|
Marion King Hubbert
Marion King Hubbert (October 5, 1903 – October 11, 1989) was an American geologist and geophysicist. He worked at the Shell research lab in Houston, Texas. He made several important contributions to geology, geophysics, and petroleum geology, most notably the Hubbert curve and Hubbert peak theory (a basic component of peak oil), with important political ramifications. He was often referred to as "M. King Hubbert" or "King Hubbert". Biography Hubbert was born in San Saba, Texas. He attended the University of Chicago, where he received a Bachelor of Science in 1926, a Master of Science in 1928, and a Doctor of Philosophy in 1937, studying geology, mathematics, and physics. He worked as an assistant geologist for the Amerada Petroleum Company for two years while pursuing the PhD, additionally teaching geophysics at Columbia University. He also served as a senior analyst at the Board of Economic Warfare. He joined the Shell Oil Company in 1943, retiring from that firm in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Saba, Texas
San Saba is a city located in, and the county seat of, San Saba County, Texas, United States. It was settled in 1854 and named for its location on the San Saba River. Its population was 3,099 at the 2010 census. Geography San Saba is located at (31.195298, –98.725003). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 1.8 sq mi (4.7 km), all of it land. The city is located northwest of Austin, Texas, Austin, and miles north of San Antonio. Climate The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen climate classification, San Saba has a humid subtropical climate, ''Cfa'' on climate maps. Demographics 2020 census As of the 2020 United States census, there were 3,117 people, 1,022 households, and 653 families residing in the city. 2010 census As of the census of 2010, people, households, and 680 families resided in the city. The population density was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to the Master of Arts degree, the Master of Science degree is typically granted for studies in sciences, engineering and medicine and is usually for programs that are more focused on scientific and mathematical subjects; however, different universities have different conventions and may also offer the degree for fields typically considered within the humanities and social sciences. While it ultimately depends upon the specific program, earning a Master of Science degree typically includes writing a thesis. The Master of Science degree was first introduced at the University of Michigan in 1858. One of the first recipients of the degree was De Volson Wood, who was conferred a Master of Science degree at the University of Michigan in 1859. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-market Economics
Economic anthropology is a field that attempts to explain human economic behavior in its widest historic, geographic and cultural scope. It is an amalgamation of economics and anthropology. It is practiced by anthropologists and has a complex relationship with the discipline of economics, of which it is highly critical. Its origins as a sub-field of anthropology began with work by the Polish founder of anthropology Bronislaw Malinowski and the French Marcel Mauss on the nature of reciprocity as an alternative to market exchange. For the most part, studies in economic anthropology focus on exchange. Post-World War II, economic anthropology was highly influenced by the work of economic historian Karl Polanyi. Polanyi drew on anthropological studies to argue that true market exchange was limited to a restricted number of western, industrial societies. Applying formal economic theory (Formalism) to non-industrial societies was mistaken, he argued. In non-industrial societies, exch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
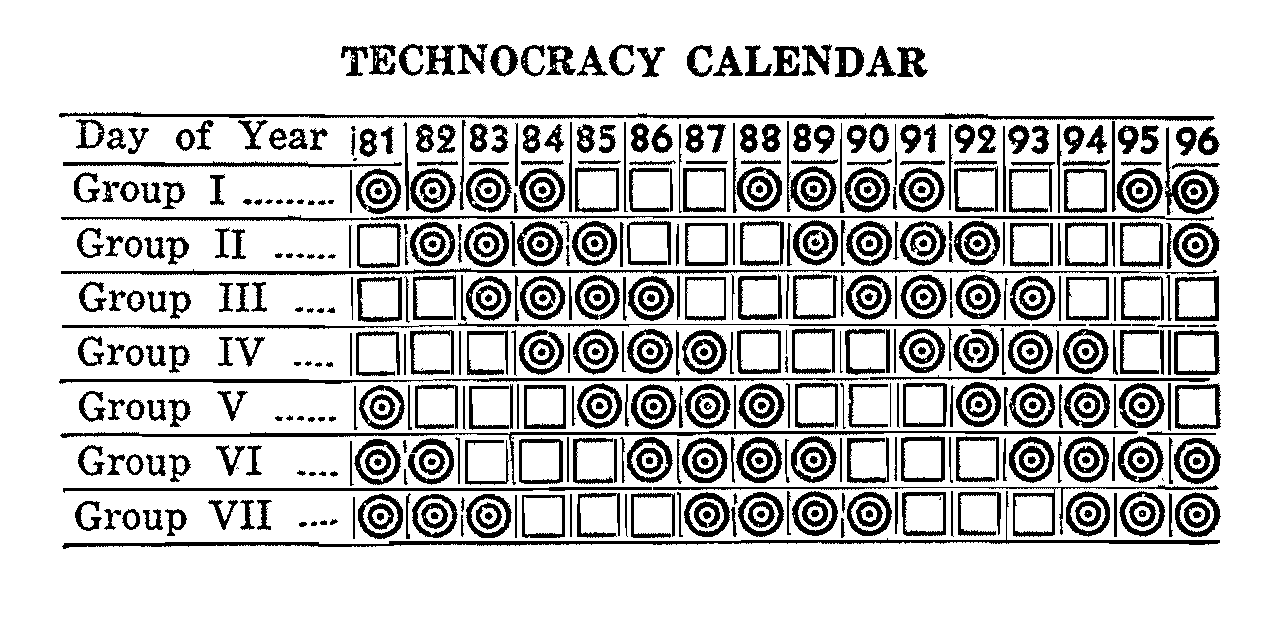
Technocracy Study Course
The ''Technocracy Study Course'' is a technocratic critique of the price system, written by M. King Hubbert and first published in 1934. It is the ideological basis for the Technocracy movement, highlighting economic and social consequences of the capitalist price system In economics, a price system is a system through which the valuations of any forms of property (tangible or intangible) are determined. All societies use price systems in the allocation and exchange of resources as a consequence of scarcity. Even ... and suggests an alternative socioeconomic system based on physical laws and constraints. References {{reflist Capitalism Technocracy movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Scott
Howard Scott (April 1, 1890 – January 1, 1970) was an American engineer and founder of the Technocracy movement. He formed the Technical Alliance and Technocracy Incorporated. Early life Little is known about Scott's background or his early life and he has been described as a "mysterious young man". He was born in Virginia in 1890 and was of Scottish-Irish descent. He claimed to have been educated in Europe, but his training did not include any formal higher education. In 1918, shortly before the end of WWI, Scott appeared in New York City. Scott worked in various construction camps, where he picked up on-the-job engineering experience, and in 1918 was working in a cement pouring gang at Muscle Shoals. Following this, Scott established himself in Greenwich Village as "a kind of Bohemian engineer". Scott also ran a small business called ''Duron Chemical Company'' which made paint and floor polish at Pompton Lakes, New Jersey. Scott's job was to deliver his goods and show his cust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technocracy Incorporated
The technocracy movement was a social movement active in the United States and Canada in the 1930s which favored technocracy as a system of government over representative democracy and concomitant Partisan (politics), partisan politics. Historians associate the movement with engineer Howard Scott's Technical Alliance and Technocracy Incorporated, prior to the internal Political faction, factionalism that dissolved the latter organization during the Second World War. Technocracy was ultimately overshadowed by other proposals for dealing with the crisis of the Great Depression. The technocracy movement proposed replacing partisan politicians and businessperson, business people with scientists and engineers who had the technical expertise to manage the economy. But the movement did not fully aspire to scientocracy.Peter J. TaylorTechnocratic Optimism, H.T. Odum, and the Partial Transformation of Ecological Metaphor after World War II''Journal of the History of Biology'', Vol. 21, No. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technocracy Movement
The technocracy movement was a social movement active in the United States and Canada in the 1930s which favored technocracy as a system of government over representative democracy and concomitant partisan politics. Historians associate the movement with engineer Howard Scott's Technical Alliance and Technocracy Incorporated, prior to the internal Political faction, factionalism that dissolved the latter organization during the Second World War. Technocracy was ultimately overshadowed by other proposals for dealing with the crisis of the Great Depression. The technocracy movement proposed replacing partisan politicians and businessperson, business people with scientists and engineers who had the technical expertise to manage the economy. But the movement did not fully aspire to scientocracy.Peter J. TaylorTechnocratic Optimism, H.T. Odum, and the Partial Transformation of Ecological Metaphor after World War II''Journal of the History of Biology'', Vol. 21, No. 2, June 1988, p. 213 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant university and the founding campus of the University of California system. Its fourteen colleges and schools offer over 350 degree programs and enroll some 31,800 undergraduate and 13,200 graduate students. Berkeley ranks among the world's top universities. A founding member of the Association of American Universities, Berkeley hosts many leading research institutes dedicated to science, engineering, and mathematics. The university founded and maintains close relationships with three national laboratories at Berkeley, Livermore and Los Alamos, and has played a prominent role in many scientific advances, from the Manhattan Project and the discovery of 16 chemical elements to breakthroughs in computer science and genomics. Berkeley is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is considered among the most prestigious universities in the world. Stanford was founded in 1885 by Leland and Jane Stanford in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., who had died of typhoid fever at age 15 the previous year. Leland Stanford was a U.S. senator and former governor of California who made his fortune as a railroad tycoon. The school admitted its first students on October 1, 1891, as a coeducational and non-denominational institution. Stanford University struggled financially after the death of Leland Stanford in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, provost of Stanford Frederick Terman inspired and supported faculty and graduates' entrepreneu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Economic Warfare
The Office of Administrator of Export Control (also referred to as the Export Control Administration) was established in the United States by Presidential Proclamation 2413, July 2, 1940, to administer export licensing provisions of the act of July 2, 1940 (54 Stat. 714). Brigadier General Russell Lamont Maxwell, United States Army, headed up this military entity. It was abolished by Presidential Executive Order 8900, September 15, 1941, and its functions were transferred to the Economic Defense Board, which had been established by Presidential Executive Order 8839, July 30, 1941, to develop policies and programs to strengthen U.S. international economic relations.Edward S. Miller, ''Bankrupting the Enemy: The U.S. Financial Siege of Japan Before Pearl Harbor'' (Annapolis: Naval Institute Press, 2007), pps. 87, 205, 286 n. 1. The name was changed to Board of Economic Warfare by Presidential Executive Order 8982, December 17, 1941. In turn, it was abolished by Executive Order 9361 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhattan, Columbia is the oldest institution of higher education in New York and the fifth-oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. It is one of nine colonial colleges founded prior to the Declaration of Independence. It is a member of the Ivy League. Columbia is ranked among the top universities in the world. Columbia was established by royal charter under George II of Great Britain. It was renamed Columbia College in 1784 following the American Revolution, and in 1787 was placed under a private board of trustees headed by former students Alexander Hamilton and John Jay. In 1896, the campus was moved to its current location in Morningside Heights and renamed Columbia University. Columbia scientists and scholars have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |