|
Markov Theorem
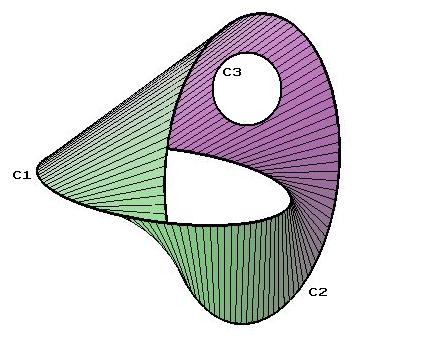
In mathematics the Markov theorem gives necessary and sufficient conditions for two braids to have closures that are equivalent knots or links. The conditions are stated in terms of the group structures on braids. Braids are algebraic objects described by diagrams; the relation to topology is given by Alexander's theorem which states that every knot or link in three-dimensional Euclidean space is the closure of a braid A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair. The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-strande .... The Markov theorem, proved by Russian mathematician Andrei Andreevich Markov Jr. describes the elementary moves generating the equivalence relation on braids given by the equivalence of their closures. More precisely Markov's theorem can be stated as follows:, p.95 given two braids represented by elements \beta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braid (mathematics)
A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing three or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair. The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-stranded structure. More complex patterns can be constructed from an arbitrary number of strands to create a wider range of structures (such as a fishtail braid, a five-stranded braid, rope braid, a French braid and a waterfall braid). The structure is usually long and narrow with each component strand functionally equivalent in zigzagging forward through the overlapping mass of the others. It can be compared with the process of weaving, which usually involves two separate perpendicular groups of strands (warp and weft). Historically, the materials used have depended on the indigenous plants and animals available in the local area. During the Industrial Revolution, mechanized braiding equipment was invented to increase production. The braiding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (mathematics)
In mathematics, a knot is an embedding of the circle into three-dimensional Euclidean space, (also known as ). Often two knots are considered equivalent if they are ambient isotopic, that is, if there exists a continuous deformation of which takes one knot to the other. A crucial difference between the standard mathematical and conventional notions of a knot is that mathematical knots are closed — there are no ends to tie or untie on a mathematical knot. Physical properties such as friction and thickness also do not apply, although there are mathematical definitions of a knot that take such properties into account. The term ''knot'' is also applied to embeddings of in , especially in the case . The branch of mathematics that studies knots is known as knot theory and has many relations to graph theory. Formal definition A knot is an embedding of the circle () into three-dimensional Euclidean space (), or the 3-sphere (), since the 3-sphere is compact. Two knots ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link (knot Theory)
In mathematical knot theory, a link is a collection of knots which do not intersect, but which may be linked (or knotted) together. A knot can be described as a link with one component. Links and knots are studied in a branch of mathematics called knot theory. Implicit in this definition is that there is a ''trivial'' reference link, usually called the unlink, but the word is also sometimes used in context where there is no notion of a trivial link. For example, a co-dimension 2 link in 3-dimensional space is a subspace of 3-dimensional Euclidean space (or often the 3-sphere) whose connected components are homeomorphic to circle A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is const ...s. The simplest nontrivial example of a link with more than one component is called the Hop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is a set and an operation that combines any two elements of the set to produce a third element of the set, in such a way that the operation is associative, an identity element exists and every element has an inverse. These three axioms hold for number systems and many other mathematical structures. For example, the integers together with the addition operation form a group. The concept of a group and the axioms that define it were elaborated for handling, in a unified way, essential structural properties of very different mathematical entities such as numbers, geometric shapes and polynomial roots. Because the concept of groups is ubiquitous in numerous areas both within and outside mathematics, some authors consider it as a central organizing principle of contemporary mathematics. In geometry groups arise naturally in the study of symmetries and geometric transformations: The symmetries of an object form a group, called the symmetry group of the ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander's Theorem
In mathematics Alexander's theorem states that every knot or link can be represented as a closed braid; that is, a braid in which the corresponding ends of the strings are connected in pairs. The theorem is named after James Waddell Alexander II, who published a proof in 1923. Braids were first considered as a tool of knot theory by Alexander. His theorem gives a positive answer to the question ''Is it always possible to transform a given knot into a closed braid?'' A good construction example is found in Colin Adams's book. However, the correspondence between knots and braids is clearly not one-to-one One-to-one or one to one may refer to: Mathematics and communication *One-to-one function, also called an injective function *One-to-one correspondence, also called a bijective function *One-to-one (communication), the act of an individual comm ...: a knot may have many braid representations. For example, conjugate braids yield equivalent knots. This leads to a second fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrey Markov Jr
Andrey, Andrej or Andrei (in Cyrillic script: Андрей, Андреј or Андрэй) is a form of Andreas/ Ἀνδρέας in Slavic languages and Romanian. People with the name include: *Andrei of Polotsk ( – 1399), Lithuanian nobleman *Andrei Alexandrescu, Romanian computer programmer *Andrey Amador, Costa Rican cyclist *Andrei Arlovski, Belarusian mixed martial artist * Andrey Arshavin, Russian football player *Andrej Babiš, Czech prime minister *Andrey Belousov (born 1959), Russian politician *Andrey Bolotov, Russian agriculturalist and memoirist *Andrey Borodin, Russian financial expert and businessman *Andrei Chikatilo, prolific and cannibalistic Russian serial killer and rapist *Andrei Denisov (weightlifter) (born 1963), Israeli Olympic weightlifter *Andrey Ershov, Russian computer scientist *Andrey Esionov, Russian painter *Andrei Glavina, Istro-Romanian writer and politician *Andrei Gromyko (1909–1989), Belarusian Soviet politician and diplomat * Andrey Ivanov, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugacy Class
In mathematics, especially group theory, two elements a and b of a group are conjugate if there is an element g in the group such that b = gag^. This is an equivalence relation whose equivalence classes are called conjugacy classes. In other words, each conjugacy class is closed under b = gag^. for all elements g in the group. Members of the same conjugacy class cannot be distinguished by using only the group structure, and therefore share many properties. The study of conjugacy classes of non-abelian groups is fundamental for the study of their structure. For an abelian group, each conjugacy class is a set containing one element (singleton set). Functions that are constant for members of the same conjugacy class are called class functions. Definition Let G be a group. Two elements a, b \in G are conjugate if there exists an element g \in G such that gag^ = b, in which case b is called of a and a is called a conjugate of b. In the case of the general linear group \operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |