|
Maritime Radionavigation-satellite Service
Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (short: MRNSS) is – according to ''Article 1.45'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.45, definition: ''maritime radionavigation-satellite service'' – defined as «''A radionavigation-satellite service in which earth stations are located on board ships''.» This service is a so-called safety-of-life service, must be protected for Interferences, and is essential part of Navigation. ;See also: Classification This ''radiocommunication service'' is classified in accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) as follows: Radiodetermination service (article 1.40) *Radionavigation service (article 1.42) **Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43) **Maritime radionavigation service (article 1.44) ***Maritime radionavigation-satellite service ** Aeronautical radionavigation service (article 1.46) *** Aero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Radionavigation Service
Aeronautical radionavigation service (short: ARNS) is – according to ''Article 1.46'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as "''A radionavigation service intended for the benefit and for the safe operation of aircraft''." This service is a so-called safety-of-life service, must be protected against interference, and is an essential part of navigation. Classification This ''radiocommunication service'' is classified in accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) as follows: Radiodetermination service (article 1.40) * Radiodetermination-satellite service (article 1.41) * Radionavigation service (article 1.42) **Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43) **Maritime radionavigation service (article 1.44) ***Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.45) **Aeronautical radionavigation service (article 1.46) *** Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.47) Frequency allocation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision. Satellite navigation devices supporting both GPS and GLONASS have more satellites available, meaning positions can be fixed more quickly and accurately, especially in built-up areas where buildings may obscure the view to some satellites. GLONASS supplementation of GPS systems also improves positioning in high latitudes (north or south). Development of GLONASS began in the Soviet Union in 1976. Beginning on 12 October 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
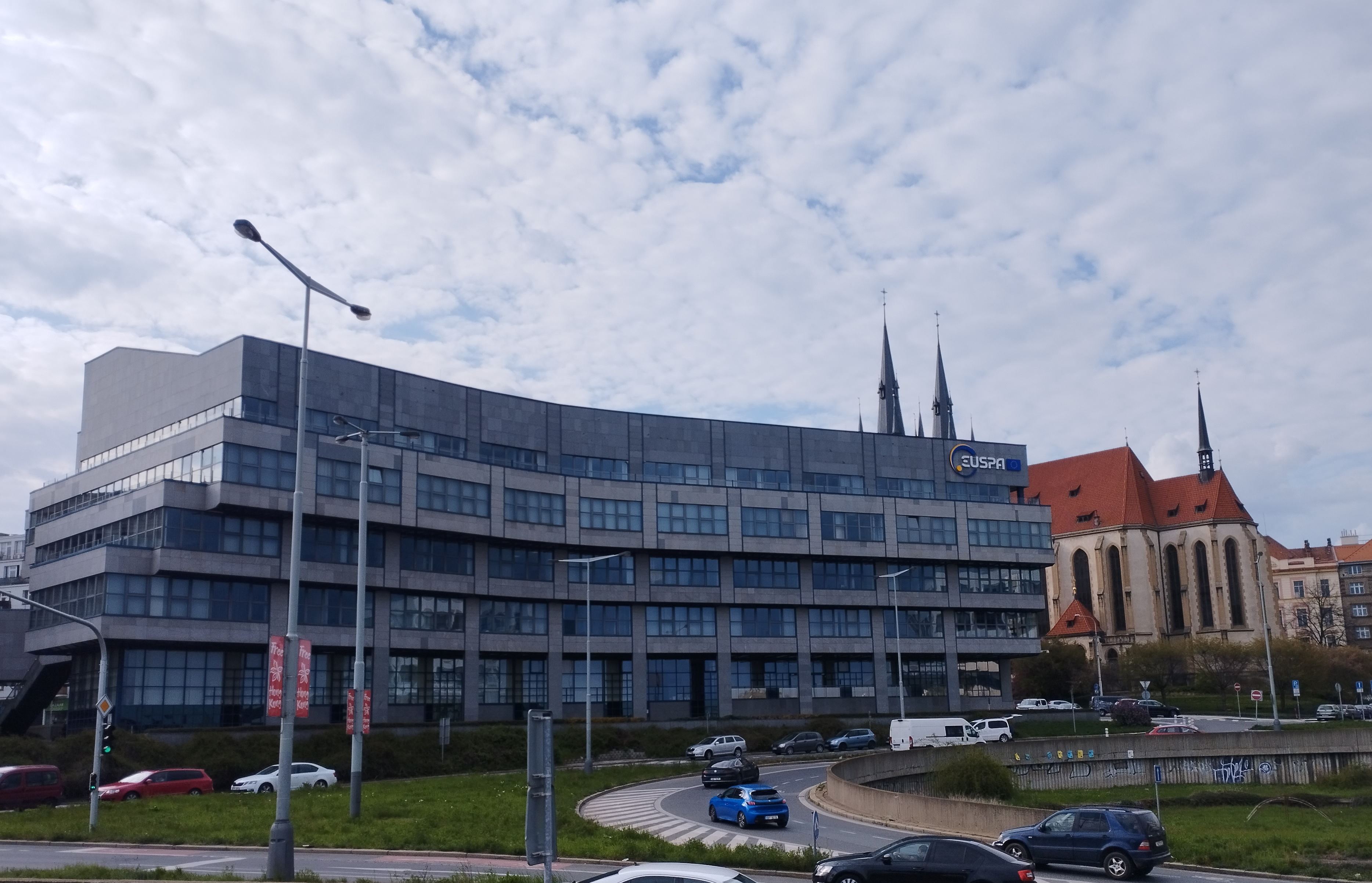
Galileo (satellite Navigation)
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA), operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, with two ground operations centres in Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open to everyone. A fully encrypted higher-precision service is available for free to government-authorized users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1 m precision. Galileo is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feeder Link
A feeder link is – according to ''Article 1.115'' of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.115, definition: ''feeder link'' – defined as: Each ''station'' shall be classified by the ''service'' in which it operates permanently or temporarily. See also * Radio station * Radiocommunication service Radio communication service or radiocommunication service is according to Article 1.19 of the International Telecommunication Union's Radio Regulations (ITU RR),ITU Radio Regulations, Section III – Radio services, Article 1.19, definition: Ra ... References International Telecommunication Union (ITU) {{Radio station ITU Radio stations and systems ITU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Radio System
Space radio system (also: ''space system'') is – according to ''article 1.110'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.110, definition: ''space radio system / space system'' – defined as «''Any group of cooperating earth stations and/or space stations A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ... employing space radiocommunication for specific purposes''.» Each ''system'' shall be classified by the ''service'' in which it operates permanently or temporarily. ;See also: References / sources International Telecommunication Union (ITU){{Radio station ITU Radio stations and systems ITU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Radio System
Satellite radio system (also: ''satellite system'') is – according to ''article 1.111'' of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.111, definition: ''space radio system / space system'' – defined as «''A space system using one or more artificial earth satellites''.» Each ''system'' shall be classified by the ''service'' in which it operates permanently or temporarily. See also *Radio station *Radiocommunication service Radio communication service or radiocommunication service is according to Article 1.19 of the International Telecommunication Union's Radio Regulations (ITU RR),ITU Radio Regulations, Section III – Radio services, Article 1.19, definition: Ra ... References / sources International Telecommunication Union (ITU){{Radio station ITU Radio stations and systems ITU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionavigation Mobile Station
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio frequencies to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction. Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination. The basic principles are measurements from/to electric beacons, especially * Angular directions, e.g. by bearing, radio phases or interferometry, * Distances, e.g. ranging by measurement of time of flight between one transmitter and multiple receivers or vice versa, * Distance ''differences'' by measurement of times of arrival of signals from one transmitter to multiple receivers or vice versa * Partly also velocity, e.g. by means of radio Doppler shift. Combinations of these measurement principles also are important—e.g., many radars measure range and azimuth of a target. Bearing-measurement systems These systems used some form of directional radio antenna to determine the location of a broadcast station on the ground. Conventional navigation techniques ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Radionavigation-satellite Service
Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite (short: ARNSS) is – according to ''Article 1.47'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.47, definition: ''aeronautical radionavigation service '' – defined as «''A radionavigation service in which earth stations are located on board aircraft''.» This service is a so-called safety-of-life service, must be protected for Interferences, and is essential part of navigation. Classification This ''radiocommunication service'' is classified in accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) as follows: Radiodetermination service (article 1.40) * Radiodetermination-satellite service (article 1.41) * Radionavigation service (article 1.42) **Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43) **Maritime radionavigation service (article 1.44) ***Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.45) **Aeronautical radionavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Radionavigation Service
Maritime radionavigation service (short: MRNS) is – according to ''Article 1.44'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.44, definition: ''maritime radionavigation service'' – defined as "''A radionavigation service intended for the benefit and for the safe operation of ships''." This service is a so-called safety-of-life service, must be protected for interferences, and is essential part of navigation. ; Classification This ''radiocommunication service'' is classified in accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) as follows: Radiodetermination service (article 1.40) *Radionavigation service (article 1.42) **Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43) **Maritime radionavigation service ***Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.45) **Aeronautical radionavigation service (article 1.46) ***Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, making it the oldest UN agency. The ITU was initially aimed at helping connect telegraphic networks between countries, with its mandate consistently broadening with the advent of new communications technologies; it adopted its current name in 1932 to reflect its expanded responsibilities over radio and the telephone. On 15 November 1947, the ITU entered into an agreement with the newly created United Nations to become a specialized agency within the UN system, which formally entered into force on 1 January 1949. The ITU promotes the shared global use of the radio spectrum, facilitates international cooperation in assigning satellite orbits, assists in developing and coordinating worldwide technical standards, and works to improve tele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
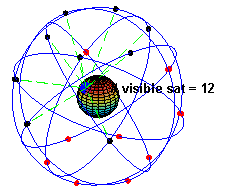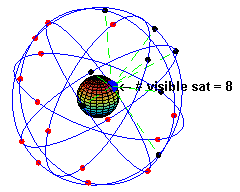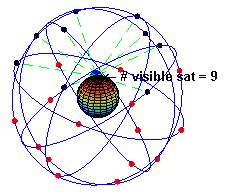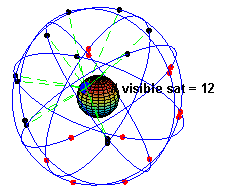
Radionavigation-satellite Service
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |