|
Mark Richards (politician)
Mark Richards (July 15, 1760August 10, 1844) was an American politician. He served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from Vermont and as the ninth lieutenant governor of Vermont. Biography Richards was born in Waterbury in the Connecticut Colony on July 15, 1760, and received limited schooling. In 1776, he enlisted for the American Revolution. A private in the Continental Army, he served for several years, including the Battle of Red Bank, the 1777-1778 winter encampment at Valley Forge, the Battle of Monmouth, and the Battle of Stony Point. Richards moved to Boston after the war to work in a general store. In 1796 he moved to Westminster, Vermont to open his own store. Richards was a member of the Vermont House of Representatives from 1801 to 1805. He served as sheriff of Windham County from 1806 to 1810 and was a Presidential elector in 1812. He served on the Governor’s council from 1813 to 1816. Richards was elected as a Democratic-Republican to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Olin
Henry Olin (May 7, 1768August 18, 1837) was an American lawyer and politician. He served as a United States representative from Vermont and eighth lieutenant governor of Vermont. Biography Olin was born in Shaftsbury in the New Hampshire Grants (now Vermont) on May 7, 1768 to Justin Olin and Sally Dwinell Olin. He attended the common schools. He studied law and was admitted to the bar. He moved to Leicester in the Vermont Republic in 1788 and began the practice of law. Olin served in the Vermont House of Representatives from 1799 to 1804, 1806 to 1815, 1817 to 1819 and 1822 to 1824. He was a delegate to the State constitutional conventions in 1814, 1822, and 1828. He was associate judge and then chief judge of the Addison County Court from 1801 to 1824. He served as a member of the executive council in 1820 and 1821. Olin was elected to the Eighteenth Congress as a Democratic-Republican candidate to fill the vacancy caused by the death of Charles Rich. He served in Congress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States House Of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the Lower house, lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States Senate, Senate being the Upper house, upper chamber. Together they comprise the national Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the United States. The House's composition was established by Article One of the United States Constitution. The House is composed of representatives who, pursuant to the Uniform Congressional District Act, sit in single member List of United States congressional districts, congressional districts allocated to each U.S. state, state on a basis of population as measured by the United States Census, with each district having one representative, provided that each state is entitled to at least one. Since its inception in 1789, all representatives have been directly elected, although universal suffrage did not come to effect until after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th United States Congress
The 16th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1819, to March 4, 1821, during the third and fourth years of James Monroe's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Third Census of the United States in 1810. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority. Major events * A "speech for Buncombe County, North Carolina" given by North Carolina representative Felix Walker in 1820 was credited with introducing into the language the term "bunkum". * March 6, 1819: '' McCulloch v. Maryland'': Supreme Court ruled that the Bank of the United States is constitutional. * July 3, 1820: United States House of Representatives elections, 1820 began in Louisiana * August 7, 1820: 1820 United States Census conducted, eventually determining a population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th United States Congress
The 15th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in the Old Brick Capitol in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1817, to March 4, 1819, during the first two years of James Monroe's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Third Census of the United States in 1810. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority. Letter of December 1818 Two major treaties with the United Kingdom were approved, finalized and signed during the 15th Congress, both the Rush–Bagot Treaty and the Treaty of 1818, both of which pertained to the United States-Canada border, and both of which were overwhelmingly popular in the United States. President James Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams were credited with the accomplishments. A letter signed by many members of congress expressing "Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US House Of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they comprise the national bicameral legislature of the United States. The House's composition was established by Article One of the United States Constitution. The House is composed of representatives who, pursuant to the Uniform Congressional District Act, sit in single member congressional districts allocated to each state on a basis of population as measured by the United States Census, with each district having one representative, provided that each state is entitled to at least one. Since its inception in 1789, all representatives have been directly elected, although universal suffrage did not come to effect until after the passage of the 19th Amendment and the Civil Rights Movement. Since 1913, the number of voting representatives ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidential Elector
The United States Electoral College is the group of presidential electors required by the Constitution to form every four years for the sole purpose of appointing the president and vice president. Each state and the District of Columbia appoints electors pursuant to the methods described by its legislature, equal in number to its congressional delegation (representatives and senators). Federal office holders, including senators and representatives, cannot be electors. Of the current 538 electors, an absolute majority of 270 or more ''electoral votes'' is required to elect the president and vice president. If no candidate achieves an absolute majority there, a contingent election is held by the United States House of Representatives to elect the president, and by the United States Senate to elect the vice president. The states and the District of Columbia hold a statewide or districtwide popular vote on Election Day in November to choose electors based upon how they have pled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
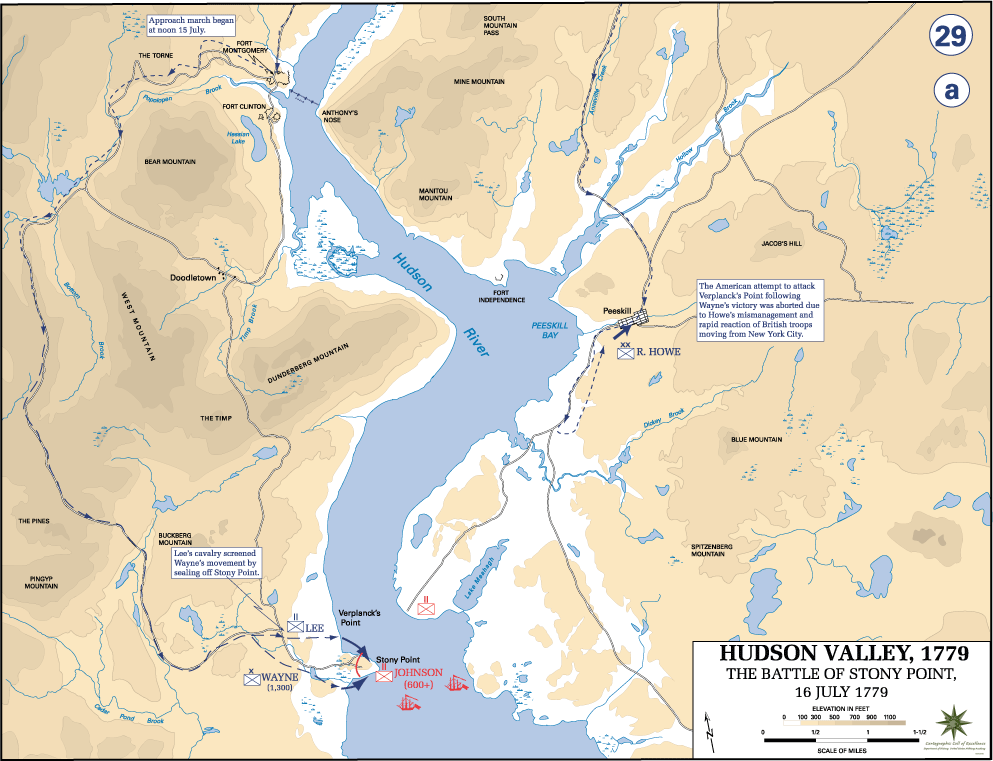
Battle Of Stony Point
The Battle of Stony Point took place on July 16, 1779, during the American Revolutionary War. In a well-planned and -executed nighttime attack, a highly trained select group of George Washington's Continental Army troops under the command of Brigadier General "Mad Anthony" Wayne defeated British troops in a quick and daring assault on their outpost in Stony Point, New York, approximately north of New York City. The British suffered heavy losses in a battle that served as an important victory in terms of morale for the Continental Army. While the fort was ordered evacuated quickly after the battle by General Washington, this key crossing site was used later in the war by units of the Continental Army to cross the Hudson River on their way to victory over the British. Background Following the surrender of General John Burgoyne after the Battles of Saratoga in October 1777 and the subsequent entry of France into the war as an American ally, British strategy in dealing with the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Monmouth
The Battle of Monmouth, also known as the Battle of Monmouth Court House, was fought near Monmouth Court House in modern-day Freehold Borough, New Jersey on June 28, 1778, during the American Revolutionary War. It pitted the Continental Army, commanded by General George Washington, against the British Army in North America, commanded by General Sir Henry Clinton. It was the last battle of the Philadelphia campaign, begun the previous year, during which the British had inflicted two major defeats on Washington and occupied Philadelphia. Washington had spent the winter at Valley Forge rebuilding his army and defending his position against political enemies who favored his replacement as commander-in-chief. In February 1778, the French-American Treaty of Alliance tilted the strategic balance in favor of the Americans, forcing the British to abandon hopes of a military victory and adopt a defensive strategy. Clinton was ordered to evacuate Philadelphia and consolidate his army. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Forge
Valley Forge functioned as the third of eight winter encampments for the Continental Army's main body, commanded by General George Washington, during the American Revolutionary War. In September 1777, Congress fled Philadelphia to escape the British capture of the city. After failing to retake Philadelphia, Washington led his 12,000-man army into winter quarters at Valley Forge, located approximately 18 miles (29 km) northwest of Philadelphia. They remained there for six months, from December 19, 1777 to June 19, 1778. At Valley Forge, the Continentals struggled to manage a disastrous supply crisis while retraining and reorganizing their units. About 1,700 to 2,000 soldiers died from disease, possibly exacerbated by malnutrition. Today, Valley Forge National Historical Park protects and preserves over 3,500 acres of the original encampment site. Pre-encampment In 1777, Valley Forge consisted of a small proto-industrial community located at the juncture of the Valley Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Red Bank
The Battle of Red Bank was a battle fought on October 22, 1777 during the American Revolutionary War in which a British and Hessian force was sent to take Fort Mercer on the left bank (or New Jersey side) of the Delaware River just south of Philadelphia, but was decisively defeated by a far inferior force of colonial defenders. Although the British did take Fort Mercer a month later, the victory supplied a sorely-needed morale boost to the American cause, delayed British plans to consolidate gains in Philadelphia, and relieved pressure on General George Washington's army to the north of the city. Prelude to battle After the British capture of Philadelphia on September 26, 1777 and the failure of the American surprise attack against the British camp at the Battle of Germantown on October 4, the Americans tried to deny the British use of the city by blockading the Delaware River. To that end, two forts were constructed commanding the river. One was Fort Mercer on the New Jersey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was established by a resolution of Congress on June 14, 1775. The Continental Army was created to coordinate military efforts of the Colonies in their war for independence against the British, who sought to keep their American lands under control. General George Washington was the commander-in-chief of the army throughout the war. The Continental Army was supplemented by local militias and volunteer troops that were either loyal to individual states or otherwise independent. Most of the Continental Army was disbanded in 1783 after the Treaty of Paris formally ended the fighting. The 1st and 2nd Regiments of the Army went on to form what was to become the Legion of the United States in 1792. This became the foundation of what is now the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |