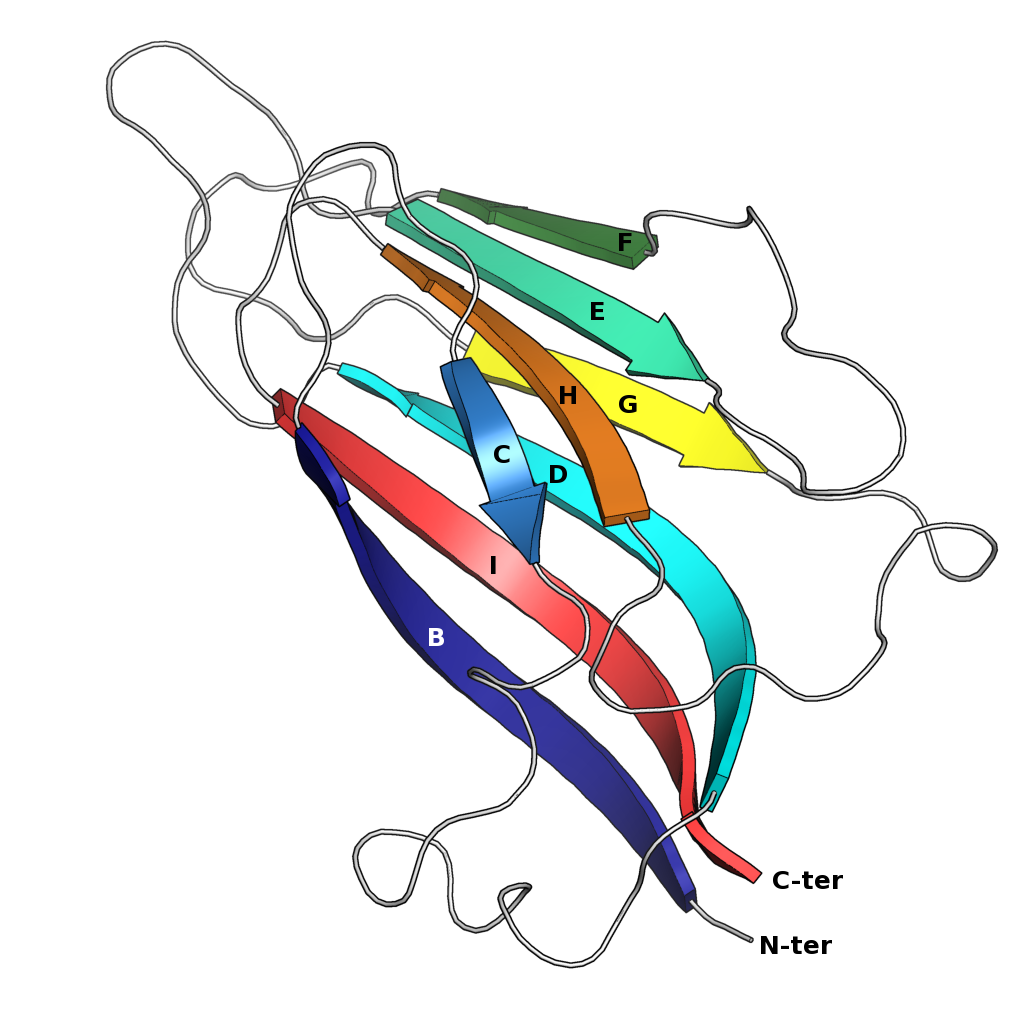
Jelly Roll Fold
The jelly roll or Swiss roll fold is a protein fold or supersecondary structure composed of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded sheets. The name of the structure was introduced by Jane S. Richardson in 1981, reflecting its resemblance to the jelly or Swiss roll cake. The fold is an elaboration on the Greek key motif and is sometimes considered a form of beta barrel. It is very common in viral proteins, particularly viral capsid proteins. Taken together, the jelly roll and Greek key structures comprise around 30% of the all-beta proteins annotated in the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database. Structure The basic jelly roll structure consists of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded antiparallel beta sheets which pack together across a hydrophobic interface here citation... uniprot The strands are traditionally labeled B through I for the historical reason that the first solved structure, of a jelly roll capsid protein from the tomato bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marnaviridae Virion
''Marnaviridae'' is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. The first species of this family that was isolated is ''Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus'' (HaRNAV) in the genus ''Marnavirus'', that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, ''Heterosigma akashiwo''. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family. HaRNAV was isolated from water collected in the Strait of Georgia in British Columbia, Canada, from a concentrated virus assemblage using the host ''Heterosigma akashiwo'' (NEPCC 522). It must not be confused with two other unrelated viruses that infect this host, ''Heterosigma akashiwo virus 01'' (HaV-1, isolate: HaV53) in the genus ''Raphidovirus'', and '' Heterosigma akashiwo Nuclear Inclusion Virus'' (HaNIV). Taxonomy The family contains the following seven genera: *'' Bacillarnavirus'' *'' Kusarnavirus'' *'' Labyrnavirus'' *'' Locarnavirus'' *''Marnavirus'' *'' Salish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marnaviridae Genome Edit
''Marnaviridae'' is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order ''Picornavirales''. The first species of this family that was isolated is ''Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus'' (HaRNAV) in the genus ''Marnavirus'', that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, ''Heterosigma akashiwo''. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family. HaRNAV was isolated from water collected in the Strait of Georgia in British Columbia, Canada, from a concentrated virus assemblage using the host ''Heterosigma akashiwo'' (NEPCC 522). It must not be confused with two other unrelated viruses that infect this host, ''Heterosigma akashiwo virus 01'' (HaV-1, isolate: HaV53) in the genus ''Raphidovirus'', and '' Heterosigma akashiwo Nuclear Inclusion Virus'' (HaNIV). Taxonomy The family contains the following seven genera: *'' Bacillarnavirus'' *'' Kusarnavirus'' *'' Labyrnavirus'' *'' Locarnavirus'' *''Marnavirus'' *'' Salish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosigma Akashiwo Nuclear Inclusion Virus
''Heterosigma akashiwo'' is a species of microscopic algae of the class Raphidophyceae. It is a swimming marine alga that episodically forms toxic surface aggregations known as harmful algal bloom. The species name ''akashiwo'' is from the Japanese for "red tide". Synonyms include ''Olisthodiscus luteus'' (Hulburt 1965), and ''Entomosigma akashiwo'' (Hada 1967). ''H. akashiwo'' and ''H. inlandica'' have been recognized as two species of ''Heterosigma''. However, Hara and Chihara (1987) described both specimens as one species, validly describing them as ''H. akashiwo''. Description ''H. akashiwo'' cells are relatively small, ranging in size from 18 to 34 μm in diameter. They appear golden brown, and appear in clusters. Morphology is highly variable, but does not appear to vary significantly between locations. One culture may contain flat or round individual cells. Molecular techniques for identification (including quantitative PCR) are preferred over traditional micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphidovirus
''Raphidovirus'' (likely misspelled ''Rhaphidovirus'') is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Phycodnaviridae ''Phycodnaviridae'' is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid (polyhedron with 20 fac ...''. Alga serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: ''Heterosigma akashiwo virus 01'' (HaV01). Structure Viruses in ''Raphidovirus'' are enveloped, with icosahedral and round geometries, and T=169 symmetry. The diameter is around 100-220 nm. Genomes are linear, around 295kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is nucleo-cytoplasmic. Replication follows the DNA strand displacement model. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by lysis via lytic phospholipids. Alga serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Georgia
The Strait of Georgia (french: Détroit de Géorgie) or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately long and varies in width from .Environmental History and Features of Puget Sound , NOAA-NWFSC Along with the and , it is a constituent part of the |
Raphidophyte
The raphidophytes, formally known as Raphidomonadea or Raphidophyceae (formerly referred to as Chloromonadophyceae and Chloromonadineae), are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes both marine and freshwater species. All raphidophytes are unicellular, with large cells (50 to 100 μm), but no cell walls. Raphidophytes possess a pair of flagella, organised such that both originate from the same invagination (or gullet). One flagellum points forwards, and is covered in hair-like mastigonemes, while the other points backwards across the cell surface, lying within a ventral groove. Raphidophytes contain numerous ellipsoid chloroplasts, which contain chlorophylls a, c1 and c2. They also make use of accessory pigments including β-carotene and diadinoxanthin. Unlike other heterokontophytes, raphidophytes do not possess the photoreceptive organelle (or eyespot) typical of this group. In terms of ecology, raphidophytes occur as photosynthetic autotrophs across a range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


